Whether you’re new to polymer recycling, trying to build your next project, or an engineer, to fully understand the injection molding process, you must first understand the basics of how it all works. In this article, we will try to make the description of the injection molding process as simple as possible to help you learn everything that goes into molding plastic parts.
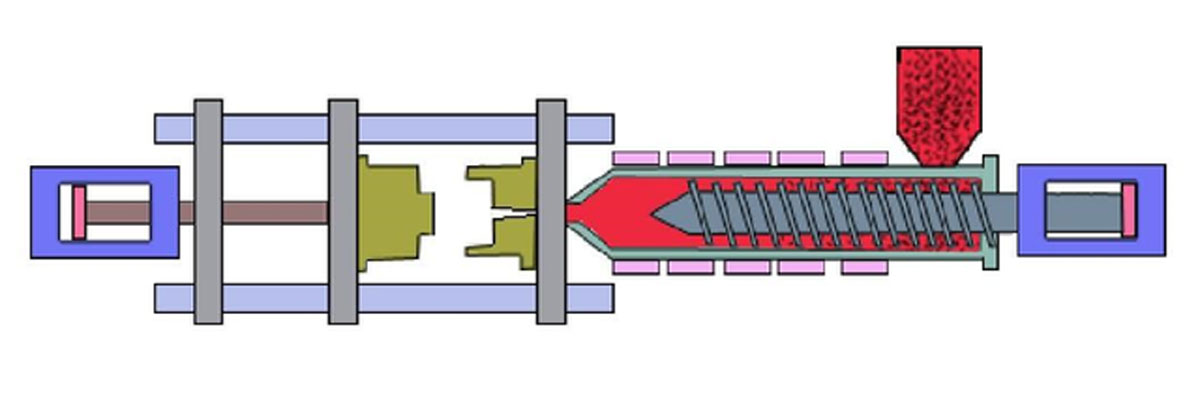
#1 What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is the most common manufacturing process for making plastic parts. The process involves designing a product, tooling a mold, and then producing plastic polymer pellets and using pressure to inject them into the mold.After the plastic is plasticized in the heating barrel of the injection molding machine, it is injected into the cavity of the closed mold by the plunger or the reciprocating screw to form the plastic processing method of the product. This method can process products with complex shapes, precise dimensions or inserts, and has high production efficiency. Most thermoplastics and some thermosetting plastics (such as phenolic plastics) can be processed by this method. Materials used for injection molding must have good fluidity in order to fill the mold cavity to obtain products. Since the 1970s, there has been an injection molding with a chemical reaction, called reaction injection molding, which has developed rapidly.
#2 Plastic Injection Molding Process
To make it as simple and straightforward as possible, we have divided the plastic injection molding process into 3 parts:
- Product engineering design
- Mold design and development
- Manufacturing process
1.Product Engineering Design
When it comes to producing an injection molded part, the design of the part is absolutely critical. You must ensure that the part is designed with the injection molding process in mind.
Some important elements of product design include:
- Uniform wall thickness to avoid dents and voids
- Draft angles so that the part can effectively push the product out of the mold
- Determining the choice of material during the design phase is critical to ensuring performance is met, as each material has a different shrinkage, melting and flow rate, changing the material can result in degraded part performance or out of tolerance.
Another aspect of product design that is often overlooked is the part tolerance for injection molding. There are many reasons why the tolerances of injection molded parts are wider than metal, such as the degree of shrinkage is not a uniform percentage (they are average), tool location (close vs. fixed dimensions), wall thickness, injection site, pressure and material flow all play a vital role in repeatability. Anyone can make a good part once, but who can make 100,000 or 1,000,000 repeatable units is what matters in production.
2.Mold Design And Development
Part quality starts with a quality mold. A common mistake we all make when purchasing a new injection molded component is trying to cut corners to reduce mold costs. If the instrument is built incorrectly, you may experience quality issues in the future, it may take 1 month, 6 months or 2 years.
To prevent defects and meet certain quality requirements, you and your toolmaker must work together to develop a mold that will properly produce the parts you need. This is a challenging task as mold design sometimes requires redesigning the part.
Tools are usually made from hardened tool steel or aluminum, depending on what you need. Aluminum tooling is typically used for prototyping or when a small number of parts are needed. Steel is the more expensive material, but is generally the most durable of the two options. Manufacturers requiring more than 10,000 parts will almost always use a steel mould.
