Countersink holes play a crucial role in various industries, from manufacturing to construction. These precision-engineered features enhance the functionality, aesthetics, and structural integrity of countless products. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of countersink holes, exploring their purpose, types, applications, and best practices. Whether you are a professional in the field or a curious enthusiast, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the importance of countersink holes and their impact on modern engineering.
Understanding Countersink Holes
Countersink holes are precision-engineered features that are strategically created on the surface of a material, such as metal, wood, or plastic. These holes are conical in shape and are designed to accommodate the head of a screw, bolt, or rivet. The purpose of countersink holes is twofold: to allow the fastener to sit flush or below the material surface and to distribute the load evenly, ensuring a secure and aesthetically pleasing connection.
1.Definition and Purpose of Countersink Holes
The primary function of a countersink hole is to create a recess that accommodates the shape of the fastener head. By recessing the fastener, it avoids protrusion, allowing the material to sit flat against another surface or providing a clean finish. This is particularly important in applications where a smooth or streamlined appearance is desired, such as in cabinetry, furniture, or automotive manufacturing.
Additionally, countersink holes help to distribute the load evenly across the material and the fastener. By creating a conical recess, the material around the hole is thickened, providing greater support and preventing the fastener from damaging or weakening the material. This ensures a secure and durable connection that can withstand various forces, including tension, compression, and shear.Countersink holes find applications in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, woodworking, and metal fabrication. In the aerospace industry, countersink holes are used to flush mount fasteners, allowing for streamlined surfaces and reducing drag. In construction, countersink holes enable the seamless installation of screws or bolts in drywall, wood flooring, or metal structures.
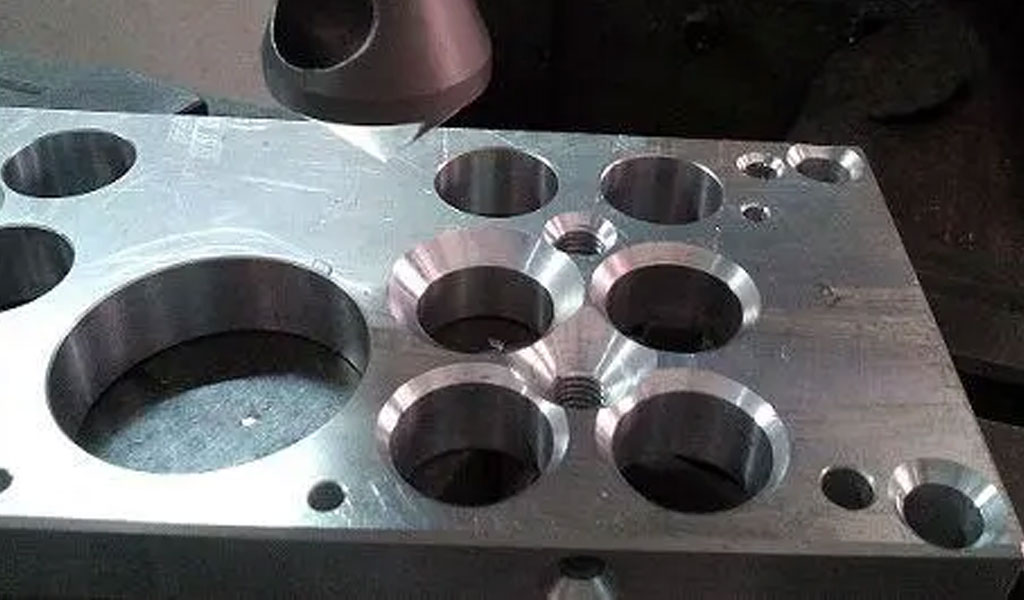

In woodworking, countersink holes provide a way to conceal screw heads and achieve a clean, finished look. These are just a few examples of the many applications where countersink holes are vital for both functionality and aesthetics.
Countersink holes are conical recesses created on the surface of a material to accommodate the heads of fasteners. They serve the purpose of allowing the fasteners to sit flush or below the material surface, distributing the load evenly, and providing a secure and visually appealing connection. By understanding the definition and purpose of countersink holes, engineers, manufacturers, and craftsmen can utilize this essential feature to enhance the performance and appearance of their products.
2.Basic Structure and Design
The structure and design of countersink holes are essential for achieving proper functionality and ensuring a secure connection between the fastener and the material. While the specific design may vary depending on the application and material being used, there are some common elements and considerations to keep in mind when creating countersink holes.
