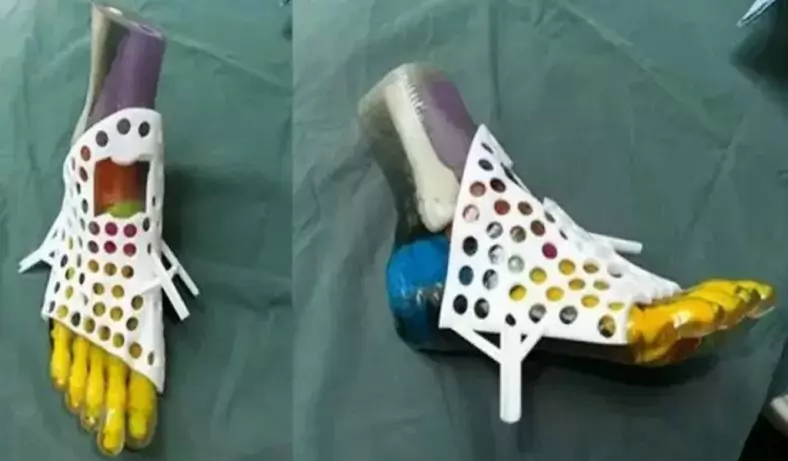
Medical Parts
- Global delivery as fast as 10 days,Rapid prototypes in as fast as 1 days.
- 100+metals and plastics
- Tolerances down to +-0.001mm
- ISO 9001:2015, ITAF 16949
- One-Stop Custom Medical Parts In China
>>>All uploaded drawings are strictly confidential, check the confidentiality agreement
Custom Medical Components – Rapid Prototyping For Medical Parts
Rapid prototyping and more manufacturing methods allow you to quickly obtain high precision, high quality custom parts by relying on qualified suppliers at every stage of the product lifecycle. be-cu.com can do this by designing and implementing unique solutions to completely unique problems in the medical industry at a controlled cost, which allows engineers and designers to build products that better meet customer requirements. The desired model is available at the click of a button, without the need for a senior engineer or supervision of the machine. Support for high-mix, low-volume production of customised parts in maintenance and production.Be-cu offers made to spec non-stanard custom medical parts created with high quality, China manufactured medical spare parts at a low cost. Contact us today to get a quote!

The Prototype Materials for Medical Devices Parts
“The term ‘medical device’ is a broad umbrella term that covers a wide range of instruments and equipment such as band-aids, dental floss, blood pressure cuffs, defibrillators, MRI scanners and many more. The design of medical devices is an important part of the field of mechanical engineering.
The development process for medical devices is no different to any other device: design, prototype, test and repeat. However, medical devices have more stringent material requirements. Many medical device prototypes require biocompatible or sterilisable materials due to the requirements of testing and clinical trials.
Biocompatible Materials For Medical
For plastics, the most stringent requirement is the USP Class 6 test. the USP Class 6 test involves three in vivo bioreactivity assessments on animals, including:
- Acute systemic toxicity test: this test measures irritation when samples are taken orally, applied to the skin and inhaled.
- Intradermal test: This test measures the irritation of the sample when in contact with living subcutaneous tissue.
- Implantation test: This test measures the irritation of a sample when implanted intramuscularly into a test animal over a five day period.
3D printing can produce almost any geometry, which is useful for rapid iteration of complex designs. CNC machining is suitable for prototyping and end-use production of medical device parts. More materials are available and materials are more robust. However, the design requires more attention to ensure machinability.
The following materials are USP Class 6 tested and approved: POM, PP, PEI, PEEK, PSU, PPSU
If you are making an early stage prototype that will not be used in experimental or clinical trials, consider using a non-certified plastic. You don’t have to pay a higher price to get the same mechanical properties and POM 150 is an excellent material for early stage prototyping.
CNC machining is also available to produce biocompatible metal parts. There are three common options for implant grades.
- Stainless Steel 316L
- Titanium grade 5, also known as Ti6Al4V or Ti 6-4
- Cobalt-Chromium (CoCr)
Stainless steel 316L is the most commonly used of the three materials. Titanium has a better weight to strength ratio but is much more expensive. CoCr is mainly used for orthopaedic implants. We recommend that you use SS 316L for prototyping when improving your design and then use the more expensive material when the design is more mature.
Sterilisable Materials
Any reusable medical device that may come into contact with blood or body fluids must be sterilisable. Therefore, most medical devices used in medical facilities are made of sterilisable materials. There are many methods of sterilisation: heat (dry heat or autoclave/steam), pressure, chemicals, irradiation, etc.
Chemicals and irradiation are the preferred methods of sterilising plastics, as heat breaks down plastics. This is a chart outlining the compatibility of many plastics with different sterilisation methods. Autoclaves and dry heat are the common methods of sterilising metals.
All of the USP Class VI certified materials we mentioned earlier are sterilisable, as are implant-grade metals. Again, CNC machining offers the most options for sterilisable materials.
If the medical device is to be used for sterilisation at home by the patient, the material should also be compatible with sterilising chemicals such as bleach, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, iodine and hydrogen peroxide. ABS and POM are the most chemically resistant plastics.
When To Use Medical Grade Materials
When building prototypes for experimental or clinical trials, always use medical grade materials. However, for early prototype moulding and assembly, using general purpose materials can save you a lot of money.
The Case Studies Of Medical Parts
You have a complex part design, Our Custom Medical Parts service can help you turn it into a reality. With the right equipment, strong technical knowledge, and a focus on quality.. From tool design to finishing and then on to shipment, Be-cu prototpe ensure that every project is completed to a high standard and that your orders are delivered on time, every time.
-