3.Mold Design Elements:
- Sprue/chute location : This is one of the most important factors to consider during the filling phase of the injection process.
- Coolant lines : Incorrect placement or insufficient number of coolant lines leads to increased cycle times and warpage
- Heat Shrinkage : Shrinkage is typically between 0.4 – 2% and must be taken into account by the mold designer. The exact amount of shrinkage depends on several factors, including material, process conditions, and gate location.
- Part Tolerances : Tolerances and performance requirements are critical to determine prior to launch. This affects the design of the tool, affects where to stay “safe”, where to introduce material and where to discard material. We are seeing more and more parts being designed using metal tolerances, driving up costs and greatly extending lead times. An over-tolerance part can increase or decrease the tool’s budget due to additional steps, steps, or required quality checks.
The Disadvantages Of Injection Molding:
- High equipment costs : The cost of a mold depends on the number of parts needed (how many cavities will be required), the complexity of the part, and the size of the part. While single cavity prototyping tools can cost anywhere from $3,000 to $10,000, in the automotive industry, injection molding tools can range from $10,000 to $100,000 or more. These are very complex tools that are made from large blocks of hardened steel and take a long time to make by hand.
- Long Lead Time : Like mold cost, lead time depends on the complexity of the part, its size, and cavity requirements. Most companies also require prototypes before final production approval, which only adds to the lead time. Typically, you will see that a simple mold can be ready to use in 2-4 weeks, while a complex tool can take approximately 6-10 weeks.
- Difficulty to change : Since the molds are made of steel or aluminum, it can be quite difficult to make changes. If you want to increase the size of the part a little, you can always enlarge the cavity by cutting off the metal. But if you want to make the part smaller, you need to reduce the size of the mold cavity, which requires adding steel or aluminum to it. This is a complex process, and sometimes you will have to start over and discard the original form. That’s why it’s very important to use a mold prototype first.
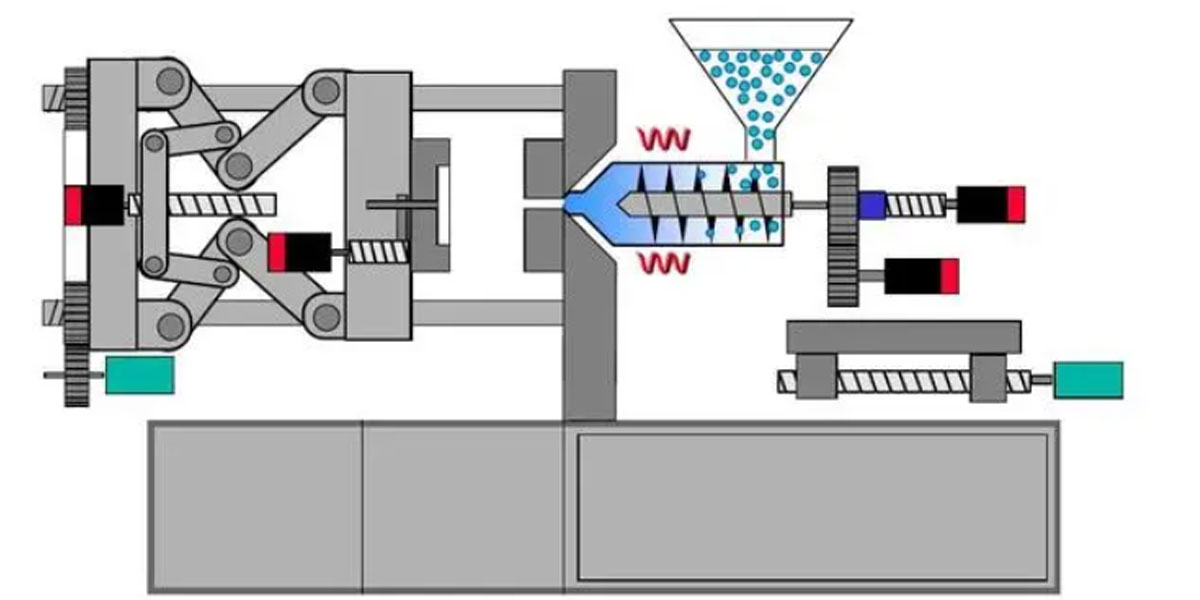
#3 Plastic Manufacturing Process
To make the production process as simple as possible, we have divided it into 5 stages. Each step is important and plays a vital role in part and mold design. The 5 steps of plastic injection molding production process include:
- 1 – Filling / melting stage : The injection molding process starts by filling the hopper with plastic pellets, which are fed into the screw barrel of the injection molding machine. The ring heaters help to melt the pellets, but it’s actually more of the plastic melting due to its compaction by the conical screw of the auger. This is because the pellets “rub” against each other, generating pure heat. By the end of the granules pass into a molten state.
