Distribution boxes, also known as electrical distribution boards or panels, are pivotal components in electrical systems, ensuring the safe and organized distribution of electrical power throughout residential, commercial, and industrial environments. These boxes house various circuit breakers, protective devices, and sometimes meters, which collectively manage and distribute electricity to different circuits within a facility. The correct choice and installation of distribution boxes are crucial for electrical safety, efficiency, and reliability. This guide provides an exhaustive overview of the different types of distribution boxes, their features, applications, and considerations for selection and installation.
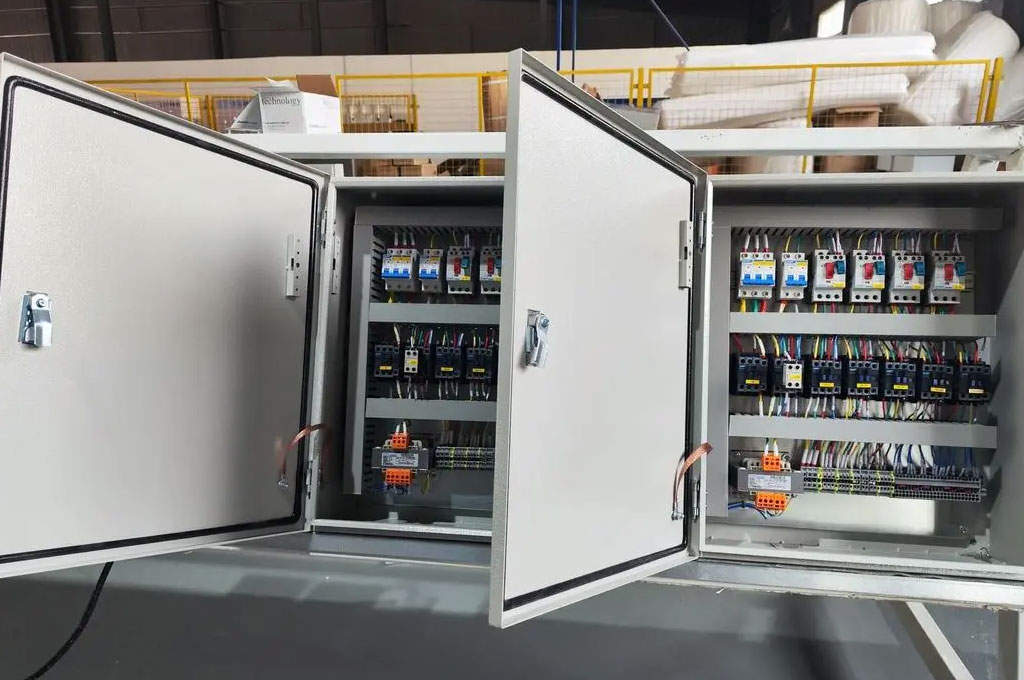

What Are Distribution Boxes?
Distribution boxes, also known as junction boxes, electrical boxes, or panelboards, are essential components in electrical distribution systems. They serve as protective enclosures for the connections, splices, and terminations of electrical wires and cables.
Distribution boxes are critical for ensuring the safety, reliability, and organization of electrical circuits in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. By housing and protecting electrical connections, these boxes help prevent electrical shocks, short circuits, and other hazards while facilitating easier maintenance and troubleshooting.
Functions of Distribution Boxes
- Protection: Distribution boxes shield electrical connections from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and physical damage. They also protect against accidental contact with live wires, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and fires.
- Organization: By consolidating multiple electrical connections in a single enclosure, distribution boxes help keep wiring organized and manageable. This organization simplifies the installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of electrical systems.
- Connection: Distribution boxes serve as central points for connecting and distributing electrical power to various circuits and devices. They house terminals, busbars, and other components that facilitate these connections.
- Safety: Distribution boxes often contain protective devices such as circuit breakers and fuses, which prevent overcurrent and short circuits by interrupting the flow of electricity in fault conditions.
