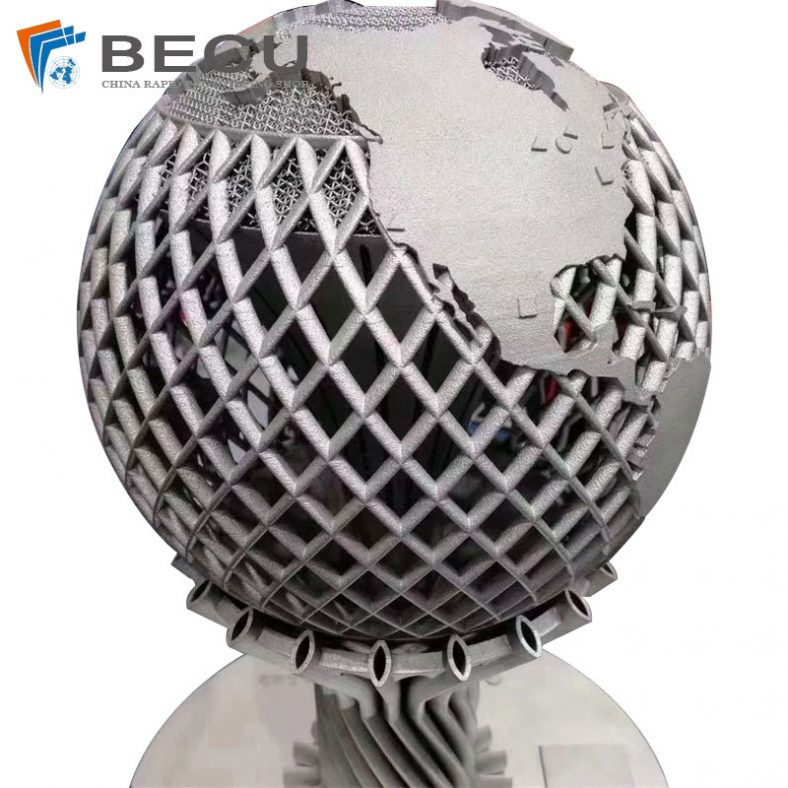
3D Printing For Titanium Alloy – What Is Titanium 3D Printing
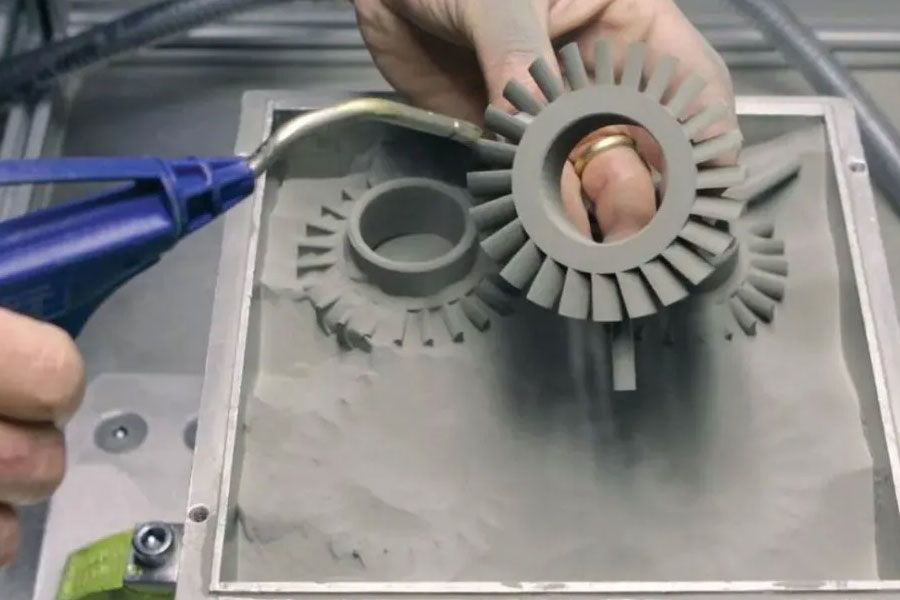
Titanium 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing with titanium, is the process of fabricating three-dimensional objects using titanium or titanium alloys. It combines the versatility and precision of 3D printing technology with the unique properties of titanium, resulting in highly functional and complex parts for various applications.