- 2 – Injection/Packing Stage : The screw then pushes the molten plastic into the mold cavity where it takes shape and begins the cooling stage. This step is important because if there is not enough pressure, the cavity will not be completely filled, which will lead to quality problems.
- 3 – Cooling stage : Coolant lines, usually filled with water, run through the mold to maintain mold temperature, which helps cool the part faster. This is very important as the cooling phase is the most time consuming step in the injection molding cycle due to the insulating properties of the plastic. As the plastic cools and solidifies, it shrinks (called “mold shrinkage”). Shrinkage is typically between 0.4 and 2% and must be taken into account by the mold designer. Depending on the material you are using, you may need to cool the mold or heat the mold with cartridge heaters or hot oil.
- 4 – Ejection stage : After cooling, the mold is opened and the plastic part is ejected by the ejection pins built into it. If you look at most of the plastic parts you have around your house, chances are you can find marks from the ejector pins. The form will then close again to repeat the process.
- 5 – Post ejection stage : one of the last stages of this process is when the machine operator must break the sprue, guide or gate from the molded part by twisting or cutting them by hand, depending on the design of the mold. The hot runner mold system with spiral and flexible heaters virtually eliminates runners and gates, which also eliminates waste. Unfortunately, the hot runner makes the mold more expensive.
#4 How To Choose The Right Injection Mold?
Injection mold types and configurations vary greatly due to the many specifications of the molded components produced.
For this reason, mold type categorization can only be applied in general terms.
Of all the mold configurations used, the two and three plate mold designs are the most recognizable in appearance.
Two and three insert designs owe their name to the number of separation or separation lines used in the instrument’s design. Rice. 1. illustrates the importance of the position of the parting line in relation to individual mold designs.
Two and three plate designs form the basis for many variations on their basic format. The following are examples to illustrate how they can be used:
- Non-contact moulds, more commonly referred to as hot runner moulds, in which the material feed system remains molten throughout the molding cycle – solidifying just at the mold exit before being ejected from the mould.
- Undercut molds produce components whose elements undercut the mold cavity or core components in such a way that a core pull or feature removal is required before the mold is opened or ejected.
- Family molds where many different components are produced with the same tool, such as model kits, kitchen utensils, etc. Family molds are often used in low volume, relatively low component volumes to reduce tooling costs.
- Stacking molds, in which impressions are stacked on either side of the mold center plates, are often used on vertical molding machines for compression molding purposes, e.g. PTFE, etc.
#5 Choosing The Right Shape
The choice of mold design and manufacturing method is determined by a number of factors and requirements for the tool designer. Mistakes can easily be made if all relevant factors and requirements are not obtained and taken into account in advance. A good mold designer will get
as much information as possible about the following:
- Integral: Obtain a final approved drawing release from the potential client. Obtain commercial information about the component, such as the cost of the component, the size of the required production batches, the estimate of the lead time acceptable to the customer, the mold life requirements, etc.
- Material to be processed: Need information about material properties such as shrinkage, cooling requirements, rheology, thermal stability, etc.
- Equipment data: Get the molding machine specification
#6 Mold Specification
Using a mold specification has a number of benefits for the mold designer in terms of reducing the chance of unnecessary errors and building the designer’s basic knowledge of related topics.
A good mold specification also provides the mold designer with a basis for a quality control system in accordance with the client’s auditor’s approval requirements, which enhances customer confidence, which is an important factor when placing additional orders.
The easiest way to write a mold specification is to use a standard formatted form with all the necessary information laid out in a logical sequence.
#7 Mold Heaters
Hot runner molds use the following types of electric heaters to keep the material in the desired state.
1.Spiral Heaters
To heat the nozzles in hot runners, powerful spiral heaters are used , which allow heating the material to high temperatures with very compact dimensions.