5 Axis CNC Machining Medical Olecranon Plate
-
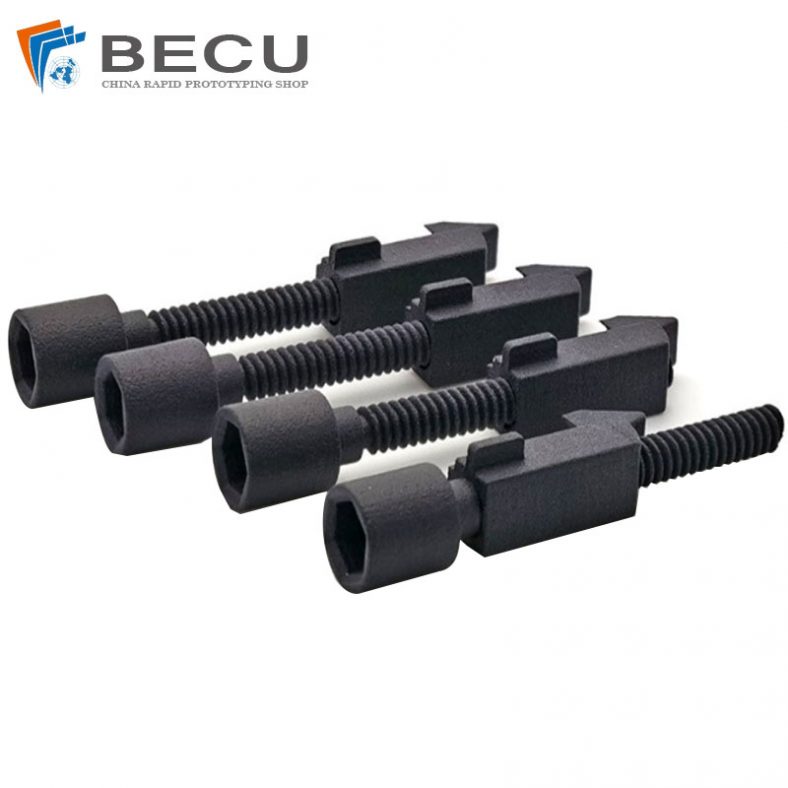

Black Nylon Medical Threaded Screw By MJF 3D Printing
