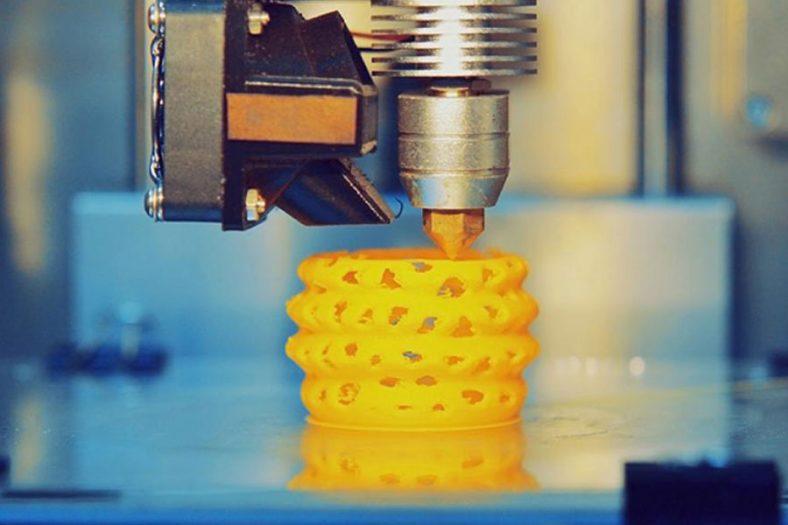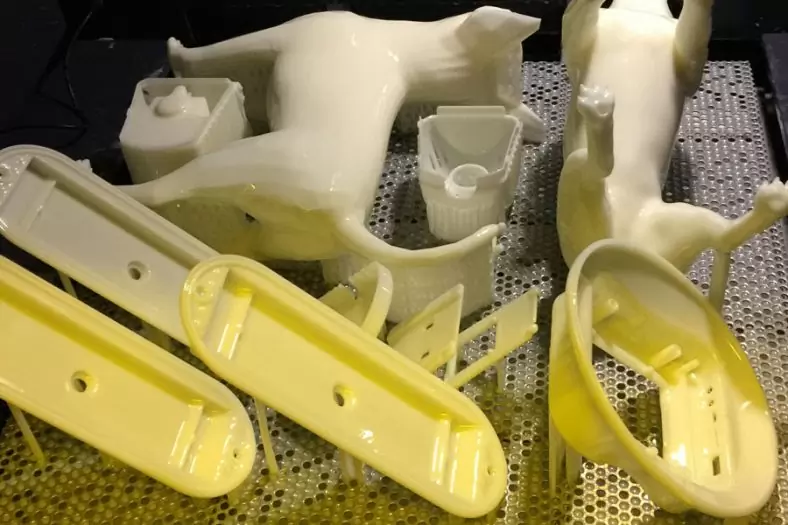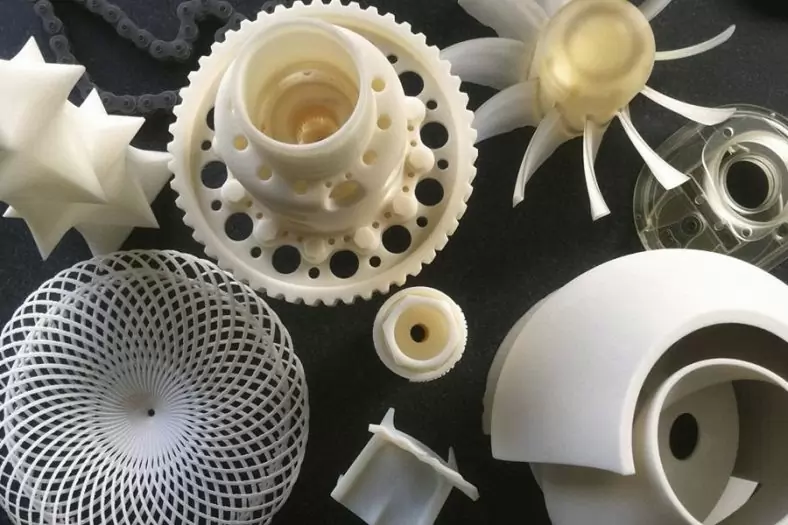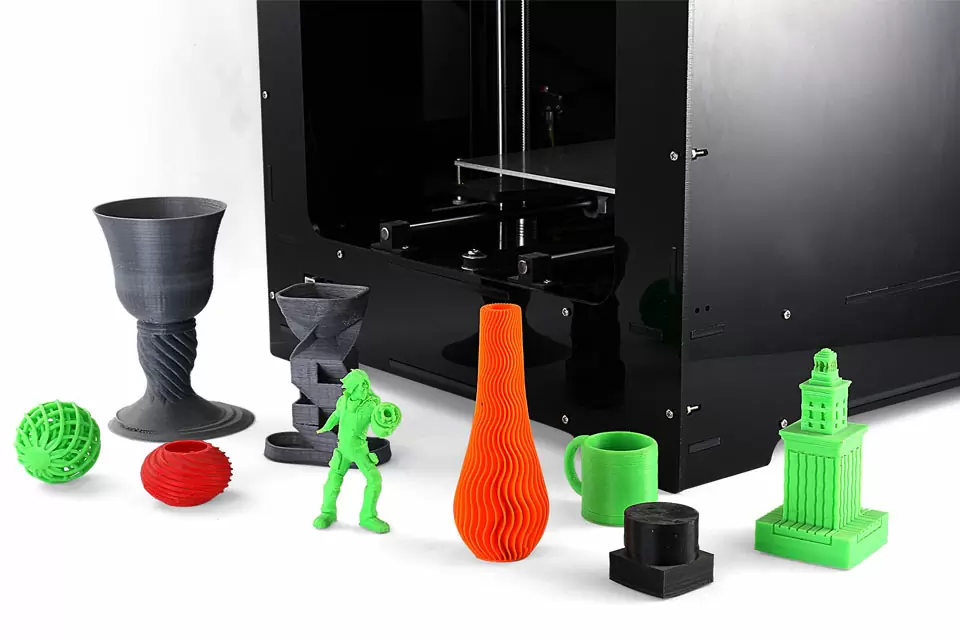
What Is Commercial 3D Printing
Commercial 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, refers to the process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer, based on a digital model. This revolutionary technology enables the production of complex geometries and customized designs that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods.
What began as a tool for rapid prototyping has now evolved into a disruptive force in various industries, spanning aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and beyond. Initially, 3D printing was primarily used for concept modeling and product validation in the design and engineering phases. However, as the technology matured, its capabilities expanded, enabling direct production of end-use parts and components.