The Heathl company manufactures spiral heating elements for GCS with five different cross-sections, three options for rectangular, one square and one round. The round cross section does not give such a tight contact with the nozzle, therefore, spiral heating elements with a rectangular cross section are mainly used for hot runner molds.
2.Flexible Heating Elements
The hot runner system consists of a manifold and sprues. For the collector, flexible heating elements are usually used , which can take any shape and are easily installed in special recesses.
Flexible heating elements have many options for shells and cross-sections, our specialists will help you choose the most suitable option for your mold by phone.
3.Cartridge Heaters
Some designs of hot runner molds may use cartridge heaters . This type of heating elements has a very high power density up to 10 W/cm2.
Cartridge heating elements are a metal tube closed on one side, in which a heating nichrome spiral is located. The spiral is insulated from the tube walls with magnesium oxide. You can choose the type of heater connection during the manufacture of heating elements from the list of options available on the page.
#8 Injection Molding Or Thermoforming For The Manufacture Of Plastic Products – Which Is Better?

If you look around, you can see that plastic is all around us. Wherever we go and whatever we do, we encounter it daily and everywhere.
Nowadays, the production of plastic parts is widespread and quite popular.
There are two main methods for the production of plastic parts:
1.Plastic Injection Molding:
This process involves melting plastic and injecting it into a special tool to give the plastic the desired shape.
The long list of standard injection molding materials is very diverse. Among others, thermoplastic rubber, antistatic plastic, biocompost material, chemically resistant plastics can also be used. And with the help of special additives, the color of the product can be anything.
The molten plastic moves in the injection molding tool along special grooves (“runners”), falling into the central cavity, which gives the part the necessary shape. The presence of cold skids on the forming tool leads to a hard bend in each forming cycle. They need to be removed from all moldings, but can be reused later. If the press tool has a hot fit, then the plastic always remains molten and takes part in the molding of the next part, hence the waste-free production.
2.Vacuum Forming:
This process allows the necessary parts to be formed by stretching a heated plastic sheet over a vacuum forming tool. The shape of the part is limited and occurs only in a single direction. The sheet of plastic is stretched over or within the mold, so this molding is not as versatile. However, it makes it possible to produce parts with significantly thinner walls.

The materials used in this method are not as diverse and numerous, but widely available (sheets of ABS transparent HIPS, UV stable HIPS & PETG, flame retardant ABS, HDPE, HIPS, conductive HIPS, HDPE, PP, PVC). The colors of the sheets are quite different, it is also possible to use sheets with special effects.
After forming, the product must be cut out of the plastic sheet (by roller cutting, manual cutting or CNC processing). Vacuum forming sometimes becomes quite expensive, due to the size of the product and the sheet itself. However, leftover sheets can be redirected to other processes.
Vacuum forming can reach reasonable tolerances, while injection molding makes it possible to achieve extremely close tolerances, allowing exactly the same parts to be produced the required number of times. Moreover, the material (in injection molding) is more controllable than in vacuum forming.
#9 Hot Runner Injection Molding
Injection of polymer raw materials under pressure is a technological production of elements and fully finished products. When using special equipment, the polymer becomes viscous and is subsequently injected under high pressure into the molding tool, where it takes the desired shape. The plastic is evenly distributed over the forming device, after which the stage of its cooling begins. When forming products under high pressure, preparatory processing of blanks is required.
High-quality equipment, exposure to optimal temperatures and experience will ensure high quality parts.
1.Where Are Injection Molded Polymer Products Used?
Due to injection molding, it is possible to obtain products from plastics of various types and complexity. The number of releases and many product options are unlimited. To understand the versatility of injection molding, consider a short list of products that can be made:
- Cases of electronic devices;
- Plastic car parts;
- Cases and plastic elements for household electrical appliances, as well as furniture;
- Devices made of plastic for medical use;
- Kids toys;
- Packaging and boxes.
2.The Advantage Of Injection Molding
Each manufacturer tries to minimize production costs. But, lowering the cost has a bad effect on the quality of the goods, which reduces the demand for it. For this reason, many companies suffer losses.
Why is it recommended to use the casting technique for the production of large series of polymer products?
Unlimited circulation. Metal molds made according to individual drawings can be used for a long time, since they are intended for a large number of work cycles.