Titanium 3D printing comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. These include the high cost of titanium materials, the need for specialized equipment and expertise, and the requirement for stringent quality control processes. However, with advancements in technology and increasing accessibility, titanium 3D printing is becoming increasingly viable and offers tremendous potential for innovation in various industries.
For precision titanium 3D Printing, Be-Cu Prototype is the company you can turn to with confidence. We work with all titanium grades and alloys, and can DMLS or SLM 3d printing even the most complex titanium parts manufacturing and titanium components at tolerances within ±0.001” or better. We offer decades of experience in titanium 3d printing, along with the custom metal finishing services your projects require.
3D Printing Titanium Parts – Titanium 3D Printing Services
As you may have noticed, choosing the most suitable titanium for your product depends on the properties and applications you want. If you are trying to develop products for medical applications, you may want to choose the grade 5 titanium. Alternatively, if you are looking for a piece with excellent performance at elevated temperatures, you should consider working with grade 6 titanium.
If you want expert support from a vendor you can trust, look no further than the 3d printing services offered by Be-Cu prototype for your next titanium project.We can be a good help. We are a team of skilled professionals, who have a huge experience in providing quality titanium 3d printing services. Whether you require SLM, DMLS, or EBM metal 3D printing service, Be-cu.com provides quick-turn and efficient online 3D printing titanium parts at competitive prices.To know more about our services, please get in touch with our experts today. You can reach out to us both, simply mail us your requirements at [email protected].
Titanium Grades We Printing With
- Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5): Ti-6Al-4V is the most commonly used titanium alloy in additive manufacturing. It consists of 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, and 4% vanadium. This alloy offers a balance between strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra-Low Interstitial): Ti-6Al-4V ELI is a medical-grade titanium alloy that meets specific requirements for biocompatibility and is commonly used for 3D printing medical implants. It has similar composition to Ti-6Al-4V but with extra-low levels of interstitial elements, such as oxygen and nitrogen.
- Other Titanium Alloys: In addition to Ti-6Al-4V and CP titanium, there are various other titanium alloys that can be used for 3D printing, such as Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo, Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al, and Ti-5Al-2.5Sn, among others. These alloys offer specific properties tailored to meet the requirements of different applications.

Certainly! Here’s a table comparing some key differences among various titanium alloys commonly used in 3D printing:
| Titanium Alloy | Composition | Strength | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) | 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium | High strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace, automotive, medical |
| Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium with extra-low interstitials | Biocompatible, medical-grade alloy | Medical implants, surgical tools |
| CP Titanium | Commercially pure titanium (99% or higher) | Excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive, marine |
| Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo | 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 2% tin, 4% zirconium, 2% molybdenum | High strength, good corrosion resistance | Aerospace, marine |
| Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al | 90% titanium, 10% vanadium, 2% iron, 3% aluminum | High strength and toughness | Aerospace, defense |
| Ti-5Al-2.5Sn | 90% titanium, 5% aluminum, 2.5% tin | Good strength and weldability | Aerospace, marine |
The specific properties and applications of these alloys may vary depending on the manufacturing process, post-processing, and specific requirements of the application. It is essential to consult with material suppliers or experts to select the most suitable titanium alloy for a specific 3D printing application.