- Shape and Angle:Countersink holes are typically conical in shape, widening from a smaller diameter at the surface to a larger diameter at the bottom of the hole. The angle of the countersink is crucial and should be carefully determined based on the type of fastener and the material being used. Common angles include 60 degrees, 82 degrees, and 90 degrees, although other angles can be used depending on specific requirements.
- Diameter and Depth:The diameter of the countersink hole is determined by the size of the fastener head, ensuring a proper fit and allowing the head to sit flush or below the material surface. The depth of the countersink hole is typically calculated to achieve the desired flushness or depth, taking into account the thickness of the material and the type of fastener being used.
- Countersink Relief:To prevent sharp edges or burrs, a countersink relief may be incorporated at the bottom of the hole. This relief is a small flat area or radius that helps transition the surface from the angled countersink to the flat bottom of the hole.
- Material Considerations:The material being used and its properties play a significant role in determining the structure and design of countersink holes. Softer materials like wood or plastic may require less aggressive angles and depths to prevent splitting or deformation, while harder materials like metal may require sharper angles and deeper holes to ensure a secure fit.
- Countersink Tooling:Various tools can be used to create countersink holes, including countersink bits, countersink cutters, or combination drill bits with built-in countersinks. These tools are designed to cut the conical shape of the countersink hole accurately. It is crucial to select the appropriate tool based on the material being worked on and the desired countersink dimensions.
- Countersink Callouts:When creating technical drawings or specifications, countersink holes can be indicated using callouts that provide specific details such as the angle, depth, and diameter of the countersink. These callouts help ensure consistency and accuracy during manufacturing and assembly processes.
It is essential to follow design guidelines and best practices when creating countersink holes to achieve optimal functionality and structural integrity. Factors such as material properties, fastener type, and intended use should be carefully considered to determine the appropriate shape, angle, diameter, and depth of the countersink hole. By paying attention to these elements, engineers and manufacturers can create countersink holes that provide secure connections, aesthetic appeal, and long-lasting performance in a wide range of applications.
3.Key Benefits and Applications
Countersink holes offer numerous benefits and find widespread applications in various industries. Understanding these benefits and applications is crucial for engineers, manufacturers, and craftsmen to harness the full potential of countersink holes. Here are some key advantages and common applications:
Benefits of Countersink Holes
- Flush Mounting: Countersink holes allow fasteners, such as screws or bolts, to sit flush or below the material surface. This creates a smooth, seamless appearance, eliminating any protrusions or obstructions that could interfere with the functionality or aesthetics of the product.
- Improved Load Distribution: By creating a conical recess, countersink holes distribute the load evenly across the material and the fastener head. This helps prevent concentrated stress points, reducing the risk of material deformation, cracking, or failure, and improving the overall structural integrity.
- Enhanced Fastener Stability: Countersink holes provide a secure seating for fastener heads, preventing them from shifting or loosening over time. This is particularly important in applications subjected to vibrations, torque, or other external forces.
- Aesthetics and Finishing: Countersink holes contribute to a clean, professional finish in various industries, such as woodworking, cabinetry, or furniture manufacturing. By concealing the fastener heads, countersink holes enhance the overall appearance of the product, creating a streamlined and polished look.
- Efficient Fastener Installation: Countersink holes simplify the installation process by guiding the fastener into the proper position, ensuring accurate alignment and reducing the risk of stripping or damaging the material. This improves efficiency and saves time during assembly or construction processes.
Applications of Countersink Holes
- Aerospace Industry: Countersink holes play a vital role in the aerospace industry, where aerodynamic efficiency and weight reduction are crucial. They are used for flush mounting fasteners, such as rivets, on aircraft surfaces, reducing drag and improving fuel efficiency.
- Woodworking and Carpentry: Countersink holes are commonly used in woodworking and carpentry to hide screw heads and achieve a clean, finished appearance. They are essential for assembling furniture, cabinetry, flooring, and other wooden structures.
- Metal Fabrication: In metal fabrication, countersink holes are employed to prepare surfaces for welding or to ensure accurate alignment during the assembly of metal components. Countersunk fasteners are commonly used in structural applications, including bridges, machinery, and automotive manufacturing.
- Construction Industry: Countersink holes find applications in the construction industry for a variety of purposes. They are used to install screws or bolts in drywall, metal framing, decking, and other construction materials, providing a flush and secure connection.