Thanks to the injection technology, it is possible to manufacture objects with the most complex design. Parts can be produced thin-walled, which is more difficult to achieve on other molding equipment. For the manufacture of such elements, it is recommended to use metal molds, the properties and design of which will accurately recreate the smallest elements of the future product. This is an excellent option for the manufacture of both the simplest products and elements with complex design ideas, recesses and a large number of slots.
High precision and economical production. The material enters the forming tool under high pressure, which allows the molten mass to be evenly distributed over the entire inner surface of the mold. When molded, the plastic completely repeats even the smallest patterns and recesses of the prototype installation.
No further labor intensive modification required. The only exceptions are very complex products that require minimal mechanical rework.
Low price for goods. Given the large circulation, the cost of plastic products is reduced, which ensures quick sales. The main costs arise at the stage of preparing the equipment for operation, more precisely during the initial start-ups.
In addition to the advantages listed above, the casting method also has some disadvantages. The cost of preliminary work is significant, and the payback period for the manufacture of products in small batches or single copies is low.
3.The Key Steps Of Plastic Injection Molding
The course of the production cycle of plastic injection molding is divided into several stages, which are divided into two groups: preparation and injection.
Preliminary work includes the reproduction of a three-dimensional model of the mold. Modeling is carried out by means of drawings, photographs or an exact description by the customer.
When the model is completed and the customer has approved it, the stage of creating a primary sample of future products begins. This is necessary to identify inaccuracies and the possibility of producing defective products. If any are found, changes are made to the drawing, and the prototype is recreated.
Then, after the approval of the actions taken, the stage of creating the design of the mold itself begins. When designing, all the smallest details are taken into account.
Making molds. Each element of the form is made separately. Subsequently, a single structure is created from them. Using the new mold, the first product is released, which is carefully checked and tested. If any deficiencies or defects are found, the form is returned for revision.
Preparation sometimes takes a long time (up to 6 months). This process is important and should not be ignored. All further work on the manufacture of plastic products depends on how well the mold is made.
#10 Molds For Plastic Injection
The purpose of the mold is predetermined by casting products from plastic raw materials. The quality of the products themselves is determined by how accurately all the rules for manufacturing molds for the production of plastics are observed. For this reason, they are trying to be made from high quality steel materials. The metal has high strength and is easily polished, which also affects the quality of the model. It happens that the surface of the steel is chrome plated (alloyed steel) to prevent distortion of the exterior of the model.
In order to cast products without breaks and defects, in the manufacture of molds they try to use as few connectors as possible. Unfortunately, compliance with such aspects is not always possible. There are products that require multiple or even more connectors to be removed so that they are not damaged by direct removal from the mould.