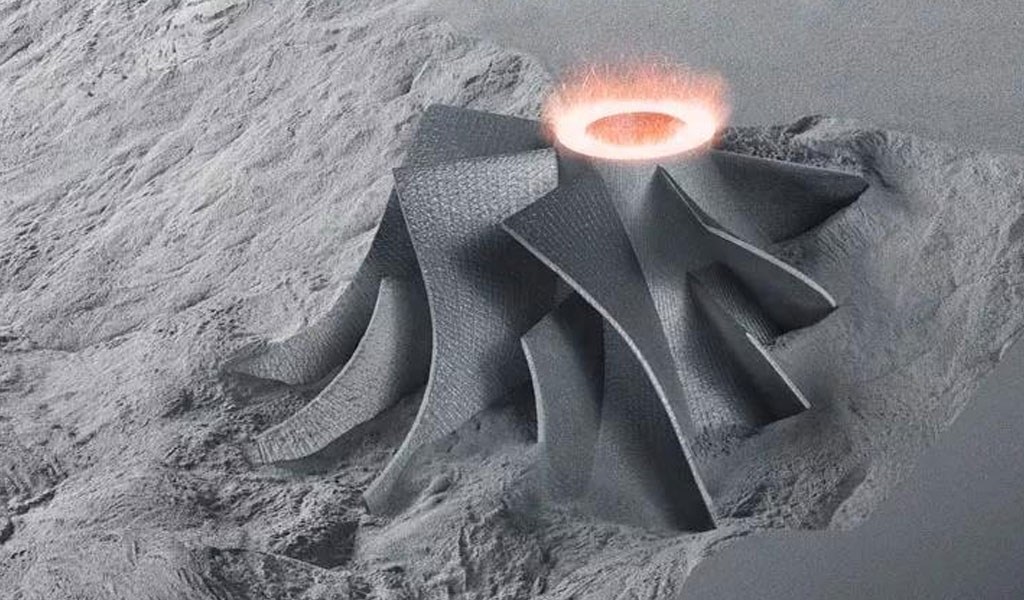
Titanium 3D Printing Capabilities
- Maximum Forming Printing Size Of Metal 3D Printer: 250x250x325mm;
- 3D printing layer thickness: 0.02mm~0.04mm;
- The Achievable Accuracy Of 3D Printing:Typical Accuracy: ±0.02-0.05 mm (Accuracy is related to geometry. It varies according to product size, printing direction, materials and post-processing methods.);
- Post-Processing: high temperature annealing, polishing, welding and other processing;
Certifications & Quality Machining
- ISO 9001:2015 certified
- Fully compliant with the exacting requirements of our customers
- Compliance in DFARS materials sourcing requirements
- Strict compliance with PPAP and Process
- FMEA for automotive customers
- Skilled in KanBan and CMM Inspection and inventory management systems
- ITAF 16949 certified
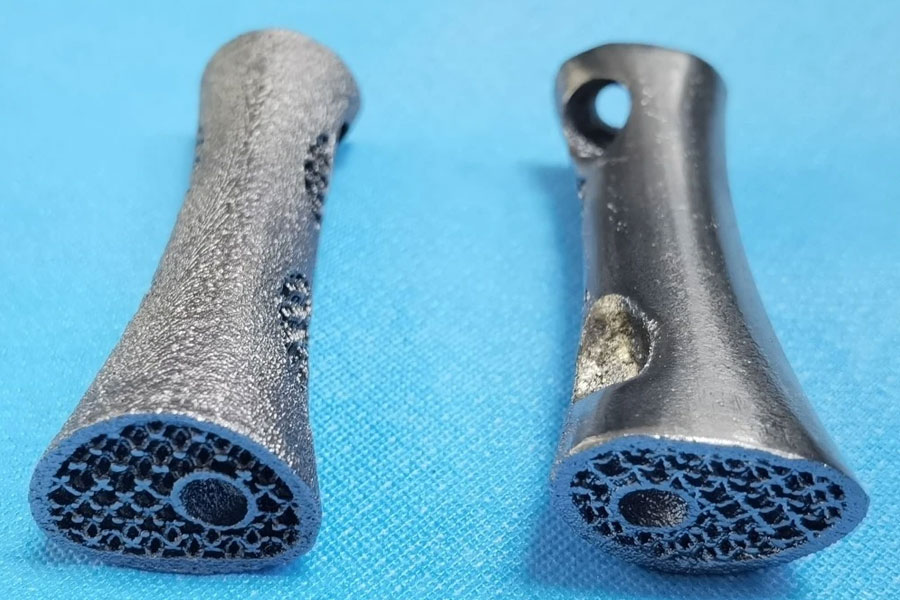