- Accessibility: Distribution boxes provide a convenient and accessible location for inspecting, testing, and repairing electrical connections. This accessibility is crucial for maintaining the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
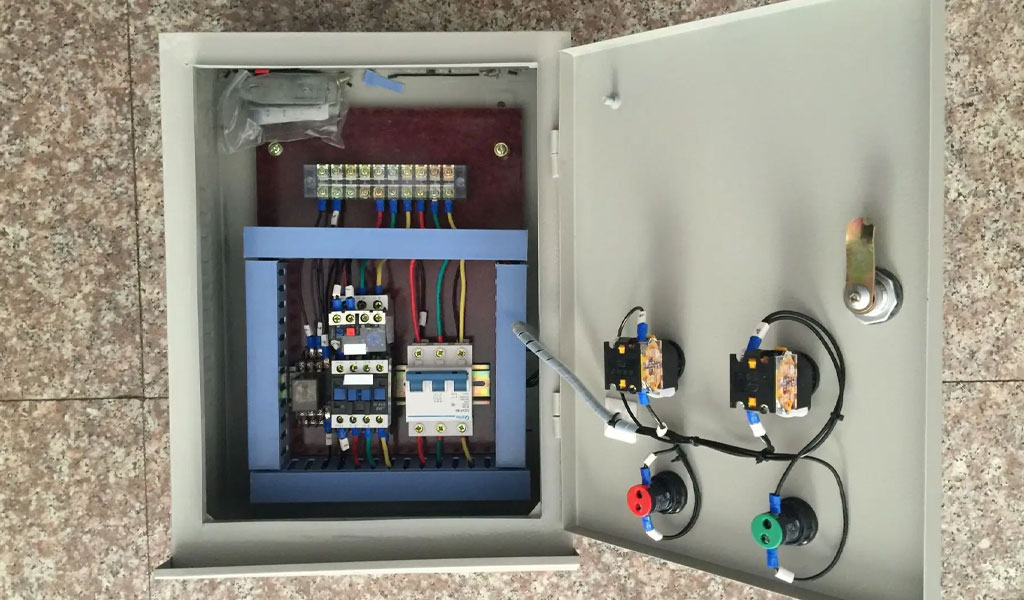
Basic Components of Distribution Boxes
Distribution boxes consist of several key components, each serving a specific function in the overall system. Understanding these components is essential for selecting, installing, and maintaining distribution boxes effectively.
1. Enclosure
The sheet metal enclosure is the outer shell of the distribution box, providing physical protection for the internal components. It is typically made from materials such as metal or plastic, chosen for their durability, insulation properties, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Material: Common materials include steel, aluminum, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polycarbonate. The choice of material depends on the application and environmental conditions.
- Design: Enclosures come in various designs, including surface-mounted, flush-mounted, and weatherproof models, to suit different installation requirements.
2. Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks are connection points within the distribution box where wires and cables are securely attached. They provide a neat and organized way to connect multiple electrical conductors.
- Screw-Type: Terminal blocks with screw connections are common, allowing wires to be secured by tightening screws.
- Spring-Loaded: Some terminal blocks use spring mechanisms to hold wires in place, offering easier and faster connections.
3. Busbars
Busbars are conductive bars or strips that distribute electrical power to various circuits within the distribution box. They are typically made of copper or aluminum due to their excellent conductivity.
- Main Busbars: Distribute power from the main supply to individual circuits.
- Neutral and Ground Busbars: Provide connection points for neutral and ground wires, ensuring proper grounding and circuit balance.
4. Circuit Breakers and Fuses
Circuit breakers and fuses are protective devices that prevent overcurrent and short circuits by interrupting the flow of electricity when a fault occurs.
- Circuit Breakers: Automatically trip to interrupt the circuit in case of an overload or short circuit. They can be reset manually after the fault is cleared.
- Fuses: Contain a wire that melts and breaks the circuit when excessive current flows through it. Fuses must be replaced after they blow.
5. Grounding Bar
The grounding bar, also known as the ground bus, provides a common point for connecting the ground wires of various circuits. Proper grounding is essential for safety, preventing electrical shocks, and ensuring the safe operation of electrical systems.
- Design: Grounding bars are typically made of copper or aluminum and feature multiple terminals for connecting ground wires.
- Function: They ensure all parts of the electrical system are at the same ground potential, reducing the risk of electrical shocks.
6. Cable Management Features
Effective cable management is crucial for maintaining an organized and safe distribution system. Distribution boxes include various features to manage and secure cables.