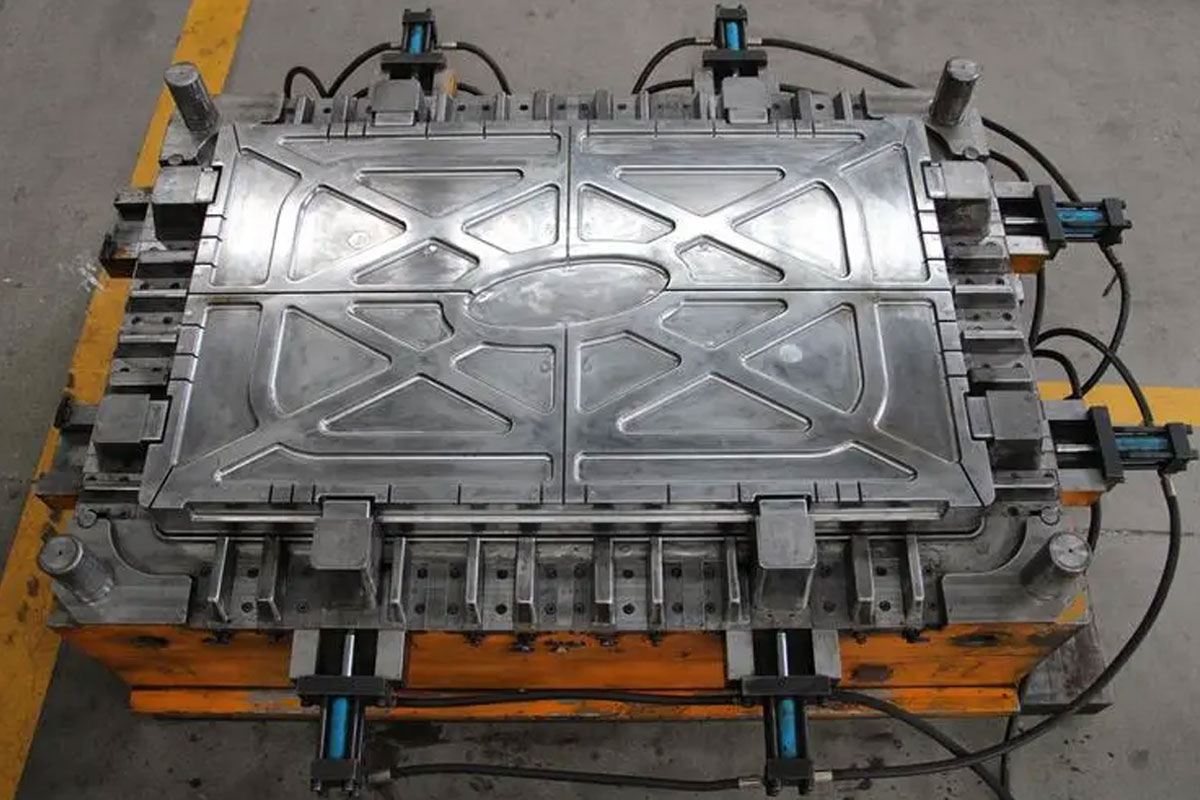
To reproduce the object with maximum accuracy, it is necessary to completely fill the mold with a polymer component. For this reason, the mold must also be equipped with a ventilation system and sprues. The ventilation device is designed to draw unwanted air from the mold. Installing the slider removes excess plastic. Some polymers are characterized by slow cooling. The greatest accuracy can be achieved with accelerated solidification, which can be provided by a cooling device in the mold itself. Often this work is done by the flow of cold water through the cooling channels. For the production of models in large quantities, it is important to have a matrix made of high quality materials that can guarantee its durability.
All units for polymer casting are divided into several types and depend on the type of casting and production volumes.
By volume, production is divided into four categories:
- production of one product;
- small-scale production;
- mass production;
- mass release.
Depending on the molding methods, there are two types of aggregates:
- closed type or the so-called piston version;
- mold by the method of smooth molding of plastics.
The piston casting method is popular and is used more often than injection molding. The principle of operation is the exact dosage of the mass to be formed. This mass (molten material) can initially be used in a variety of forms: powdered substance, bulk material, plastic raw materials. Using a mold with a casting, the polymer, after a snug fit of the fractions, is extruded from the mold. This method helps to obtain products with uniform wall thicknesses.
1.The specificity of forms in the manufacture of single and small-scale production options
In this type of manufacturing work, the molds are frequently replaced and for this reason it is more economical for economic reasons to produce them quickly and in a simpler configuration using a simple version of the mold. Manufacturing with additional machining loads (such as cutting allowances) is more economical than manufacturing a complex unit. In this industrial processing, dies are made from plastic, plaster or wood. Such matrices are not durable (for these types of work, its quality is not required), but they are economically viable. Forms are created according to master models. Gypsum molds are strengthened by the additional application of dusty quartz, quartz sand, the use of strong wire reinforcement or the injection of polyvinyl acetate emulsion liquid into the solution. After drying, varnish is applied to the model.
If the model has a small pattern, accuracy is required, the matrix is made from solutions based on synthetic resins, which can harden when cooled. Hardeners are often added to these solutions. Epoxy and acrylic resins can be used, they harden after the first plasticization. A filler is also added to the mixture: aluminum or iron powder. These forms are strong enough.
2.Specificity of forms for serial and mass production of manipulations
This type of production requires units of high strength and long service life; therefore they are smelted from steel and aluminum alloys. The development of metal forming devices is carried out by casting, cutting, grinding. Replaceable liners are installed inside to increase wear resistance.
Molds for large production operations are equipped with a horizontal connector, which provides practical installation and disassembly of the mold, excavation of models. As a rule, a double die mold is equipped with a lower and upper pull-out tool. If there is a lower matrix, there are inserts fixed with screws; guide pins for precise alignment of the two dies. The connection of the two shares occurs with the help of pins.