-
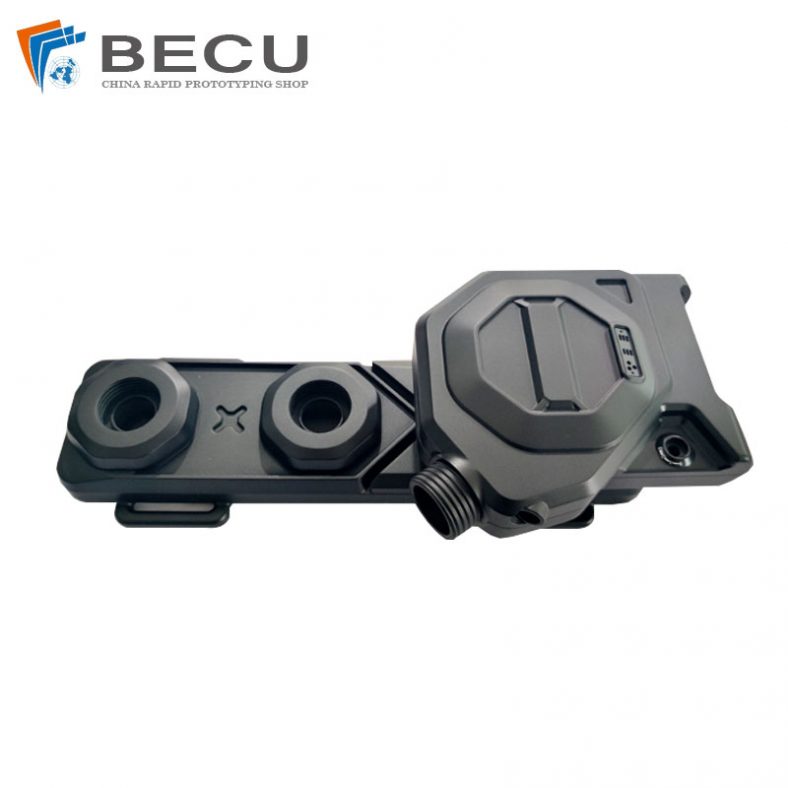

MJF 3D Printing Black Nylon Red Dot Sighting For Medical
-
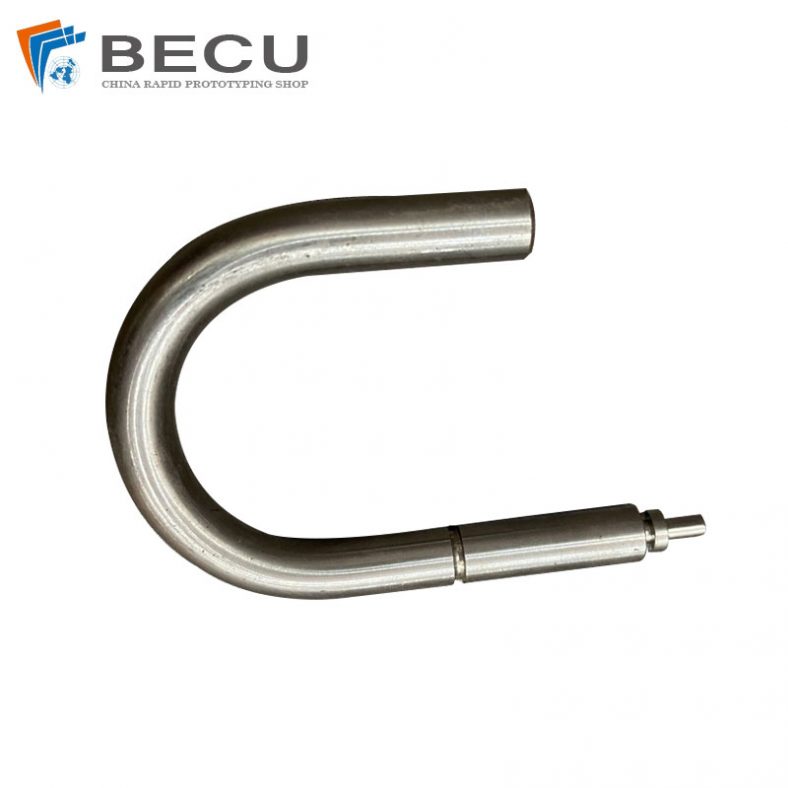