- Knockouts: Pre-punched holes in the enclosure that can be removed to create openings for cable entry.
- Cable Glands: Provide a secure and sealed entry for cables, protecting against environmental factors and mechanical stress.
- Clamps and Strain Reliefs: Secure cables inside the distribution box, preventing strain on the connections.
7. Cover and Access Panel
The cover or access panel of a distribution box provides a protective barrier, preventing accidental contact with live components. It also offers easy access for maintenance and inspection.
- Hinged Covers: Allow easy opening and closing, often secured with screws or latches.
- Transparent Covers: Some distribution boxes feature transparent covers, enabling visual inspection without opening the box.
8. Labels and Documentation
Clear labeling and documentation are essential for the safe and efficient operation of distribution boxes. Labels identify the function of each circuit, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot the system.
- Circuit Labels: Indicate the purpose of each circuit (e.g., lighting, outlets, HVAC).
- Wiring Diagrams: Often included inside the cover or enclosure, providing a reference for the layout and connections.
Distribution boxes are vital components in electrical systems, providing protection, organization, and safety for electrical connections. Understanding the basic components of distribution boxes helps in selecting the right box for specific applications and ensures proper installation and maintenance. As technology and materials continue to evolve, distribution boxes will remain integral to the safe and efficient distribution of electrical power in various settings.
History and Evolution of Distribution Boxes
The history and evolution of distribution boxes reflect the broader development of electrical systems and technology over the past two centuries.
From their rudimentary beginnings to the advanced systems we see today, distribution boxes have undergone significant changes in design, materials, and functionality to meet the growing demands for safety, efficiency, and reliability in electrical installations.
Early Electrical Systems (Late 19th Century)
The late 19th century marked the advent of electrical power systems. Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla were pioneers in the development of direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) systems, respectively. As electrical power began to be distributed for residential and industrial use, the need for safe and reliable methods to connect and distribute electricity became apparent.
- Basic Junction Boxes: Early distribution systems utilized simple junction boxes, which were basic enclosures that housed electrical connections. These were often made of wood or metal and provided minimal protection against electrical hazards.
- Fuses and Switches: To protect against overcurrent and short circuits, early systems employed fuses and mechanical switches within these junction boxes. These devices were the precursors to modern circuit breakers and protective relays.
The Rise of Circuit Breakers (Early to Mid-20th Century)
As electrical systems grew more complex and widespread, the limitations of fuses and basic junction boxes became evident. The early 20th century saw significant advancements in the development of circuit breakers, which could automatically interrupt electrical flow in the event of an overload or fault.
- Metal Enclosures: Distribution boxes evolved to include sturdier metal enclosures, providing better protection against physical damage and environmental factors.
- Standardization: The development of national and international electrical standards began to shape the design and construction of distribution boxes. Standards like the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States and similar regulations in other countries set guidelines for safety and performance.
Post-War Expansion and Residential Use (Mid-20th Century)
The post-World War II era witnessed a boom in residential construction and the widespread adoption of electrical appliances. This period saw significant changes in the design and use of distribution boxes in homes.
- Residential Panels: The development of residential electrical panels, also known as breaker panels or fuse boxes, became standard in home construction. These panels housed circuit breakers or fuses for individual circuits, providing a centralized point for managing household electrical systems.
- Plastic Enclosures: Advances in materials science introduced the use of plastic enclosures, which were lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and provided adequate protection for residential applications.
Industrial Advancements and Modular Designs (Late 20th Century)
The late 20th century saw rapid industrialization and technological advancements, leading to more sophisticated electrical distribution systems in commercial and industrial settings.
- Modular Distribution Boxes: The introduction of modular designs allowed for greater flexibility and scalability. Modular distribution boxes could be customized and expanded to meet the specific needs of industrial facilities and large commercial buildings.
- Advanced Protection Devices: The development of more advanced protection devices, such as residual-current devices (RCDs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), enhanced the safety of electrical systems.
