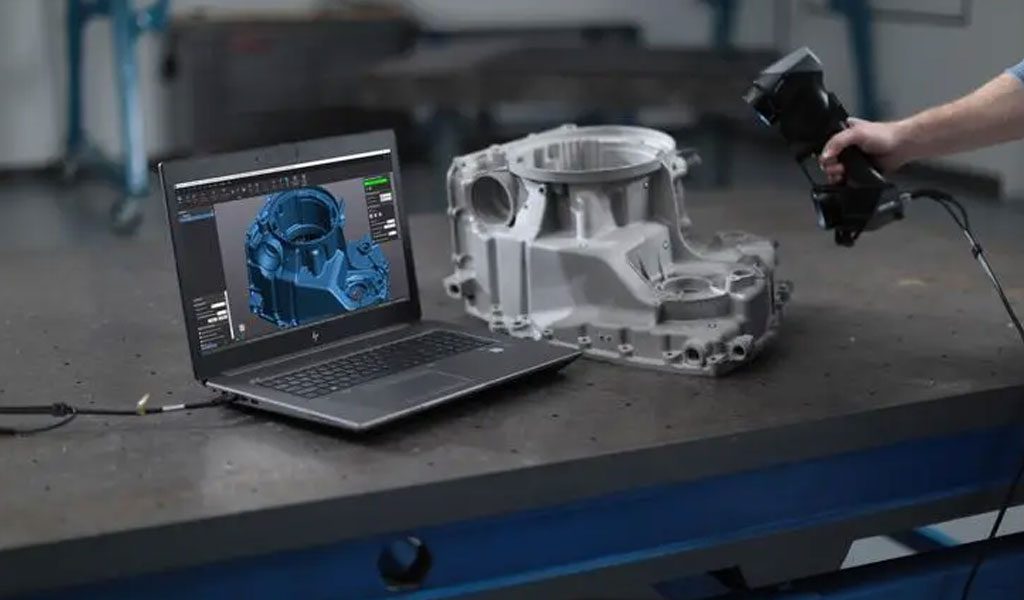

The Initial Data Of 3D Scanning And Photogrammetry
The Soviet jet fighter MiG-19 is the world’s first mass-produced supersonic aircraft. Its length is 10 meters and its weight is about 7500 kg. The aircraft’s left wing is in poor condition and may have some degree of damage. The challenge is to scan the left wing and reconstruct it so the engineers can repair the damaged part.
An industrial 3D scanner KSCAN-Magic is used as equipment. This handheld 3D reverse engineering scanner offers five working modes: large area scan, fast scan, precise scan, deep hole scan and built-in photogrammetry system. These features ensure that KSCAN-Magic can solve various 3D scanning tasks with superior quality. It can easily capture complex surface data with an accuracy of 0.020mm.
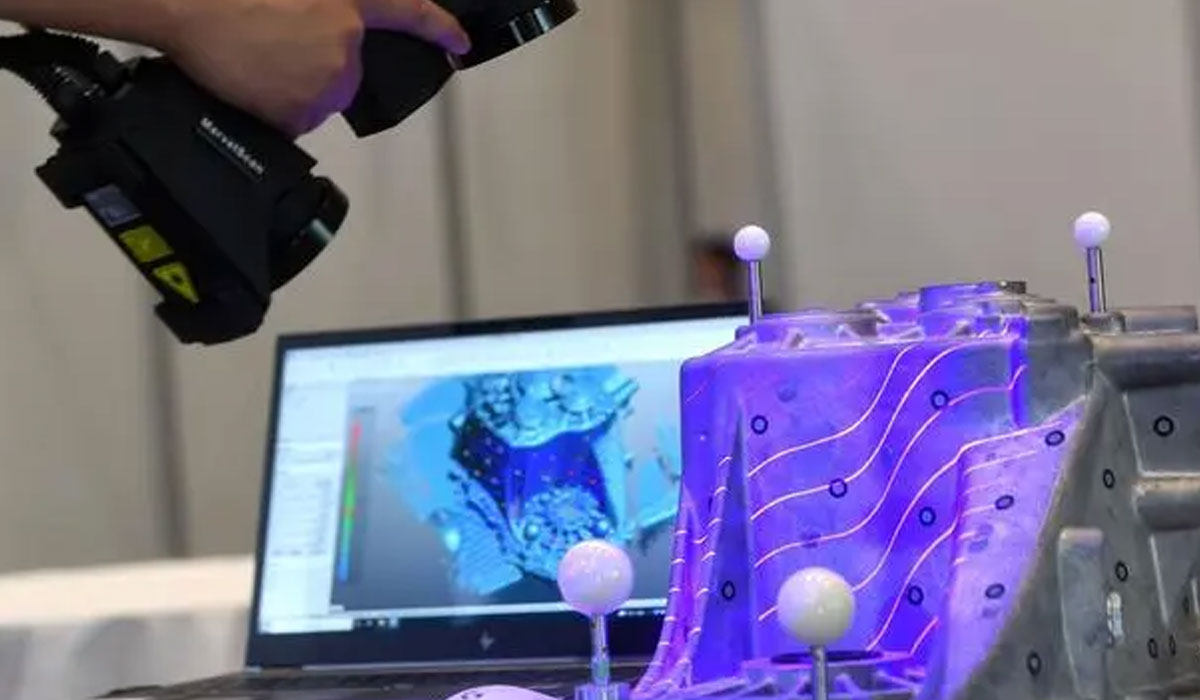

Ways And Methods Of Work
Preparation
What Should Be Done Before Scanning?