Automatic Swiss Turning Stainless Steel 316L U-bolt
-

Laser Cut Nitinol Stent For Bile Duct
-
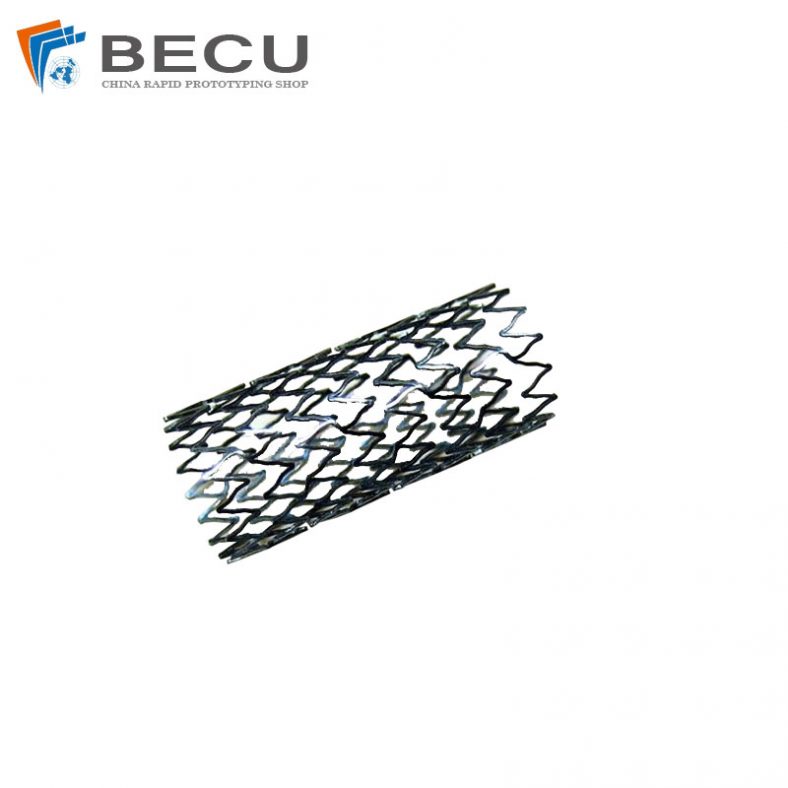

Stents For Carrying Valves And Venous Valve Replacement Devices
-
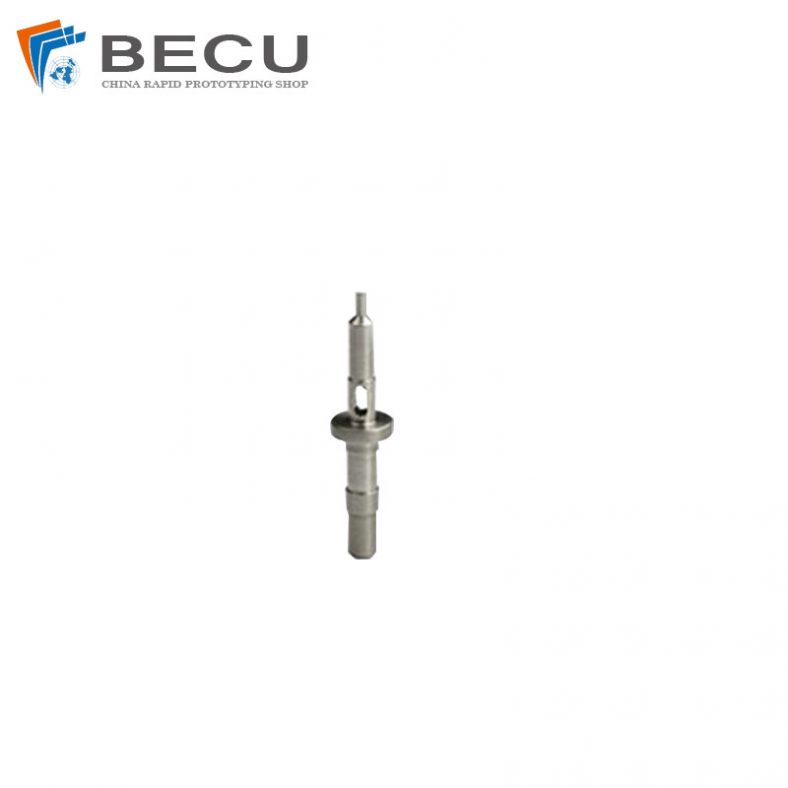