Digital Revolution and Smart Technology (21st Century)
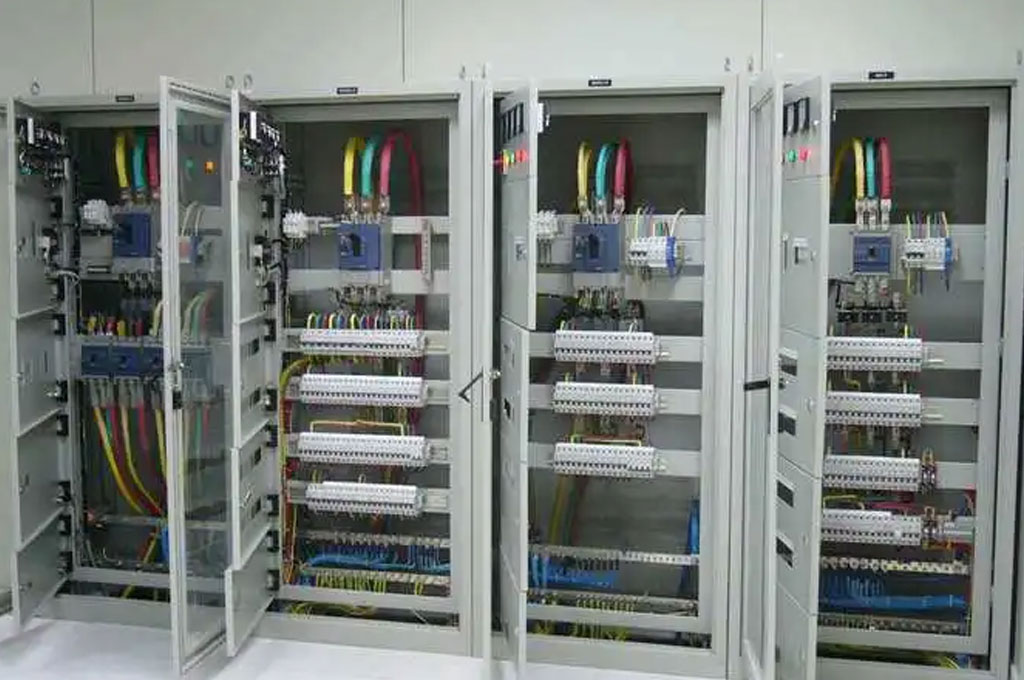

The 21st century has brought about the digital revolution, significantly impacting the design and functionality of distribution boxes. The integration of digital technologies has transformed traditional distribution systems into intelligent, interconnected networks.
- Smart Distribution Boxes: Modern distribution boxes often incorporate smart technology, enabling remote monitoring and control via the Internet of Things (IoT). These smart boxes can provide real-time data on electrical usage, identify faults, and optimize energy consumption.
- Enhanced Safety and Efficiency: Advances in materials and engineering have led to more efficient and safer distribution boxes. Features such as arc fault detection, surge protection, and advanced circuit breakers have become standard in many systems.
Future Trends and Innovations
The evolution of distribution boxes continues as new technologies and materials emerge. Future trends are likely to focus on further enhancing safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
- Energy Management: As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources and decentralized power generation, distribution boxes will play a crucial role in managing and distributing energy from diverse sources.
- Sustainable Materials: The use of sustainable and environmentally friendly materials in the construction of distribution boxes is expected to increase, aligning with global efforts to reduce environmental impact.
- Integration with Smart Grids: Distribution boxes will become integral components of smart grids, enabling more efficient and reliable distribution of electricity across interconnected networks.
The history and evolution of distribution boxes reflect the dynamic nature of electrical engineering and technology. From their humble beginnings as simple enclosures for electrical connections, distribution boxes have evolved into sophisticated components that ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of modern electrical systems. As technology continues to advance, distribution boxes will undoubtedly continue to play a vital role in the future of electrical power distribution.
Types of Distribution Boxes
Distribution boxes, essential in electrical systems, come in various types tailored for different applications and environments. Understanding the distinctions between residential, commercial, industrial, and specialized distribution boxes is crucial for selecting the appropriate solution for specific electrical needs.
1. Residential Distribution Boxes
Residential distribution boxes are designed for use in homes and smaller residential buildings. They are typically compact, user-friendly, and cater to the electrical demands of typical household applications.

Main Distribution Board (MDB):
- Central hub for distributing electrical power throughout the home.