One significant milestone in the evolution of commercial 3D printing was the development of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) by Scott Crump in the late 1980s. FDM brought 3D printing capabilities to a broader audience, offering a more accessible and affordable option for creating prototypes and functional parts.
The turn of the millennium witnessed a surge in interest and investment in 3D printing technologies, driven by advancements in materials science, hardware innovation, and software development. Companies like Stratasys, 3D Systems, and EOS played pivotal roles in pushing the boundaries of what was possible with additive manufacturing.
Commercial 3D Printing Service – Large Commercial Resin 3D Printing
As 3D printers became more reliable, accurate, and versatile, their adoption spread across industries seeking to leverage the technology for production applications.BE-CU online 3D printing service enables you to Commercial 3D print your custom part on demand.
Today, commercial 3D printing encompasses a wide range of processes, We offer eight Commercial 3D printing technologies to transform your 3D files into plastic, metal, and elastomeric parts,including selective laser sintering (SLS), SLA 3D Printing,SLM 3D Printing,FDM 3D Printing,MJF 3D Printing,DLP 3D Printingg,direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), and binder jetting, each offering unique advantages for specific applications.
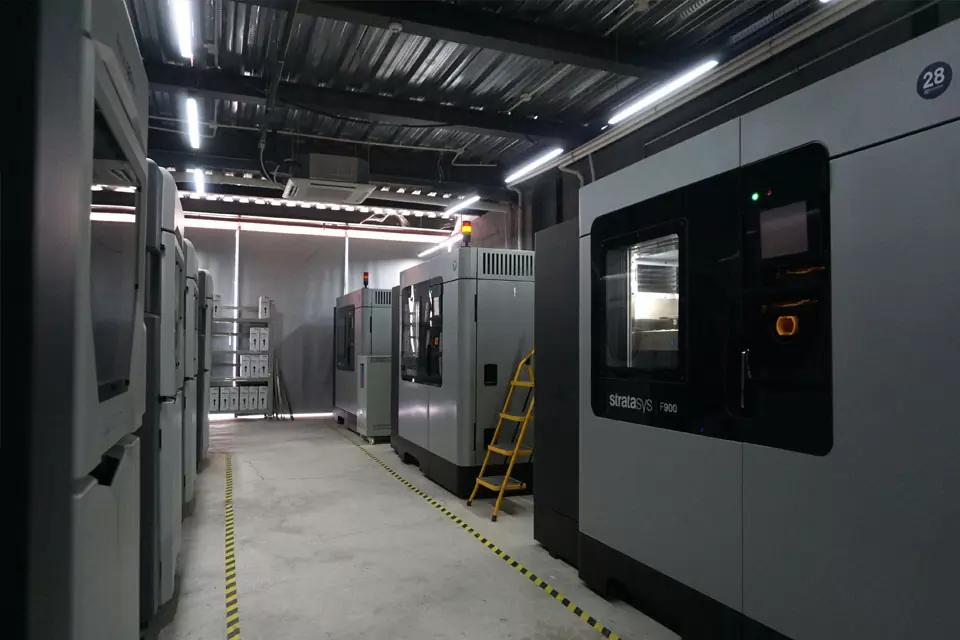
With more than 120 3D printers, we have unmatched capacity that reliably delivers parts within days. In addition to a broad material selection, we offer several post-processing options to improve cosmetics or enhance mechanical properties.
The Advantage Of Commercial 3D Printing Company