Micro CNC Machining Kovar 4J29 Medical Implant
-
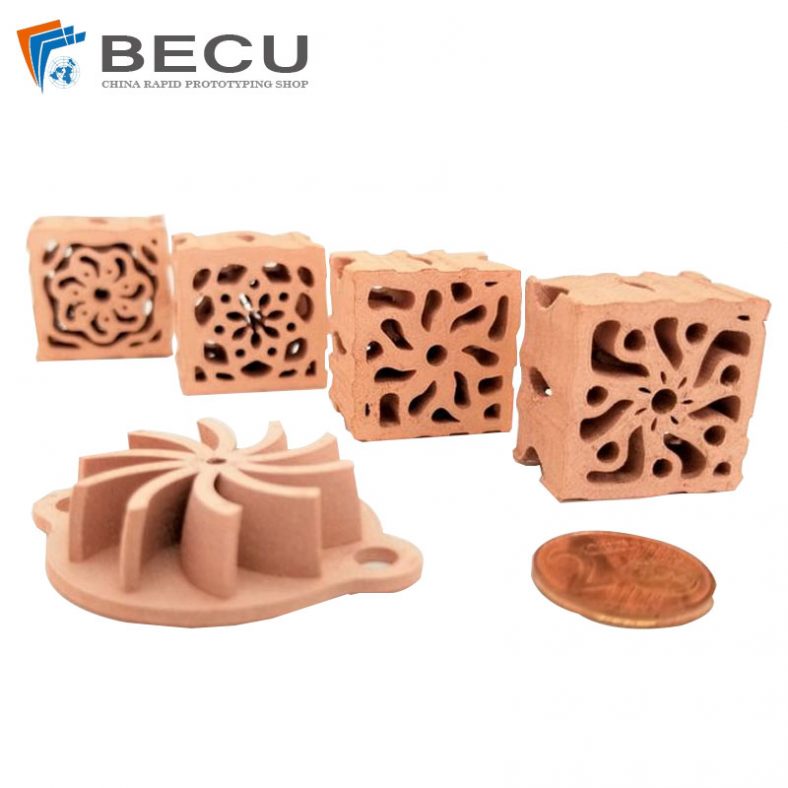

FFF Fused Wire Extrusion 3D Printed Pure Copper Parts
-
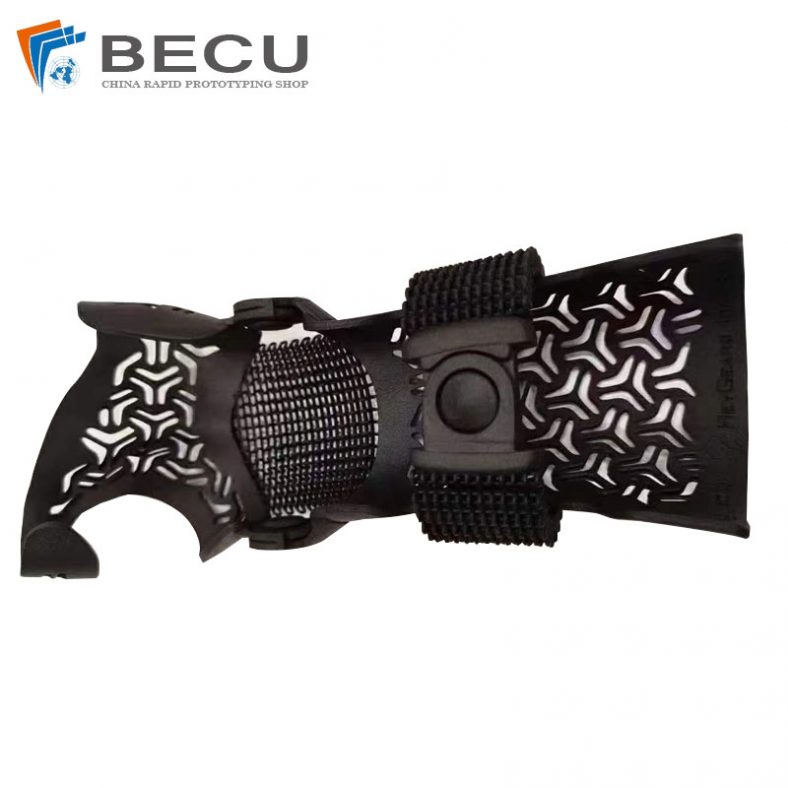