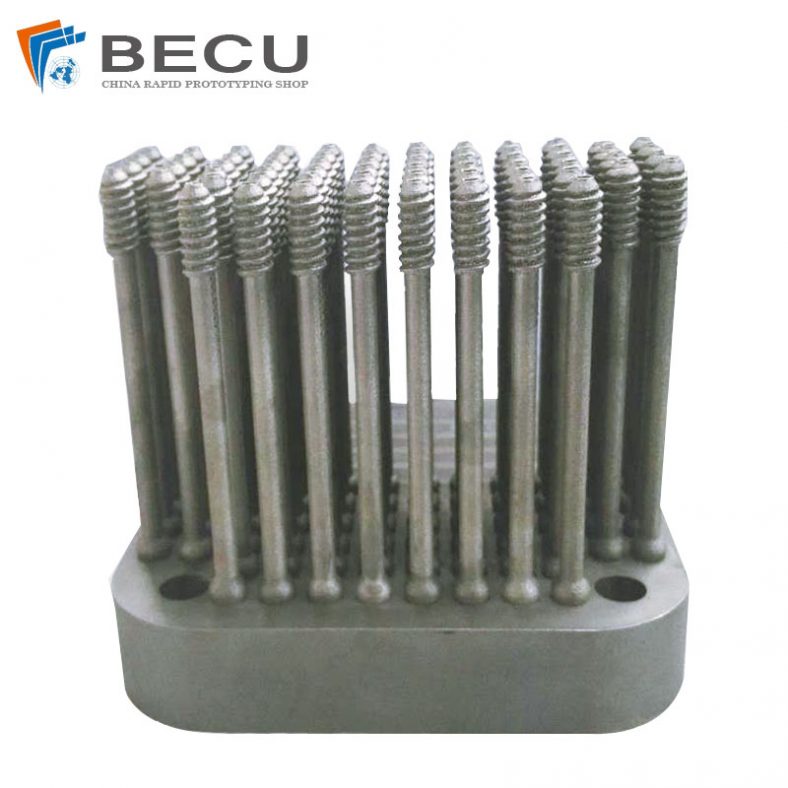
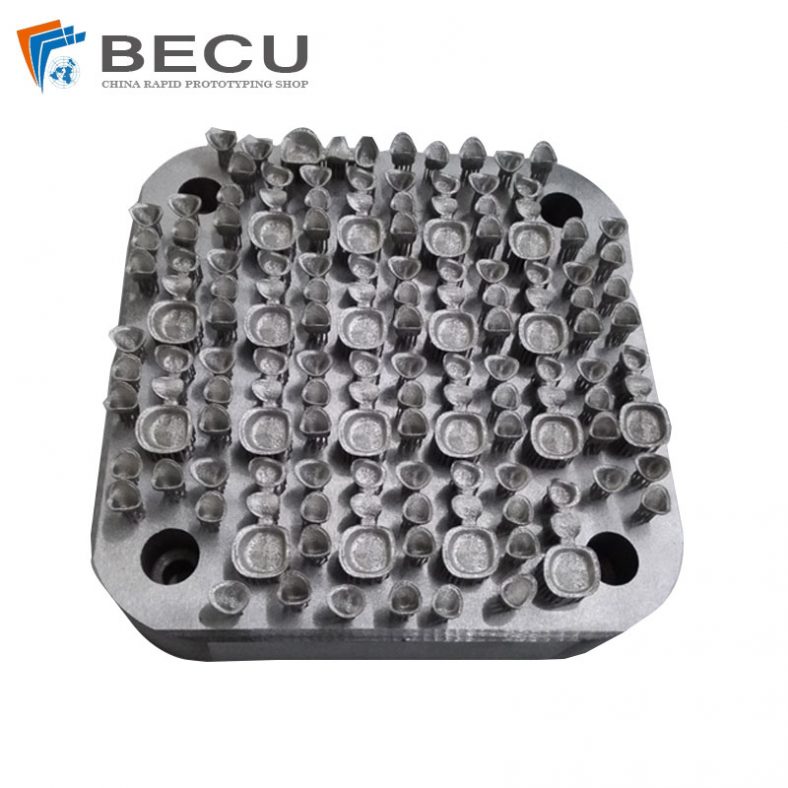
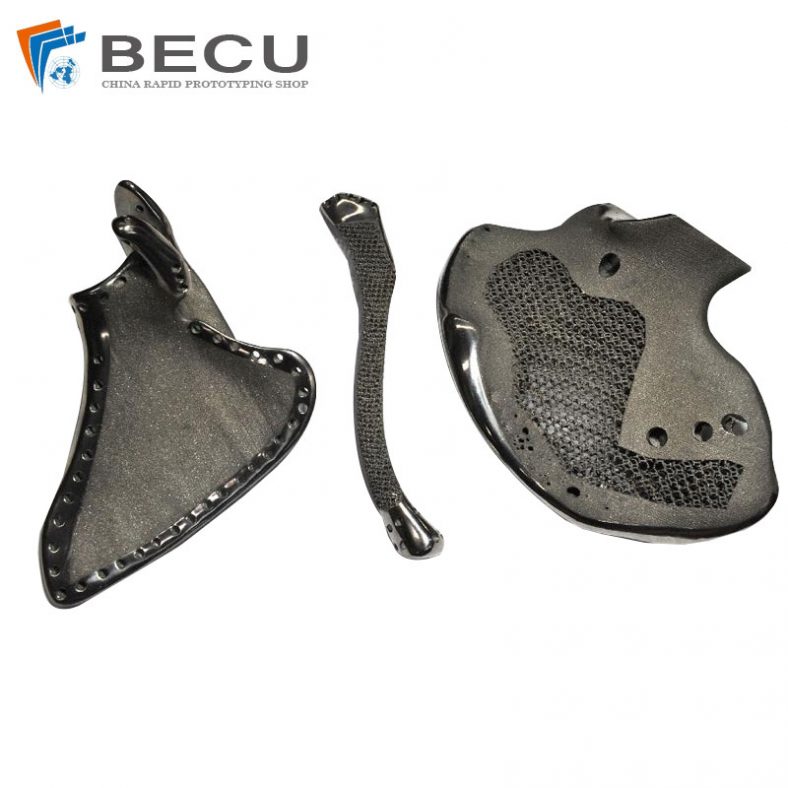
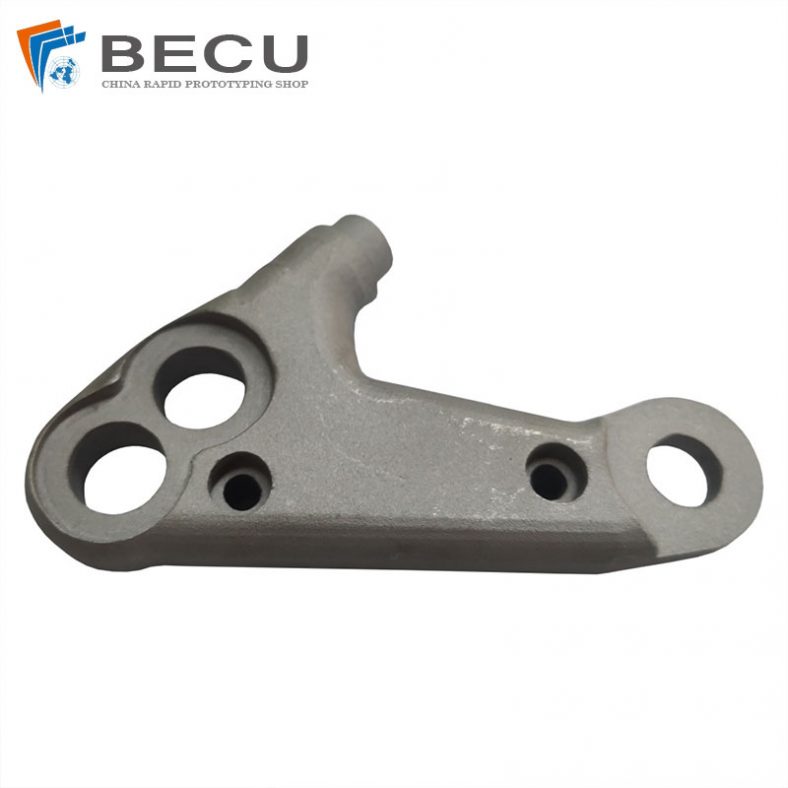
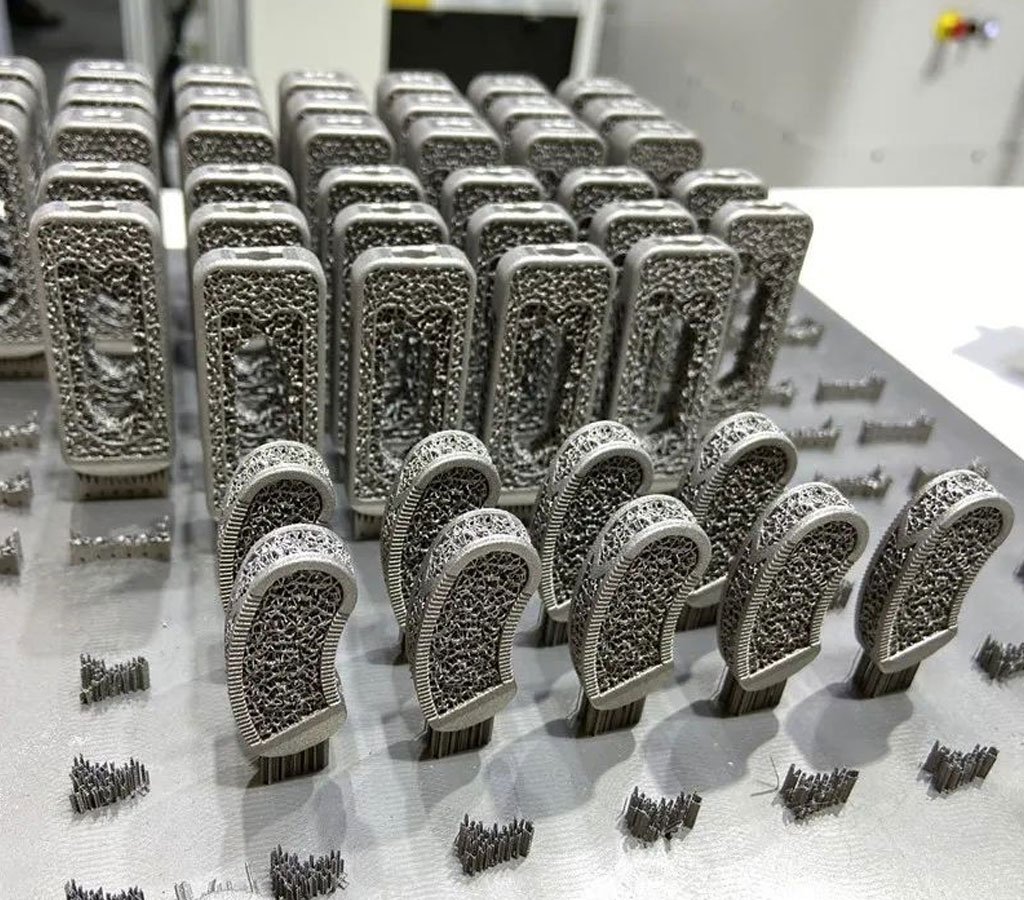
Top China Titanium 3D Printing Parts & Case Studies
The metal 3D printer distributes even layers of metallic powder and the powdered metal is selectively melted to previous layers, which allows 3D metal parts to be fabricated of a bed of powdered metal. Using metal 3D printing allows us to produce parts with complex geometries that using traditional manufacturing methods not capable of and with materials that are difficult to process. 3D printing metal materials including aluminum, stainless steel, cobalt chrome, nickel alloy, titanium, etc.
Titanium 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing with titanium, is transforming the manufacturing landscape by offering unprecedented possibilities for the production of complex and highly functional metal parts. With its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, titanium has long been a prized material in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and engineering. The advent of 3D printing technology has further enhanced the potential of titanium, allowing for the creation of intricate geometries, customized designs, and optimized components. We explore the world of titanium 3D printing, delving into its advantages, applications, challenges, and the future of this groundbreaking manufacturing technique.
How Titanium 3D Printing Work – The Process Of Titanium Printed
Titanium 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing with titanium, involves a multi-step process that transforms a digital design into a physical titanium part. Understanding the steps involved in the titanium 3D printing process is essential for achieving successful and high-quality results. Let’s explore the process in detail:
Designing the Part
The first step in titanium 3D printing is creating a digital design of the desired part using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This involves specifying the dimensions, features, and geometries of the part, considering factors such as functionality, structural integrity, and manufacturing feasibility.
Preparing the Digital Model
Once the part design is complete, the digital CAD file is prepared for 3D printing using specialized software. This step involves slicing the digital model into thin horizontal layers, which serve as a blueprint for the 3D printer to create the physical object layer by layer.