- Contains circuit breakers or fuses for individual circuits like lighting, outlets, and appliances.
- Usually located near the point of entry of electrical supply into the house.
Sub Distribution Boards (SDB):
- Secondary panels connected to the main distribution board.
- Serve specific areas of the house like garages, basements, or additional floors.
- Distribute power from the main board to reduce circuit loads and improve safety.
2. Commercial Distribution Boxes
Commercial distribution boxes are designed to handle larger electrical loads and more extensive electrical systems found in commercial buildings, offices, and retail spaces.
Panelboards:
- Main distribution points in commercial buildings.
- Designed to accommodate numerous circuits and high current ratings.
- Provide flexibility for adding circuits or expanding as needed.
Lighting Distribution Panels:
- Dedicated panels for managing lighting circuits throughout commercial spaces.
- Often include features for dimming, zoning, and energy management.
- Ensure efficient and safe distribution of electrical power for lighting fixtures.
3. Industrial Distribution Boxes
Industrial distribution boxes are robust solutions designed for demanding environments such as factories, manufacturing plants, and industrial facilities where electrical systems must withstand harsh conditions and heavy loads.
Motor Control Centers (MCC):
- Centralized panels for controlling and managing electric motors.
- Provide circuit protection, switching, and monitoring capabilities for motors and associated equipment.
- Essential for maintaining operational efficiency and safety in industrial settings.
Power Distribution Units (PDU):
- Distribute electrical power to equipment and machinery in data centers, industrial complexes, and large facilities.
- Often modular and scalable to accommodate changing power demands.
- Include advanced features like surge protection and remote monitoring for enhanced reliability.
4. Specialized Distribution Boxes
Specialized distribution boxes are tailored for specific applications and environments that require unique features, materials, or protection against specific hazards.
Explosion-Proof Boxes:
- Designed for use in hazardous environments where explosive gases or dust may be present.
- Constructed from materials and enclosures that can contain and mitigate explosions.
- Ensure electrical safety in volatile industrial settings such as chemical plants and refineries.
Marine Distribution Boxes:
- Specifically designed to withstand marine environments, including saltwater exposure and corrosion.
- Made from materials resistant to rust and moisture ingress.
- Ensure reliable electrical distribution aboard ships, offshore platforms, and marine vessels.
By understanding the specific requirements and characteristics of each type of distribution box, electrical engineers, contractors, and homeowners can make informed decisions to ensure efficient and safe electrical distribution in various settings.
Key Differences Between Distribution Box Types
Distribution boxes come in various types and configurations, each designed to meet specific requirements in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.The following table provides a clear understanding of the functions of each type of distribution box:
| Type | Description | Function | Location | Key Components |
| Main Distribution Board (MDB) | Main hub of electrical distribution | Receives power from transformer, distributes to sub-boards, controls building power | Building entrance | Busbars, MCCBs, metering equipment |
| Sub Distribution Board (SDB) | Extends from MDB to power specific areas | Provides localized power distribution | Specific rooms/floors | MCBs, RCDs |
| Meter Panel | Houses electrical meters | Tracks electricity usage for billing and troubleshooting | Building entrance | Meter, main switch, fuses/circuit breakers |
| Panel Fuse Bank | Load center for distribution systems | Offers over-current protection, ideal for solar power | Homes (solar panels) or Vehicles (driver’s side) | Fuses |
| Unitized Panel | Electronic meter displays electrical properties | Provides and distributes low voltage power | Commercial/industrial settings | Unitized meter, circuit breakers |
| Transfer Switch | Switches power between sources (e.g., utility, generator) | Provides backup power during outages | Homes/businesses with generators | Automatic/manual transfer switch, breaker panel |
| Consumer Unit (Fuse Box) | Residential electrical distribution box | Protects circuits from overloads in homes | Homes | Mains switch, circuit breakers, RCDs |
| Enclosed Switchgear | Complete power distribution and control system | Offers organized and safe environment for managing industrial circuits | Industrial settings | Switches, circuit breakers, control devices |
Materials Used in Distribution Boxes
Distribution boxes, crucial for protecting electrical connections and ensuring safety in electrical systems, are constructed from various materials. The choice of material depends on factors such as the application environment, durability requirements, regulatory compliance, and cost considerations. Here are some common materials used in the construction of distribution boxes:
1. Metals Distribution Boxes
Metals are widely used in distribution box construction due to their durability, strength, and suitability for various environments. Common metals include:
Steel Distribution Boxes
Applications: Ideal for industrial and commercial settings where robustness and longevity are paramount.