MJF 3D Printing Black Nylon Medical Arm Guards
-
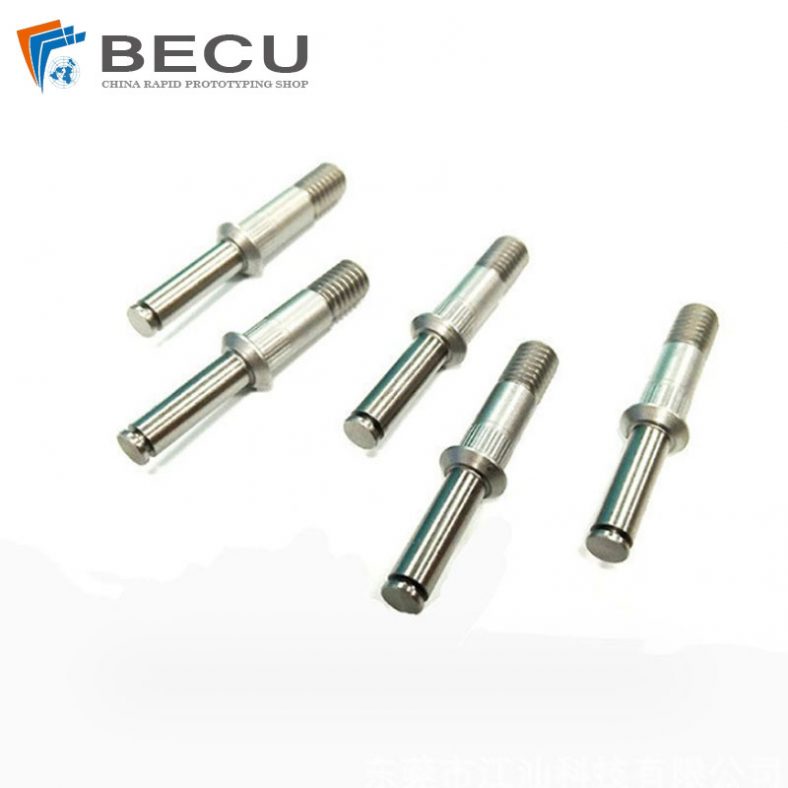

Precision Swiss Turning Titanium Alloy Medical Shaft
-
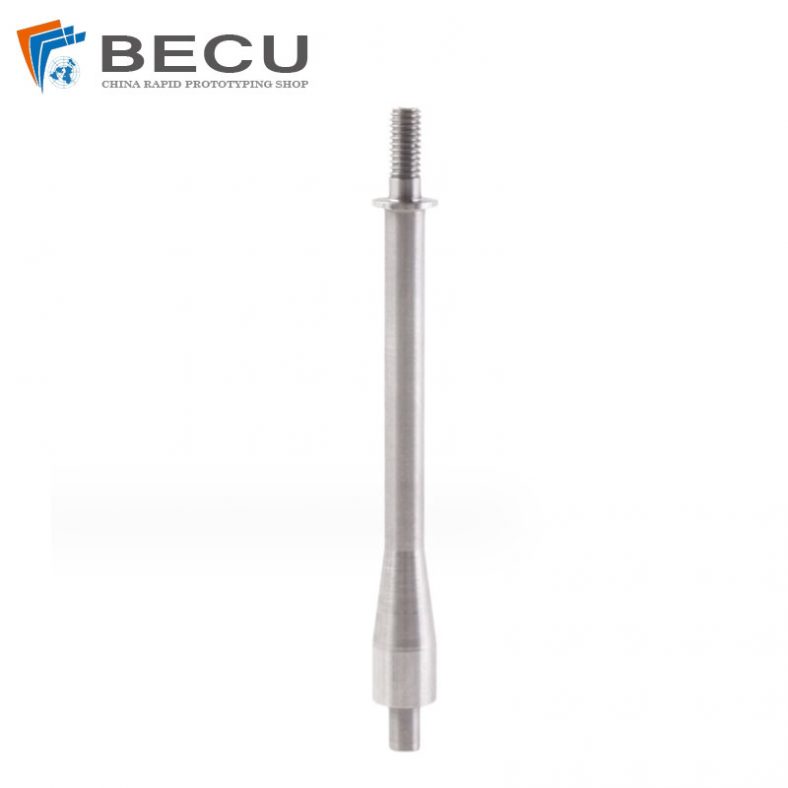