The key to successful 3D scanning is the fine tuning of the equipment. The first step is to calibrate the 3D scanner using a calibration panel, which is mandatory after transporting the equipment over long distances. Then you need to adjust the scanner according to the environment, surface and shape of the object being scanned.
Things To Consider When Scanning Outdoors
Ambient light can affect scan accuracy and scan time. When it comes to scanning outdoors, traditional scanners that are sensitive to lighting conditions can produce results with a high degree of error. The selected optical handheld laser 3D scanner KSCAN-Magic is insensitive to lighting conditions due to blue lasers and powerful scanning algorithms. Due to the short wavelength, the blue laser is more resistant to scanning interference. This portable 3D scanner can also scan large surfaces in a short time, which helps to capture outdoor 3D printing data.
Photogrammetry
When scanning a large-scale object, the scanning error accumulates due to the large amount of scanning. With a large scan area and multi-angle positioning, photogrammetry can reduce alignment errors and improve scan accuracy.
What Is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is a measurement technique that relies on photographing an object from different angles to extract 3D coordinates and geometry. When it comes to scanning a large object over 1 meter in length, it can improve the positioning accuracy of the markers and improve the accuracy of the received data.
KSCAN-Magic is unique in that it combines laser scanning technology with photogrammetry in one system, which gives greater stability and accuracy even when working with large parts. Since we did not scan the entire aircraft in this case, there was no need to use photogrammetry before scanning.
Markers
Why Should We Use Markers Before Scanning?
Markers, also known as anchor points, help in positioning the 3D scanner and obtaining the 3D coordinates of the object. Therefore, before scanning, it is necessary to put markers on the object.
How To Place Markers?
It is recommended to place the markers randomly so that the scanning software can correctly locate them. In this case, in most places the markers were placed at a distance of 250–350 mm from each other.
However, in narrow areas and edges (such as the edge of a wing), it is advisable to place them a little closer, since the edge has a limited surface area. The minimum number of markers in the scanning field in such areas should be four.
Optimal Scan Distance
What Is The Optimal Scanning Distance?
Each scanner has an optimal distance that should be between the scanner and the part being scanned (usually indicated in the manual for each scanner). To capture high quality 3D data clearly, it is important to make sure you are at the optimum distance for the scanner.
When moving the scanner, it is important to keep track of the distance to the object. The scanner moves in such a way that even when scanning from different angles, the distance is approximately the same.
Resolution Setting
What Is Permission?
Resolution is the minimum distance between captured points at a given scan distance. The higher the resolution, the denser the scan point cloud. When small details of a 3D model are important, it is worth choosing equipment with a high resolution. If not, then low-resolution scanners are suitable for the job.