Considerations: Susceptible to rust and corrosion unless properly coated or treated.
Aluminum Distribution Boxes
Applications: Used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings where weight reduction and corrosion resistance are beneficial.
Considerations: Generally more expensive than steel but offers better corrosion resistance without additional coatings.
2. Plastics Distribution Boxes
Plastics are valued for their lightweight properties, resistance to moisture, and ease of molding into various shapes. Common plastic materials include:
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Distribution Boxes
Applications: Predominantly used in residential distribution boxes and low-voltage electrical installations.
Considerations: Limited resistance to heat and impact compared to other materials.
Polycarbonate Distribution Boxes
Applications: Suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments, including industrial and commercial settings where protection against impact and weather is necessary.
Considerations: More expensive than PVC but provides superior durability and resistance to harsh conditions.
3. Fiberglass Distribution Boxes
Fiberglass is a composite material made of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. It offers unique properties beneficial for certain applications in distribution boxes:
- Advantages: Lightweight, strong, and resistant to corrosion, heat, and electrical interference.
- Applications: Commonly used in specialized distribution boxes for harsh environments such as marine, chemical plants, and telecommunications.
- Considerations: Higher cost compared to metals and plastics but offers superior durability and performance in challenging conditions.
4. Composite Materials Distribution Boxes
Composite materials combine two or more materials to achieve specific properties such as strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors:
- Advantages: Combine the strength of metals with the lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties of plastics.
- Applications: Used in distribution boxes requiring a balance of strength, durability, and weight savings.
- Considerations: Manufacturing complexity may result in higher costs.
By understanding the characteristics and considerations associated with different materials, electrical engineers, contractors, and installers can make informed decisions to select the most suitable material for distribution boxes that meet the specific needs of their applications.
China Best Distribution Boxes Sheet Metal Fabrication Company – BE-CU Prototype
Distribution boxes are essential components in electrical systems, providing a safe and organized way to manage electrical connections. Understanding the different types of distribution boxes, their construction, and their applications is crucial for selecting the right box for any given situation. Adhering to standards, following best practices for installation and maintenance, and staying informed about innovations in the field will ensure the continued safety and efficiency of electrical systems.

Founded in 1995, BE-CU is a global OEM/ODM service provider of sheet metal fabricated as well as assemblies and testing for Distribution Boxes.
BE-CU obtained ISO9001 accredit by TUV in 2007. With implementation of ERP system, Office Automation system,BE-CU has successfully integrated its business and work flow, which greatly enhanced the internal work efficiency and customer response speed.
All the inspection requirements and records are properly kept in our Quality Information System, enabling us to measure our performance and continuously improving the services to customers.
Couldn’t find the case studies you want? Contact us now, we have a strong in-housing supply chain, can sheet metal fabrication any prototype project and parts for you.