Swiss Turning 304 Stainless Steel Medical Threaded Rod
-
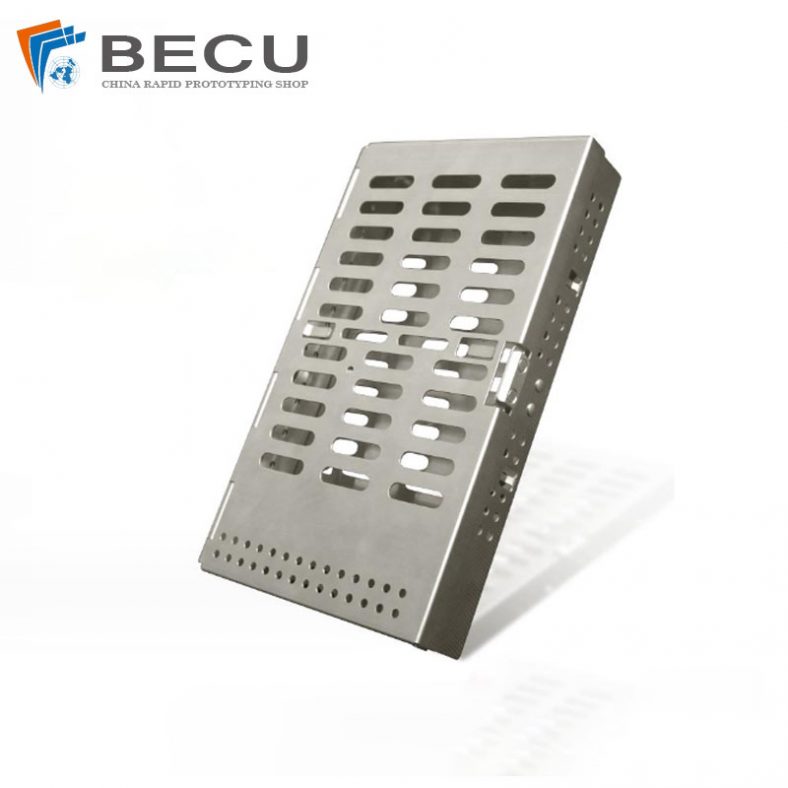

Custom Sheet Metal Surgical Instrument Sterilization Box For Beauty Salon
-
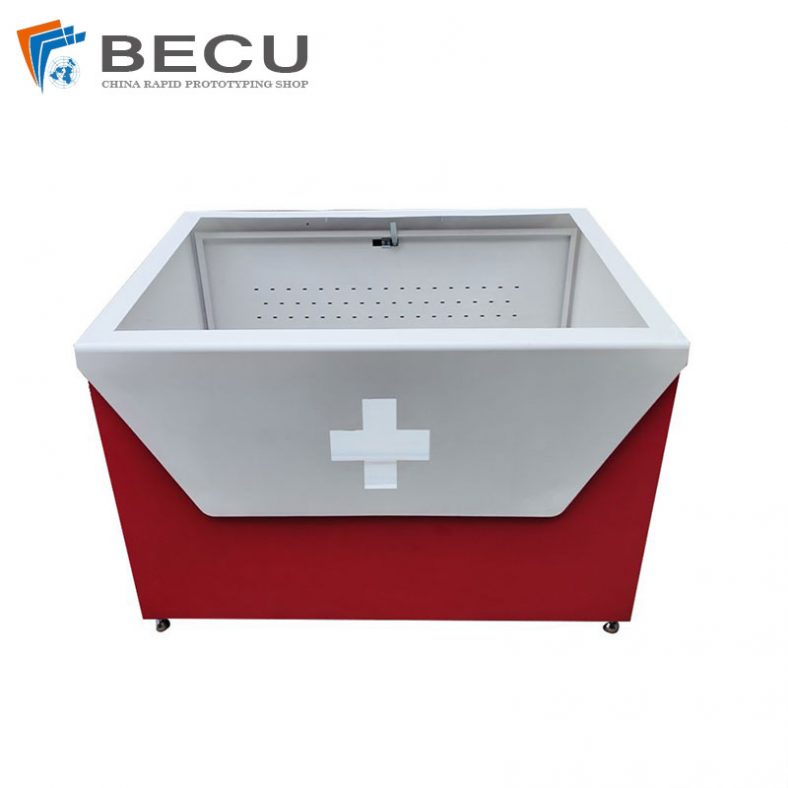