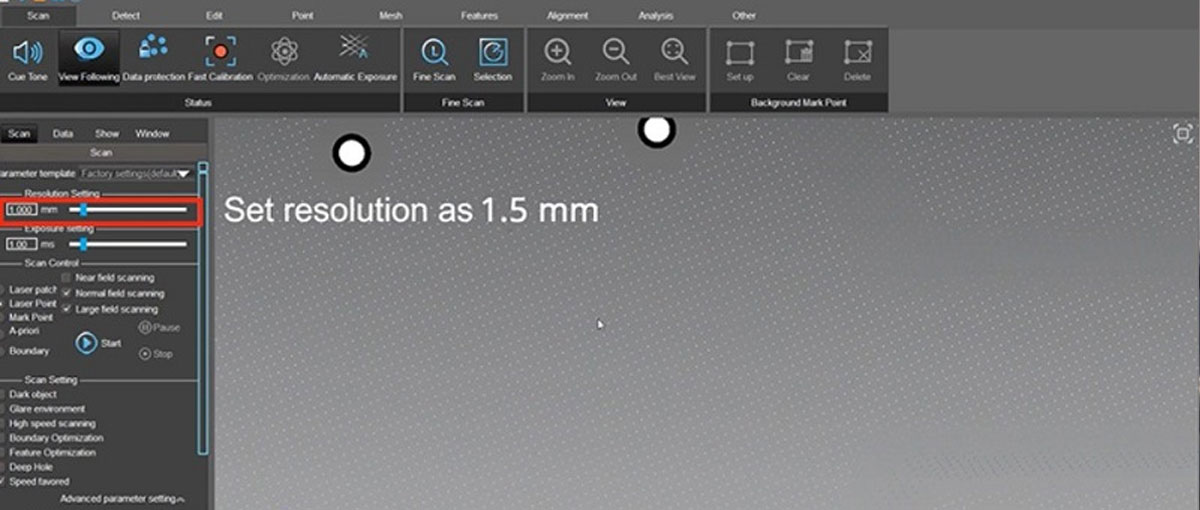
The resolution that was set to scan these details was 1.5 mm, which was sufficient to capture all the necessary details while maintaining a high scanning speed. For more complete and better results, it is recommended to frequently change scan angles and scanner positions to capture data from different directions.
Post-Processing
What Makes A Good Scan?
A scan that meets the objectives of the project can be called good. The level of precision required for projects varies depending on their purpose, such as 3D printing, digital archiving, quality control, or prototyping. When developing a product, a good scan can save you the time it takes to create a 3D model from scratch.
The scanned data is imported into the design software and then denoised and edited. Therefore, it will not be a problem for designers to have a little missing geometry. High precision is required for inspection and quality control.
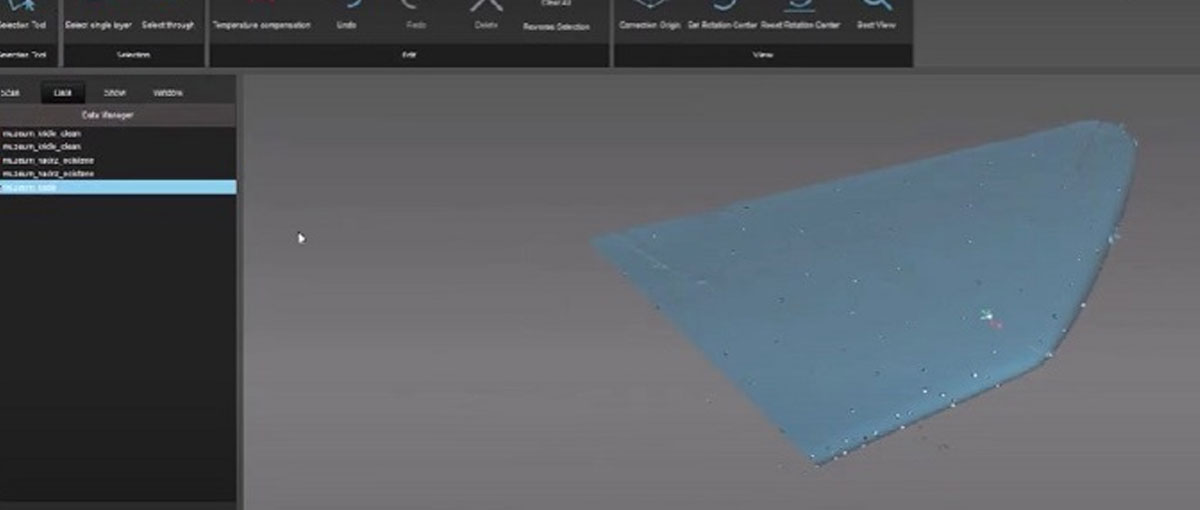
Since the engineers are aiming to reconstruct the left wing in this case, a high quality scan is required with little post-scan rework.
How To Clear a 3D point cloud?
After the 3D scan is completed, some parts of the scan may not be needed. The ScanViewer software supplied with KSCAN makes it easy to edit 3D data. Point cloud noise has been removed with just a few mouse clicks.
What Software Can Be Used?
Scanned data can be combined into a 3D model and exported in popular STL, PLY formats or as point cloud files in ASC, IGS and TXT formats.
Outcome
These are just a few useful 3D scanning facts and tips. If you have any questions about 3D scanners, please feel free to contact LIDER-3D specialists. We provide training on how to work with 3D scanners and data processing software. Our specialists are always ready to help and optimize the workflows of your business using additive technology.