-
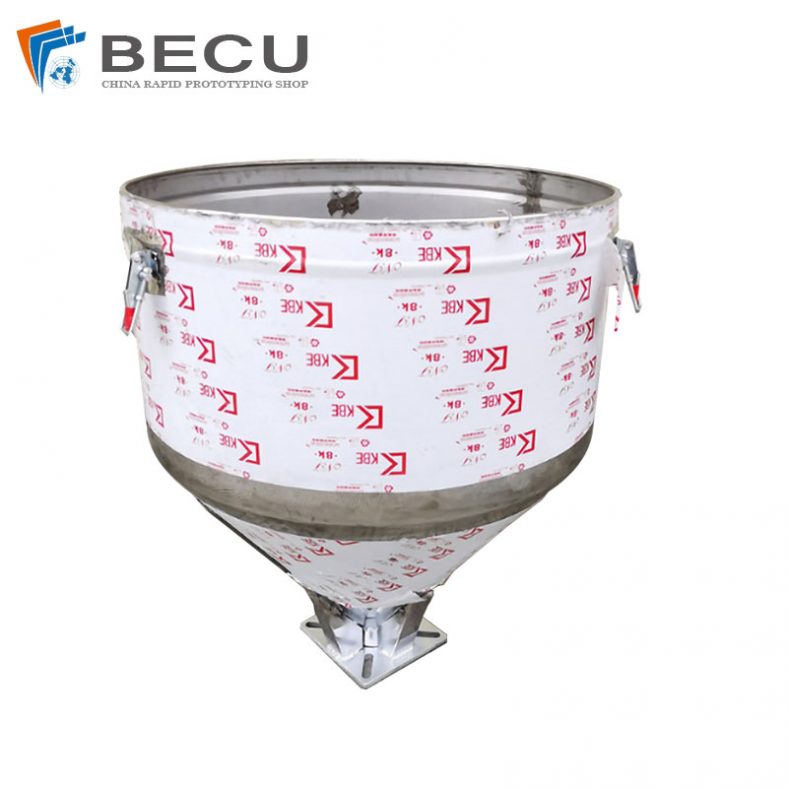

Sheet Metal Fabrication Injection Molding Machine Hopper
-
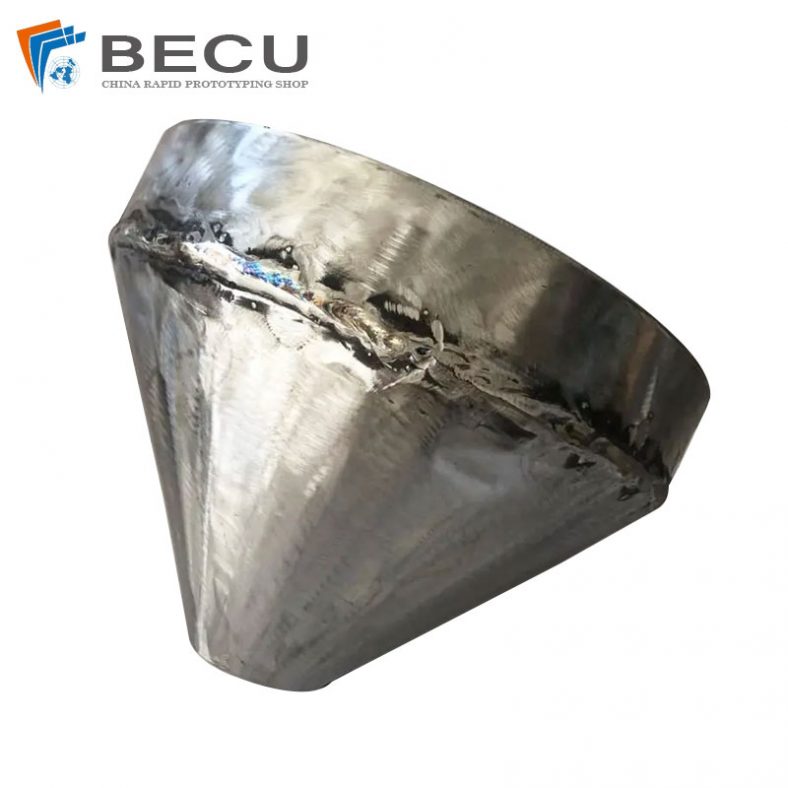

Sheet Metal Fabrication Funnel For Agricultural Machinery
-
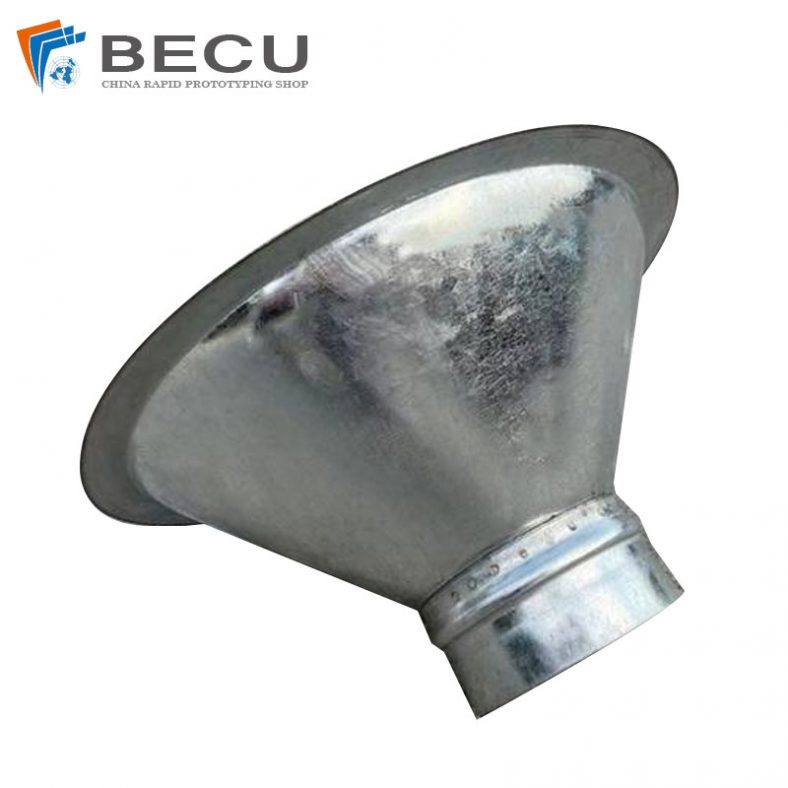

Sheet Metal Fabrication Galvanized Spiral Air Duct
-
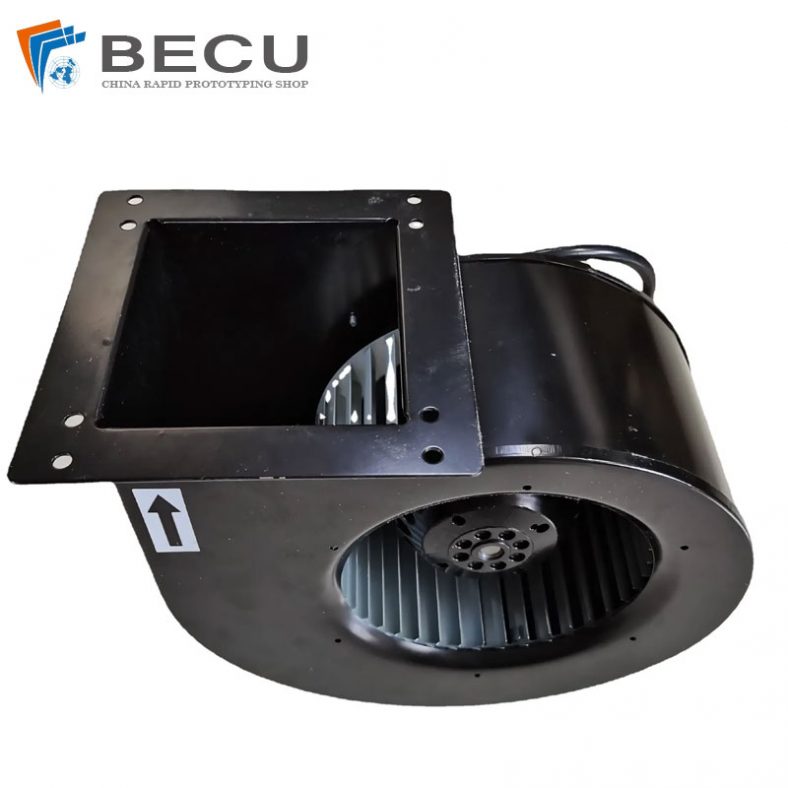

PCS Fan Ductwork Sheet Metal Housing
-

Custom Sheet Metal Surgical Instrument Sterilization Box For Beauty Salon
-

Precision Fabrication Green Energy EV Charging Station Cabinet
-

TA1TA2 Alloy Sheet Metal Manufacturing Machinery Support Parts
-

Sheet Metal Fabrication Aluminum 5052 Medical Box For Fire Fighting
With an experienced and professional engineering & service team, BE-CU defines itself as a “one stop service” provider, offering a wide range of services including design assistance, 3D rapid prototyping, production methods, engineering, project management, expertise, and flexible business approaches such as Kanban, Consignment, etc. With years’ experience, we’ve steadily built a reputation for quality and value, earning us awards from our customers, industry associations, and communities.