- ISO 9001:2015 certified and ITAF 16949 certified
- Fully compliant with the exacting requirements of our customers,High customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Average 7 days turnaround time and 99.85% on time delivery
- Multiple options of machining materials to meet specific properties.
- Skilled in KanBan and other customer driven quality and inventory management systems
- Efficient 3d printing china factory for mass production rapid prototyping service
- Fast free quotation within 24 hours after inquiry
- Rich design and manufacturing experience
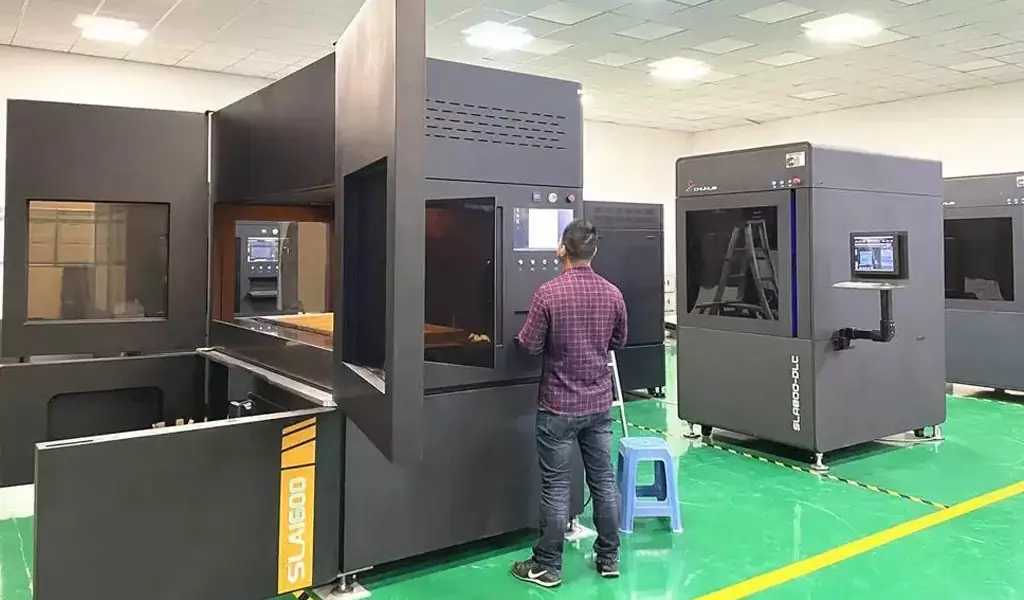

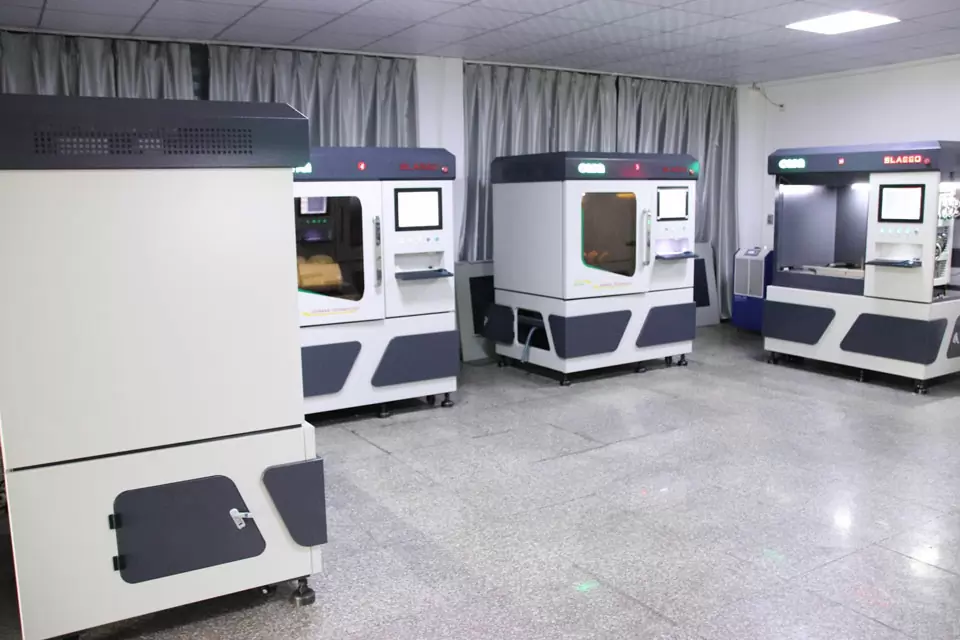
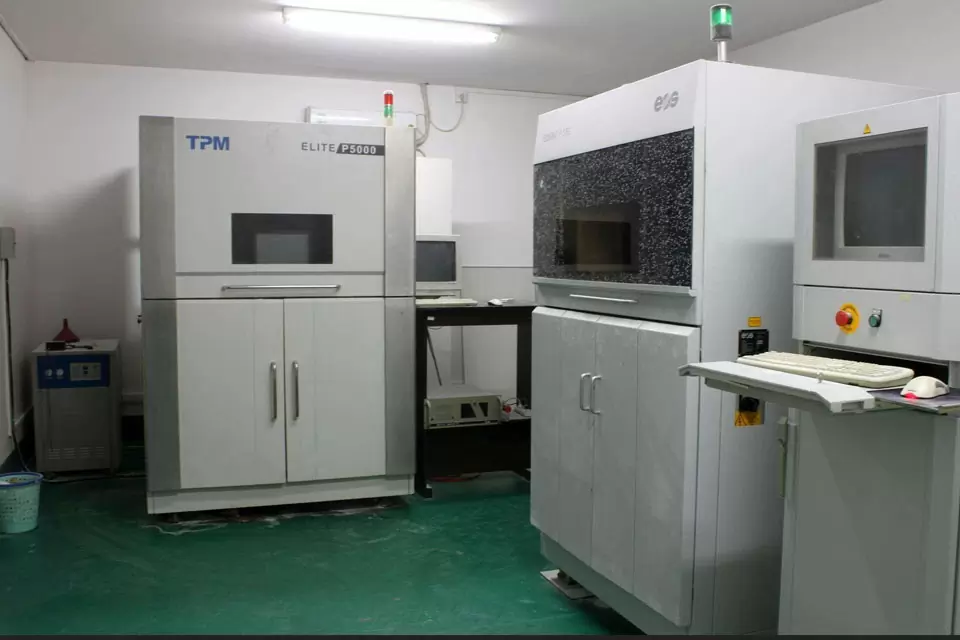
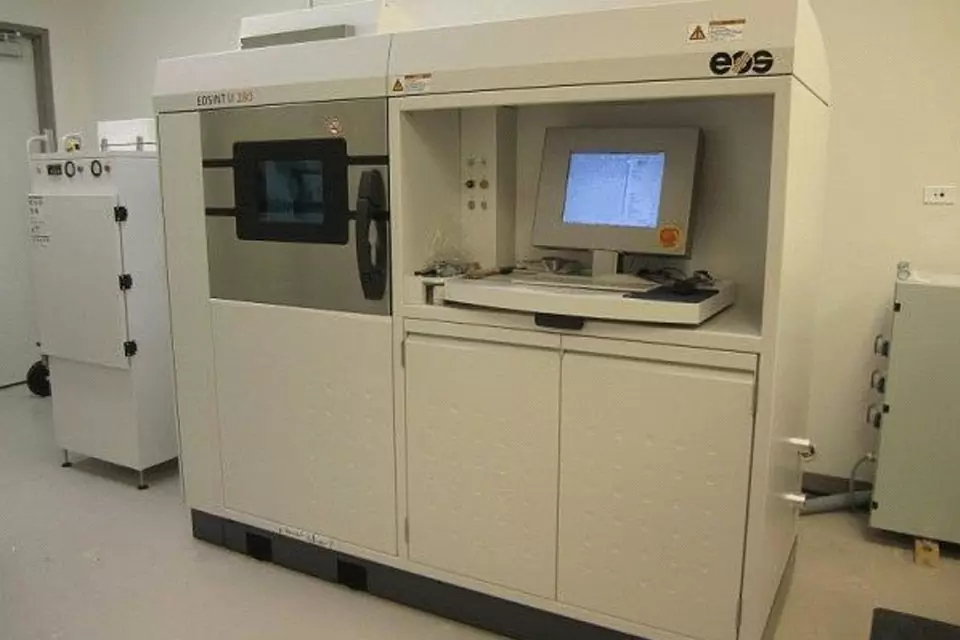
Outstanding Commercial 3D Printing Equipment
- P200 Industrial DLP 3D Printer
- ProJet MJP 5500X
- TPM ELITE P5000 SLS 3D Printer
- P480DL SLS 3D Printer
- ASM1500H SLA 3D Printer
- ASM-1200 SLS Molding Machine
- M400-4—SLM Metal 3D Printer
- DQ1200 FDM 3D printer
- Check Out BE-CU Equipment List
Commercial 3D Printing Parts Gallery and Case Studies
Today, we recommend a good china 3d printing service company to the Commercial industry. BE-CU.COM 3D printing is a brand owned by Dongguan Be-Cu prototype. Since the company was listed, it has conquered with its excellent printing quality and high-standard customer service team. Industry insiders, the printing case shown below is a masterpiece printed by BE-CU 3D. I believe that you who love Commercial will definitely be impressed by the incredible molding quality of Be-Cu!Click on a case study below to spark an idea of how to utilize Commercial 3D printing in your industry. These are great examples of what Commercial 3D printing can do and the kind of complex issues it can solve.