Sheet Metal Fabrication Aluminum 5052 Medical Box For Fire Fighting
-
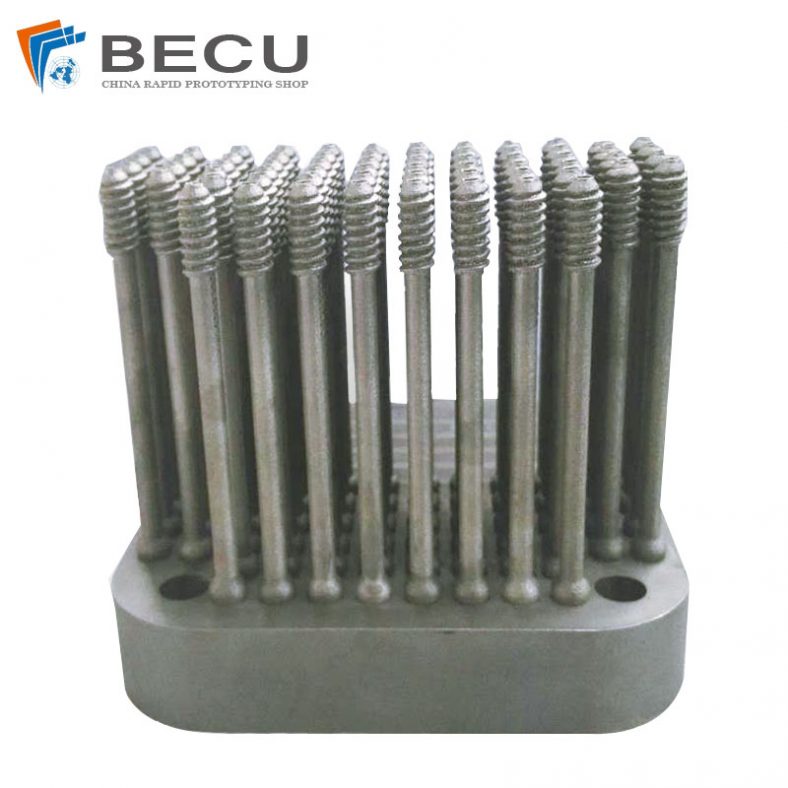

3D Printing Ti-6Al-4V Sacroiliac Screws
-
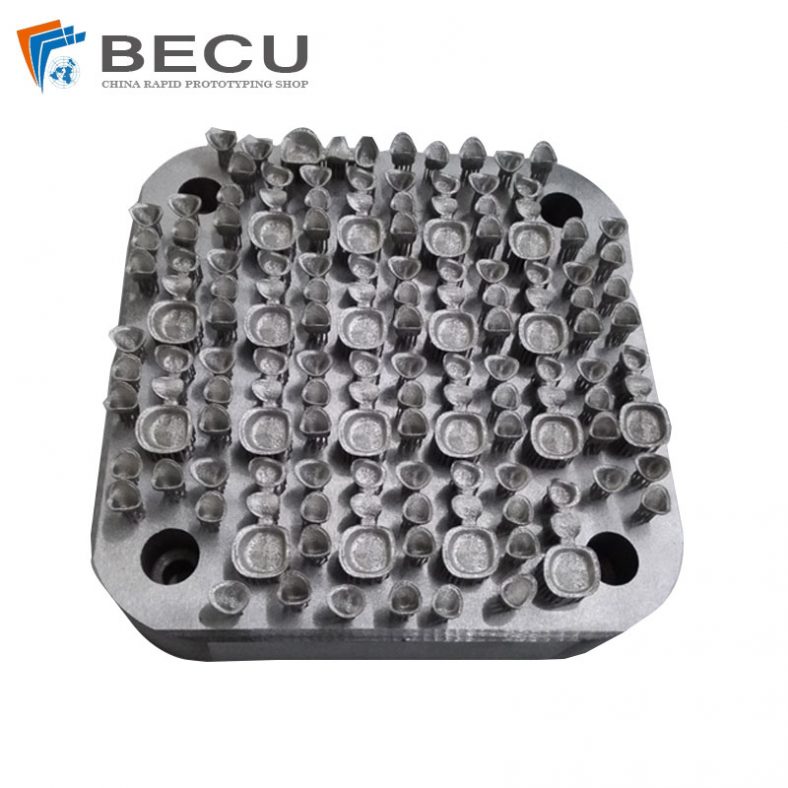

3D Printing Titanium Alloy Dental Teeth