- Electronics and Electrical Applications: Countersink holes are utilized in electronics and electrical equipment manufacturing to create recesses for mounting components, circuit boards, or panels. This allows for a neat, space-saving installation while ensuring proper alignment and security.
- Automotive Industry: Countersink holes are employed in the automotive industry for applications such as attaching body panels, securing interior components, or installing fasteners in engine components. They enhance the overall aesthetics and streamline the assembly process.
- General Manufacturing: Countersink holes are widely used in various manufacturing processes, such as sheet metal fabrication, plastic molding, or composite material assembly. They provide a reliable and aesthetically pleasing method for fastening components together.
Types of Countersink Holes
Countersink holes come in different types, each suited for specific applications and design requirements. The following are the common types of countersink holes:
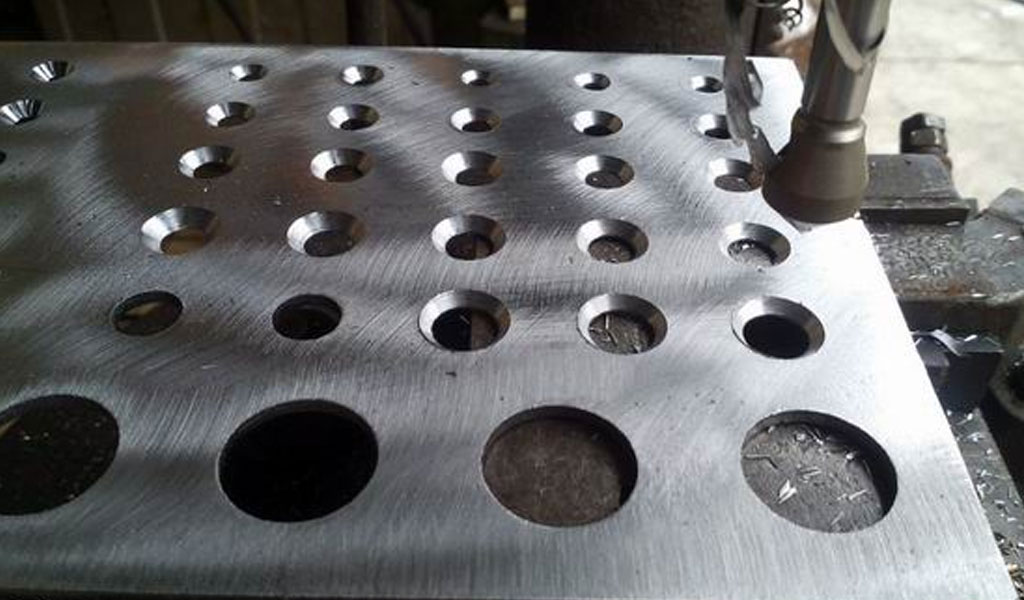

1.Traditional Countersink Holes
Traditional countersink holes are the most commonly used type of countersink holes and are characterized by their simple conical shape. They feature a straight or tapered sidewall that gradually widens from the surface to the bottom of the hole.
Traditional countersink holes are available in different angles, with the most common being 60 degrees, 82 degrees, and 90 degrees, although other angles can be used based on specific requirements.
Traditional countersink holes offer several advantages and find wide application across various industries. Traditional countersink holes are widely recognized for their simplicity, reliability, and versatility. They provide a practical and effective solution for achieving flush and concealed fastener heads in various materials and applications. By using traditional countersink holes, engineers, manufacturers, and craftsmen can enhance the aesthetics, functionality, and durability of their products while maintaining ease of assembly and installation.
2. Countersink Holes with Chamfers
Countersink holes with chamfers combine the benefits of a countersink hole with the added feature of a chamfered edge. A chamfer is a beveled or angled surface around the top edge of the countersink hole.Countersink holes with chamfers offer an attractive and functional solution for achieving both aesthetic appeal and prevention of material damage during fastener installation. By incorporating chamfers into countersink holes, engineers and manufacturers can enhance the overall appearance, improve alignment, and ensure a secure and visually appealing connection in their products.

3.Combined Countersink and Counterbore Holes
Combined countersink and counterbore holes are a specialized type of countersink hole that incorporates both a countersunk recess for the fastener head and a larger-diameter counterbore for the shank of the fastener. This combination allows the fastener to sit below the material surface while providing a flush fit for the fastener head.