-
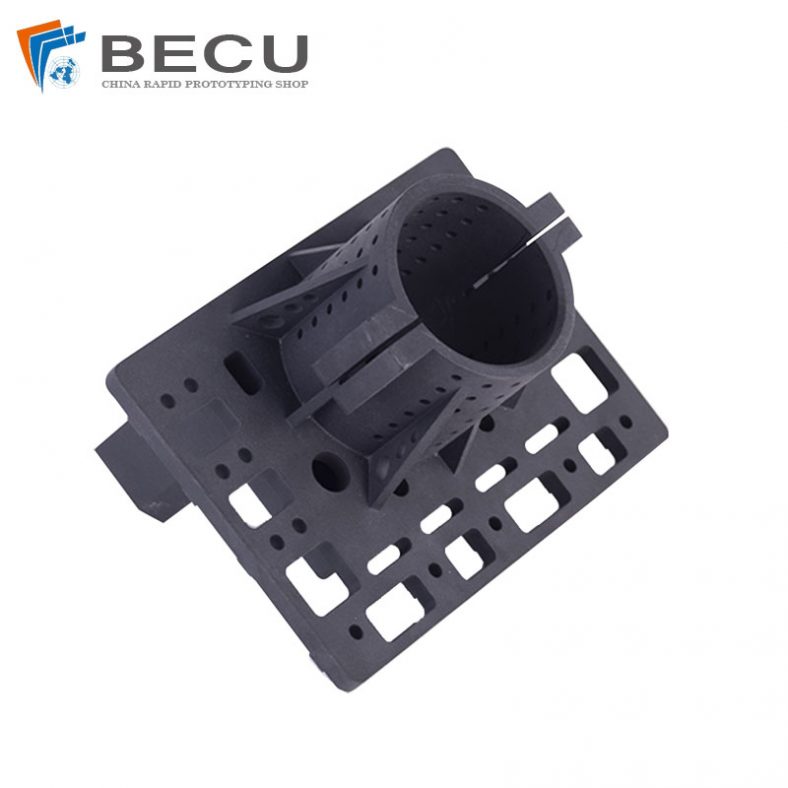

3D Printing Pool Pressure Cleaner Parts and Accessories
-
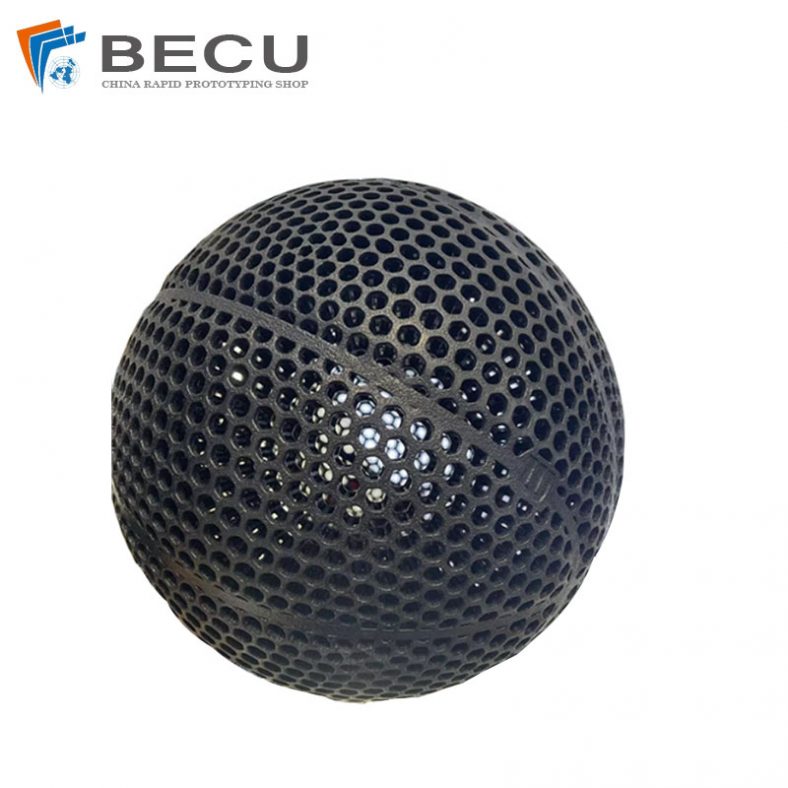

Nylon 3D Printed Size 5 Basketball
-
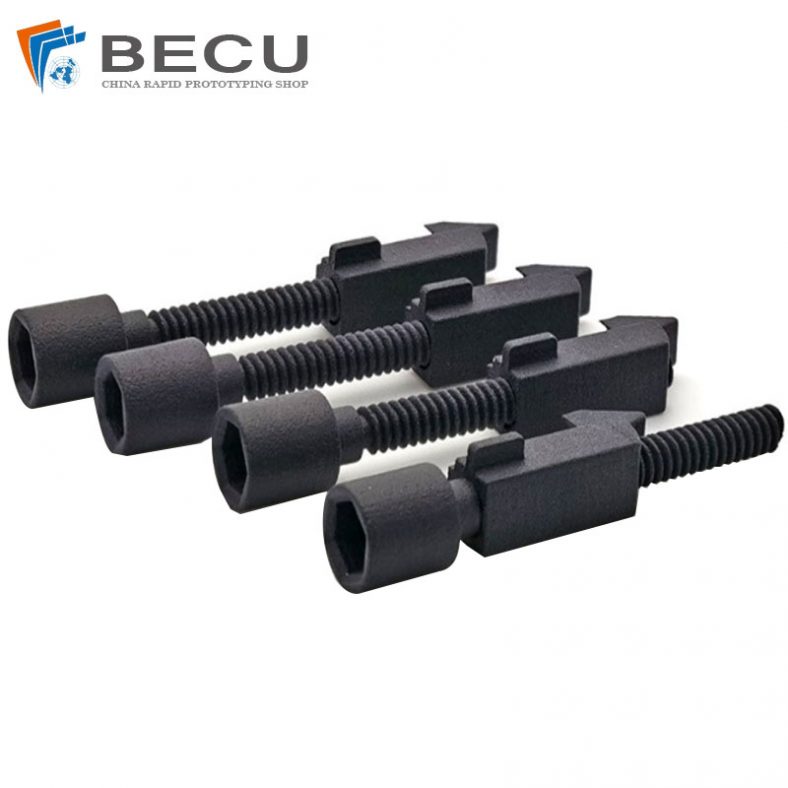

Black Nylon Medical Threaded Screw By MJF 3D Printing
-
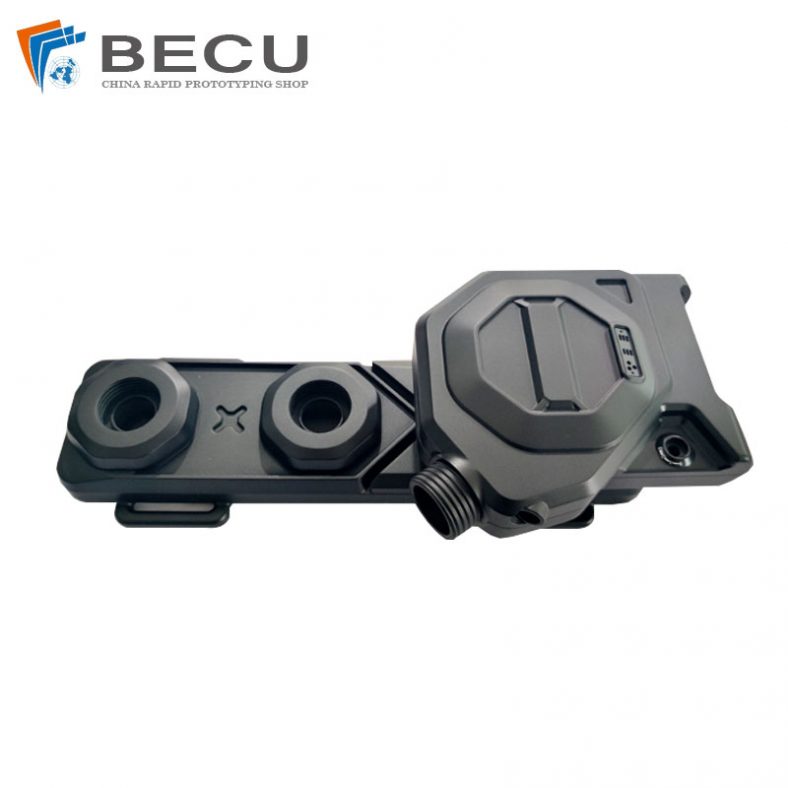

MJF 3D Printing Black Nylon Red Dot Sighting For Medical
-
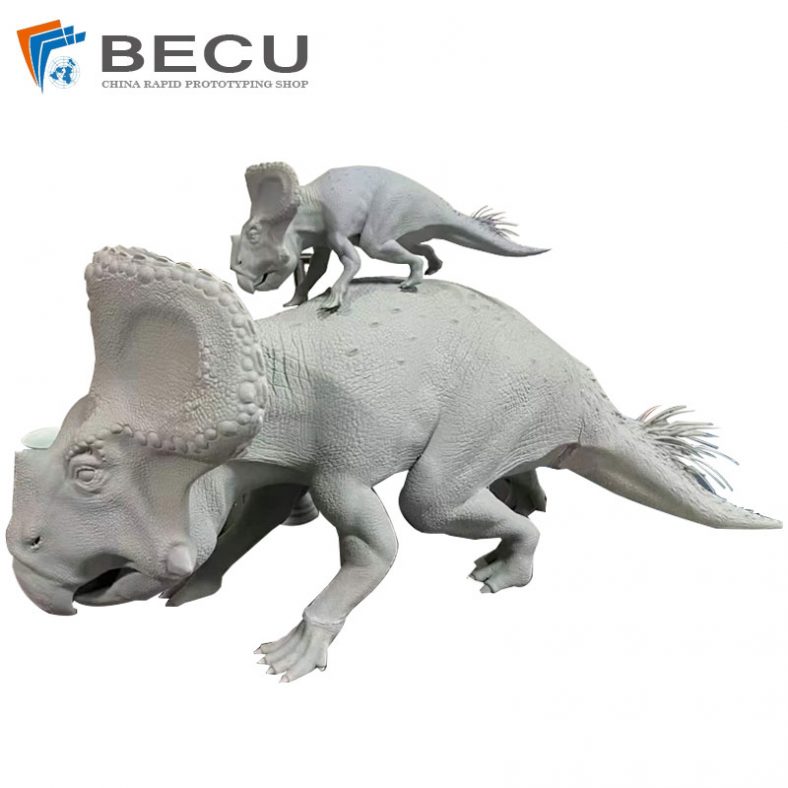

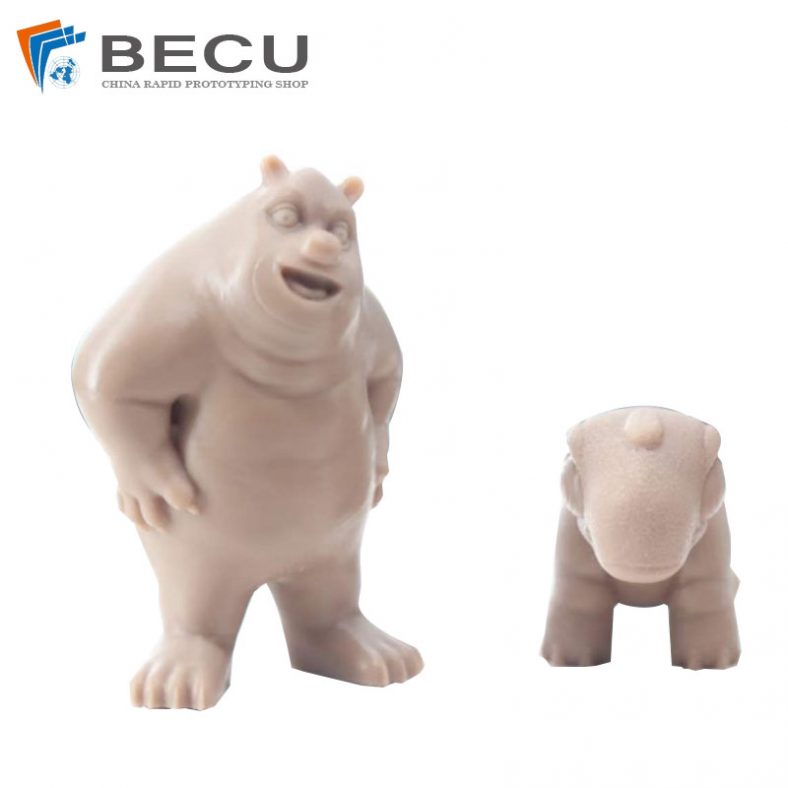
jetFusion 3D Printing Triceratops Mother and Child Sculpture