To create complicated models, molds made of steel material with a vertical split are used. In order to reduce the time spent on the execution of the model, cooling is used. To do this, narrow channels of water cooling are made in the walls, along the connector, matrix rods.
#11 Types And Design Of Molds
Injection molds are used in the molding of products with frequent temperature fluctuations up to several hundred degrees. In such a working environment, only high-precision settings can be used, the deviation in size of which cannot exceed 0.05 mm. To adhere to this rule, many designers use advanced mold production technologies that allow them to produce a full-fledged high-quality part in a fairly short period of time, taking into account the smallest elements.
1.Types of Molds
A mold is a device into which molten material is poured under high pressure. Polymers and metals are often used as materials. The mold determines all the external parameters of the manufactured product, including the shape, wall density and the smallest structural elements.
The punch is a movable element that complements the design of the mold. Designed to apply pressure to the material. The protrusions of the punch determine the internal structure of the manufactured product. In the process of cooling, the processed melt solidifies and settles on the protrusions of the punch, therefore, the recess of the finished part, after opening the mold, is carried out with the help of the punch.
Matrix – refers to the fixed component of the mold, depending on the required shape of the product, its inner surface is made with certain cavities.
Gating sleeve – a channel passage through which the material is fed into the cavity of the shaping unit.
The parting line of the mold is the surface of the convergence of the punch and the matrix.
The forming cavity of the mold is a cavity, the forum of which completely repeats the manufactured product. It is located between the matrix and the punch.
2.Double Plate Molds
This type of shaping system is one of the most common and simple installation options. Casting for such molds is cold-channel . The molten material passes freely from the central channel, then, getting into the gate, it begins to flow into the cavity of the forming device in a dosed manner. Products made by this technique can be easily identified by a noticeable round cut formed at the injection site in the very center of the part.
The fence of the finished part and the separation of the gates occurs due to the system of pushers, consisting of a shank, a special plate and the pushing devices themselves. The shape of the pushers can be very different. Cylindrical pushers leave a round imprint on the inner surface of the product.
One of the most important elements included in the molding equipment is the heat exchanger. The design of the heat exchanger includes a large number of rounded holes with a complex shape. A liquid passes through these holes, which provides cooling of the product after its molding.
3.Triple Molds
The molds, which include three plates at once, have two split lines. The first parting line is responsible for removing the finished product from the mold. The second – is intended for the intake of an already cooled sprue. This type of construction is necessary for the gate type and provides the possibility of injection not only along the perimeter of the mold, but also to its other points. The gate after opening the mold is separated automatically, and the injection point on the finished product is almost invisible, and takes only a few millimeters.
The removal cycle for three-platen installations usually begins already when the first split line is opened, which passes between the matrix and the punch, then the sprue is disconnected from the formed product. After the complete release of the part, the second split line is opened and the sprue itself is removed.
In case of avoiding any traces on the product, a method is used in which the casting is removed from the punch with a removable plate. Under such conditions, the pushing force is evenly distributed .
4.Hot Runner Molds
Hot runner systems, thanks to many advantages, of which waste-free production and accelerated production of products stand out in great demand, both from large industrial enterprises and from serial manufacturers. The equipment of such molds necessarily includes electric heaters, thanks to which the processed raw material is in the form of a homogeneous melt with uniform thermal values. Depending on the type of the hot runner casting system itself, one of two types of heaters is used: cartridge heating elements or spiral electric heaters . With these units, gate removal is eliminated, which significantly reduces the overall production cycle and the cooling phase.
The runner system of a hot runner mold consists of two main elements:
- Distribution collectors;
- Nozzle system.
The collector is located in the matrix plate and ensures the delivery of material from the nozzles of the injection equipment to the nozzles supplying the melt into the mold cavity.
Collectors and nozzles can have a variety of shapes. Due to the fact that these elements of injection molding equipment very often fail, it is desirable to use them in standard versions for the possibility of quick replacement. Elements of the original version should be purchased with a large margin and pre-order interchangeable parts.
#12 Conclusion
Plastic injection molding has improved a lot over the years and is a fantastic way to produce components on a large scale with minimal labor. While it seems like a relatively simple process of melting down plastic pellets and injecting it into a mold cavity, there are so many critical design elements, tools, and manufacturing process that will require work from you and an injection molder who knows how to meet your needs and special requirements.