Combined countersink and counterbore holes offer a practical and efficient solution for achieving flush and recessed fastener installations. They provide enhanced load distribution, precise alignment, and compatibility with a variety of materials. By using combined countersink and counterbore holes, engineers, manufacturers, and craftsmen can ensure a professional finish and reliable connections in their products.
When to Use a Countersink
Countersinks are commonly used in various applications where flush or recessed fastener installation is desired. Here are some situations where using a countersink is recommended:
1.Concealed Screw Heads
Countersinks are frequently employed when hiding or concealing the heads of screws or bolts is necessary. By creating a recessed area for the fastener head, countersinks allow the surface to remain smooth and uninterrupted, improving the overall appearance of the product. This is especially important in applications where aesthetics are a priority, such as cabinetry, furniture, or interior design.
2.Flush Mounting
When a fastener needs to sit flush or below the material surface, countersinks are essential. This is commonly seen in applications like woodworking, where joining two pieces of wood requires the fastener heads to be below the surface for a level and seamless connection. Flush mounting also helps prevent snagging or catching on the fastener heads, enhancing safety and functionality.
3.Load Distribution
Countersinks contribute to even load distribution across the fastener and the material. By creating a conical recess, countersinks help distribute the load evenly, reducing stress concentrations and minimizing the risk of material deformation or failure. This is particularly important in applications subject to various forces, such as tension, compression, or shear.
4.Improved Stability
Countersinking provides increased stability and security for fasteners. By creating a recessed area for the fastener head, countersinks prevent the fasteners from protruding or loosening over time due to vibrations, movement, or external forces. This is crucial in applications that require long-term durability and reliable fastener connections.
5.Surface Finishing
Countersinks are often used in applications that involve surface finishing or refinishing. By creating a recessed area for fasteners, countersinks allow for a smooth and level surface, facilitating a more refined finishing process. This is advantageous in industries such as automotive, aerospace, or metal fabrication, where a pristine surface appearance is desired.
6.Alignment and Positioning
Countersinks aid in proper alignment and positioning of fasteners during installation. The conical recess guides the fastener head into the correct position, ensuring accurate alignment and preventing misalignment or skewed installation. This helps streamline the assembly process and improves efficiency.
Countersinks are valuable tools in achieving flush or recessed fastener installations, improving aesthetics, load distribution, stability, and alignment. They are widely used in woodworking, cabinetry, furniture manufacturing, construction, automotive, and various other industries where secure, concealed, and aesthetically pleasing fastener connections are desired.
Here is a countersunk hole size chart for socket flat head fasteners (ANSI Inch):
| Nominal Size (Inch) | Screw Size (Inch) | Countersink Diameter (Inch) | Countersink Depth (Inch) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #2 | 0-80 | 0.094 | 0.041 |
| #4 | 2-56 | 0.141 | 0.062 |
| #6 | 4-40 | 0.169 | 0.078 |
| #8 | 6-32 | 0.197 | 0.094 |
| #10 | 8-32 | 0.225 | 0.109 |
| #12 | 10-24 | 0.253 | 0.125 |
| 1/4 | 1/4-20 | 0.345 | 0.156 |
| 5/16 | 5/16-18 | 0.394 | 0.188 |
| 3/8 | 3/8-16 | 0.444 | 0.219 |
| 7/16 | 7/16-14 | 0.494 | 0.250 |
| 1/2 | 1/2-13 | 0.544 | 0.281 |
| 9/16 | 9/16-12 | 0.594 | 0.312 |
| 5/8 | 5/8-11 | 0.657 | 0.344 |
| 3/4 | 3/4-10 | 0.782 | 0.406 |
| 7/8 | 7/8-9 | 0.907 | 0.469 |
| 1 | 1-8 | 1.032 | 0.531 |
Please note that this chart provides general guidelines and recommended dimensions. However, it is always essential to consult the specific fastener manufacturer’s guidelines and reference the appropriate standards for accurate countersunk hole dimensions.
We’ll help you dial in your designs and properly call out features like countersunk holes
Countersinks are frequently employed when hiding or concealing the heads of screws or bolts is necessary. By creating a recessed area for the fastener head, countersinks allow the surface to remain smooth and uninterrupted, improving the overall appearance of the product. This is especially important in applications where aesthetics are a priority, such as cabinetry, furniture, or interior design, and Be-Cu.com has you covered. Our manufacturing network has experts in injection molding, CNC machining, 3D printing, and urethane casting, and they’ll help you dial in your designs and properly call out features like countersunk holes.