-
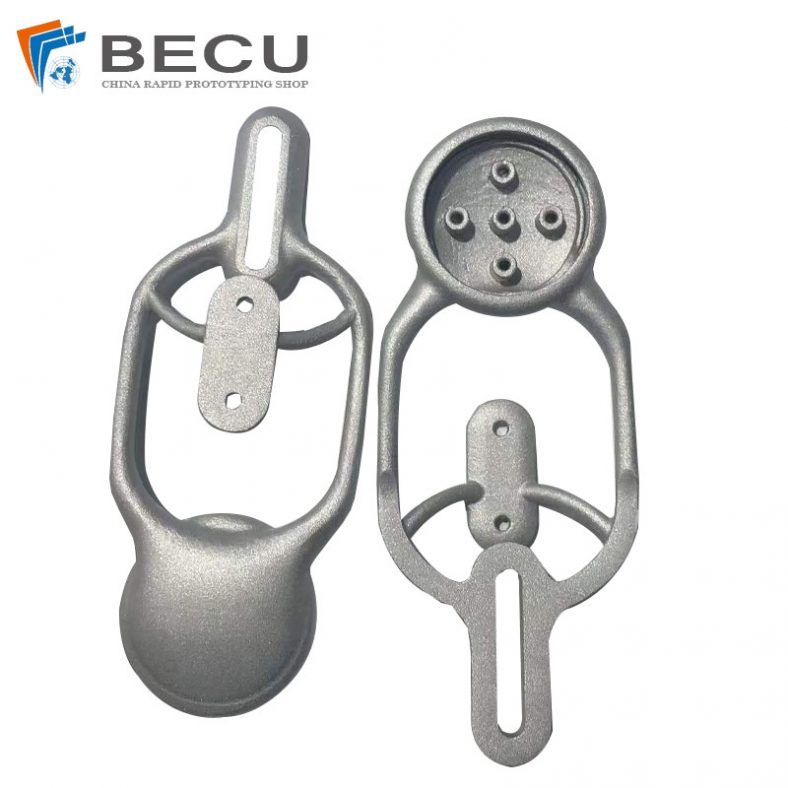

6061 Aluminum Alloy 3D Printing Black Dusting Parts
-
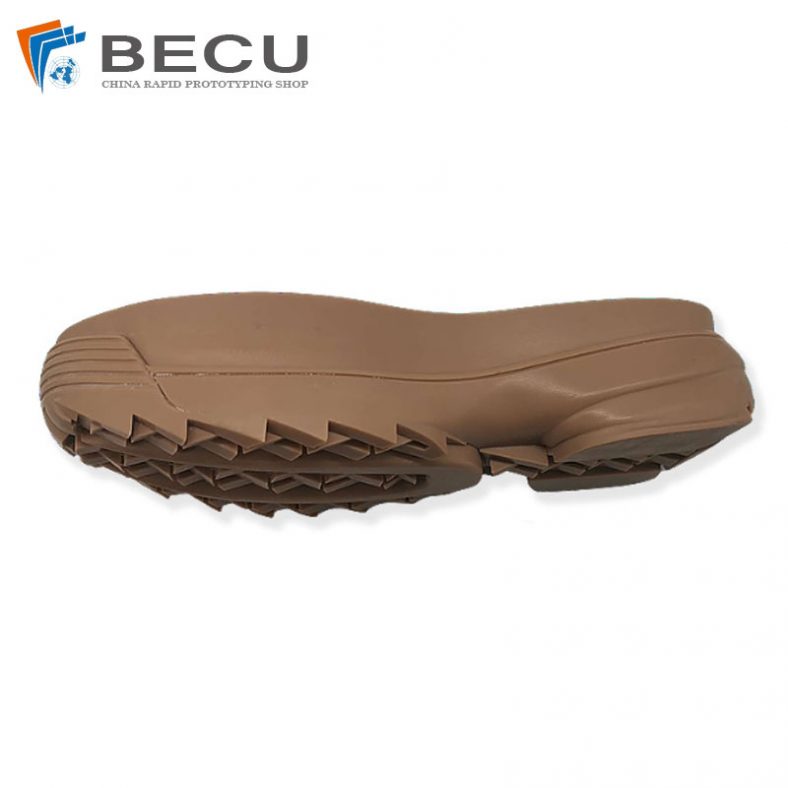

Development Resin Samples For Sports Shoes
-
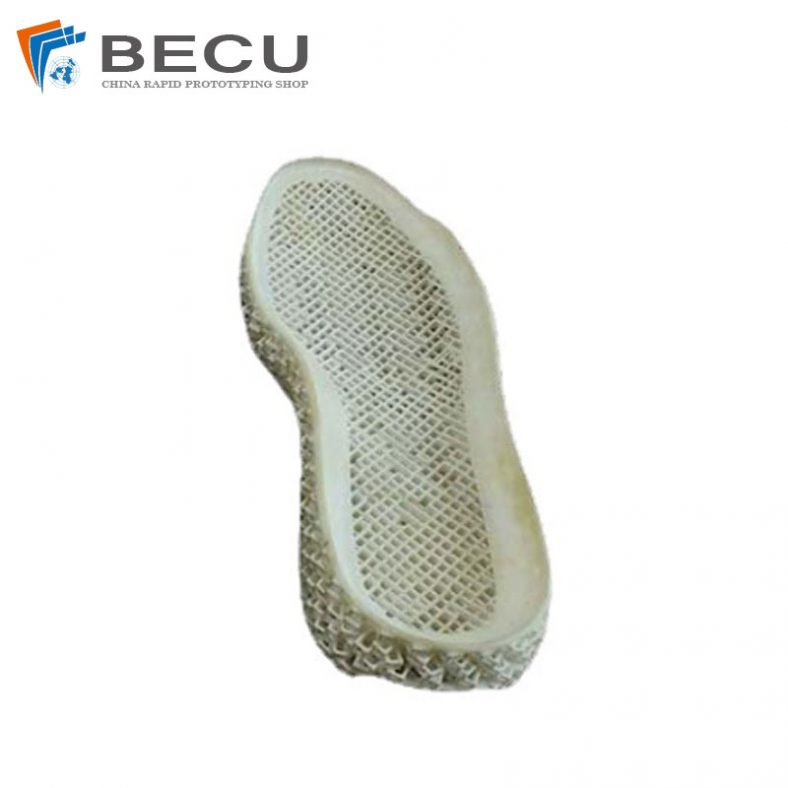

3D Printed Sports Shoes Sole Model
-
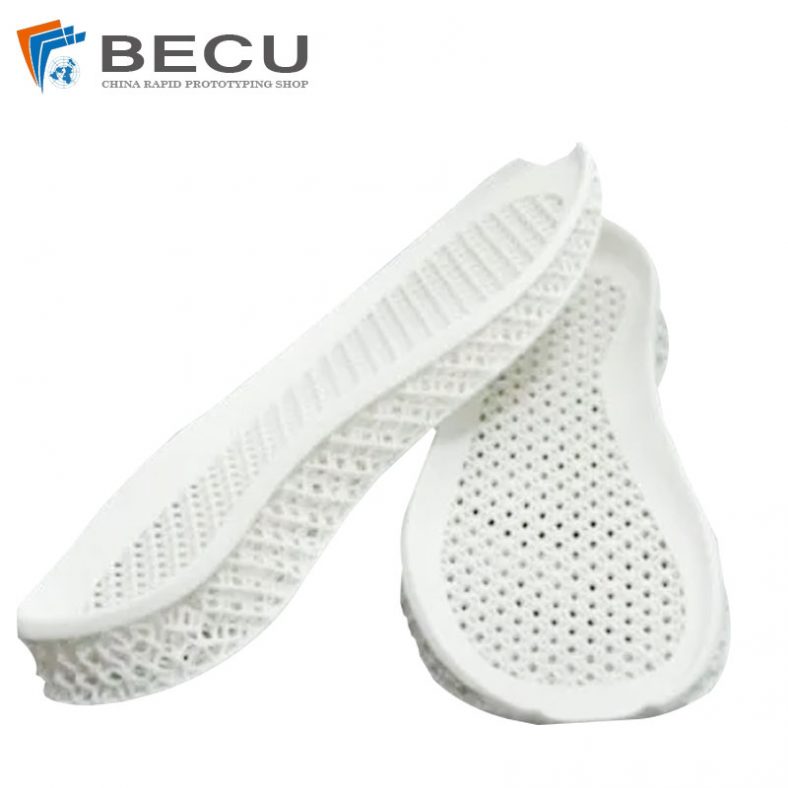

Powder Sintering 3D Printed Shoe Midsole Sample
-
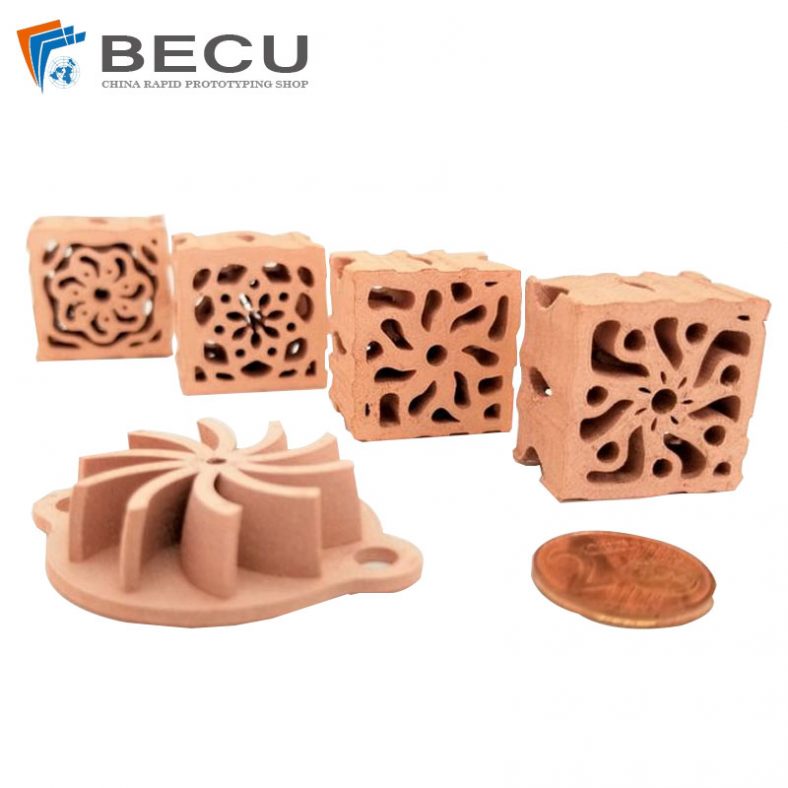

FFF Fused Wire Extrusion 3D Printed Pure Copper Parts
-
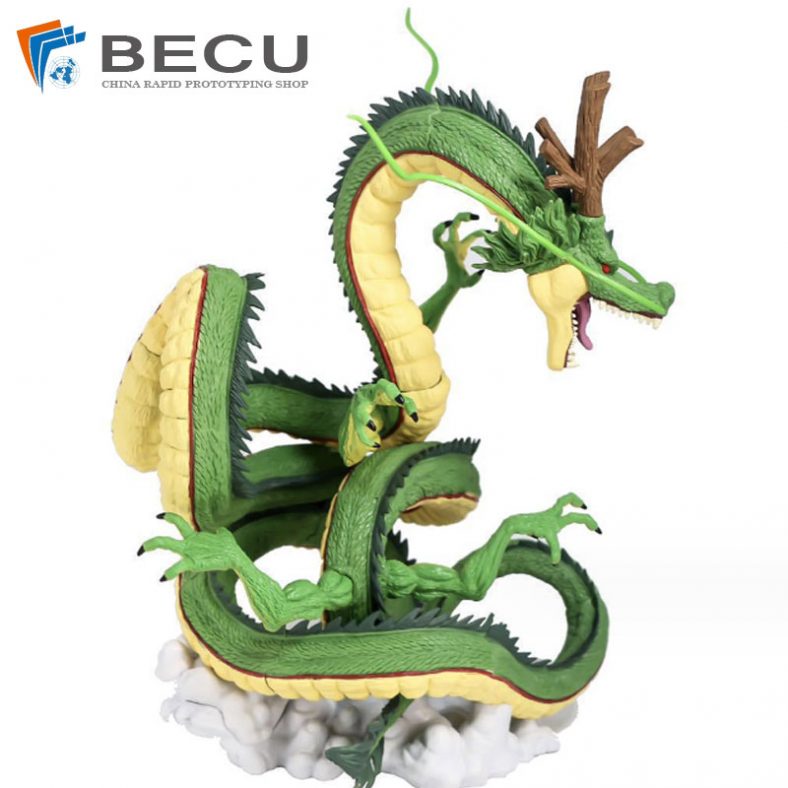

DLP 3D Printing DragonBall Dragon Desktop Ornaments
-

3D Printing Brown Wax Anime Doll
Advancements in Commercial Applications
Advancements in commercial applications of 3D printing have transformed various industries, driving innovation, customization, and sustainability. From aerospace and automotive manufacturing to healthcare and consumer goods, additive manufacturing continues to revolutionize the way products are designed, produced, and consumed. As technology continues to evolve and adoption grows, the potential for 3D printing to reshape industries and create new opportunities is virtually limitless.
A. Commercial 3D Printing For Aerospace and Aviation Industry
The aerospace and aviation industry has been at the forefront of adopting 3D printing technology for various applications, ranging from prototyping to the production of critical components. Additive manufacturing offers significant benefits to this sector, including lightweighting, design optimization, and reduced lead times.