Selecting the Titanium Powder
Choosing the right titanium powder is crucial for successful 3D printing. Different titanium alloys may be used depending on the desired properties and applications of the final part. The powder should meet specific size and quality requirements to ensure optimal printing results.
Preparing the 3D Printer
Before starting the printing process, the 3D printer needs to be set up and prepared. This includes calibrating the machine, ensuring proper alignment, and checking the condition of the printing components, such as the build plate and print head.
3D Printing Titanium Part
With the printer and digital model ready, the titanium 3D printing process begins. There are various additive manufacturing technologies used for titanium, including selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM).
- Selective Laser Melting (SLM): In SLM, a high-powered laser selectively fuses or melts titanium powder particles together, layer by layer, according to the sliced digital model. The laser scans the powder bed, selectively melting the powder particles to create a solid part.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM): EBM utilizes an electron beam instead of a laser to melt the titanium powder. The electron beam is directed onto the powder bed, causing the powder particles to melt and fuse together.
Both SLM and EBM technologies allow for precise control over the melting process, enabling the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs.
Post-Processing
Once the part is fully printed, post-processing steps are carried out to refine the printed object and prepare it for its intended use. Post-processing may include the following:
- Removing Support Structures: If the part includes support structures to maintain its stability during printing, these supports need to be removed carefully using mechanical or chemical methods.
- Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes, such as stress relief annealing or solution heat treatment, may be applied to optimize the material properties, including strength and hardness.
- Surface Finishing: The surface of the printed part can be finished through processes such as polishing, grinding, or sandblasting to achieve the desired surface texture and aesthetics.
Quality Control
Quality control measures are essential to ensure the integrity and functionality of the printed titanium part. This may involve inspecting the part for dimensional accuracy, surface defects, and material properties using techniques such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM), non-destructive testing (NDT), and material testing methods.
By understanding and carefully executing each step of the titanium 3D printing process, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, precise, and functional titanium parts suitable for a wide range of applications. Continuous monitoring, optimization, and adherence to best practices are crucial for maximizing the benefits of titanium 3D printing technology.
The Advantages Of Titanium 3D Printing
Titanium 3D printing offers numerous advantages that make it a highly valuable and sought-after technology in various industries. Here are some key advantages of titanium 3D printing:
- Design Freedom: 3D printing allows for the fabrication of complex geometries and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. This freedom enables the creation of highly customized and optimized parts for specific applications.
- Lightweight and High Strength: Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. 3D printing with titanium allows for the production of lightweight parts without compromising strength. This is especially valuable in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where weight reduction is critical for fuel efficiency and performance.
- Customization and Personalization: Titanium 3D printing enables the production of highly customized and personalized parts. It allows for easy adaptation to individual requirements, making it ideal for applications such as medical implants, where patient-specific designs and geometries are crucial for optimal performance and patient comfort.
- Material Efficiency: Additive manufacturing with titanium offers superior material efficiency compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. It only uses the necessary amount of titanium powder required for the part, minimizing waste and reducing material costs.
- Complex Internal Structures: With 3D printing, it is possible to fabricate parts with intricate internal structures, including lattice structures and hollow features. These internal structures can provide enhanced mechanical properties, such as increased strength-to-weight ratio, improved heat transfer, or optimized fluid flow.
- Reduced Lead Times: 3D printing eliminates the need for extensive tooling and setup processes associated with traditional manufacturing methods. This allows for faster production times, rapid prototyping, and on-demand manufacturing. It significantly shortens the time-to-market for new products and enables more agile and flexible production.
- Design Optimization and Iteration: Titanium 3D printing enables iterative design processes, allowing designers and engineers to quickly test and refine their designs. This iterative approach helps optimize part performance, functionality, and manufacturability, leading to better end products.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: 3D printing generates less material waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Unused titanium powder can be collected and recycled, reducing environmental impact and material costs.
- Application Versatility: Titanium 3D printing finds applications in diverse industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and engineering. It is used for manufacturing aircraft components, engine parts, medical implants, customized surgical tools, high-performance racing components, and more.
While titanium 3D printing offers significant advantages, there are also considerations such as cost, equipment requirements, post-processing, and quality control. However, as the technology continues to advance and become more accessible, the advantages of titanium 3D printing make it an increasingly attractive option for innovative manufacturing solutions.