- Prototyping and Tooling: Industrial Product 3D Printing enables rapid iteration and validation of aerospace designs, allowing engineers to test complex geometries and functional prototypes more efficiently. Additionally, additive manufacturing is used to produce customized tooling and fixtures for assembly and maintenance tasks.
- End-Use Parts Production: Aerospace companies are increasingly utilizing 3D printing to manufacture end-use components, such as brackets, ducting, and interior cabin parts. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of lightweight, high-strength parts with intricate geometries that were previously unattainable with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Engine Components: The production of engine components, including turbine blades and fuel nozzles, has been revolutionized by 3D printing. Companies like GE Aviation and Rolls-Royce have embraced additive manufacturing to create complex, performance-optimized parts that improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
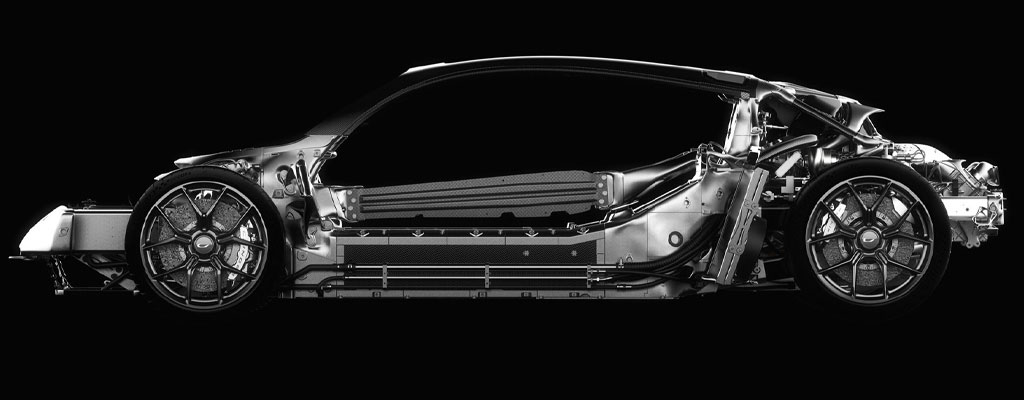

B. Commercial 3D Printing For Automotive Sector
In the automotive industry, 3D printing is driving innovation across the entire product lifecycle, from design and prototyping to production and aftermarket services. Automakers are leveraging additive manufacturing to enhance vehicle performance, reduce manufacturing costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
- Prototyping and Concept Cars: 3D printing enables automotive designers to rapidly prototype new vehicle designs and iterate on concepts with greater freedom and flexibility. Additive manufacturing also facilitates the creation of concept cars showcasing futuristic designs and advanced technologies.
- Customization and Personalization: With 3D printing, automakers can offer customized and personalized vehicles tailored to individual customer preferences. Additive manufacturing allows for the production of bespoke interior components, trim pieces, and even entire vehicle bodies with unique designs.
- Spare Parts Manufacturing: Automotive manufacturers and suppliers are utilizing 3D printing to produce spare parts on-demand, reducing inventory costs and lead times. Additive manufacturing enables the production of complex and obsolete components that may no longer be feasible to manufacture using traditional methods.
C. Commercial 3D Printing For Healthcare and Biomedical Applications
In the healthcare sector, Medical 3D printing is revolutionizing patient care, medical device manufacturing, and pharmaceutical production. Additive manufacturing technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for customization, patient-specific treatments, and advancements in regenerative medicine.
- Patient-Specific Implants: 3D printing enables the fabrication of patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and orthopedic devices tailored to individual anatomies and medical needs. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex, lightweight structures that promote tissue integration and enhance patient comfort.
- Medical Modeling and Surgical Planning: Surgeons utilize 3D-printed anatomical models and surgical guides to plan complex procedures and improve surgical outcomes. Additive manufacturing facilitates the creation of accurate and patient-specific models that enhance preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation.
- Pharmaceuticals and Drug Delivery: 3D printing is being explored for personalized drug delivery systems, dosage forms, and pharmaceutical formulations. Additive manufacturing enables the precise deposition of drug substances, allowing for controlled release profiles and tailored treatment regimens.
D. Commercial 3D Printing For Consumer Goods and Electronics
The consumer goods and electronics industries are leveraging 3D printing to drive product innovation, customization, and supply chain optimization. Additive manufacturing enables faster time-to-market, reduced inventory costs, and enhanced product performance.
- Customized Products: 3D printing allows consumers to personalize and customize products, such as footwear, accessories, and home goods, to suit their unique preferences. Additive manufacturing enables mass customization without the need for costly tooling or molds.
- Electronics Prototyping and Manufacturing: Electronics companies use consumer 3D printing for rapid prototyping of circuitry, housings, and enclosures, speeding up product development cycles and reducing time-to-market. Additive manufacturing also enables the production of lightweight, high-performance components for electronic devices.
- Supply Chain Agility: 3D printing offers supply chain flexibility by enabling on-demand production, localized manufacturing, and just-in-time inventory management. Additive manufacturing reduces the need for centralized production facilities and long-distance transportation, leading to shorter lead times and lower logistics costs.
E. Commercial 3D Printing For Architecture and Construction
In the architecture and construction industries, 3D printing is revolutionizing building design, construction methods, and material innovation. Additive manufacturing enables architects and engineers to realize complex geometries, reduce waste, and create sustainable structures.
- Architectural Prototyping and Modeling: 3D printing allows architects to create detailed scale models and prototypes of building designs, facilitating communication with clients and stakeholders. Additive manufacturing enables rapid iteration and exploration of design concepts with greater accuracy and realism.
- Construction Robotics and Automation: 3D printing is being used to fabricate building components, such as walls, columns, and facades, using robotic arms and gantry systems. Additive manufacturing in construction enables the rapid assembly of structures on-site, reducing labor costs and construction time.
- Sustainable Materials and Design: Architects and designers are exploring the use of sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics and bio-based polymers, for 3D printing construction projects. Additive manufacturing enables the precise deposition of materials, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
F. Commercial 3D Printing For Fashion and Jewelry
In the fashion and jewelry industries, 3D printing is pushing the boundaries of design innovation, customization, and sustainability. Jewelry 3d printing enables designers to create intricate, one-of-a-kind pieces with unprecedented precision and complexity.
- Custom Jewelry and Accessories: 3D printing allows jewelry designers to create custom pieces tailored to individual tastes and preferences. Additive manufacturing enables the production of complex geometries, fine details, and lightweight structures that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques.
- Fashion Prototyping and Production: Fashion designers use 3D printing to prototype clothing, footwear, and accessories, allowing for rapid iteration and experimentation with new designs. Additive manufacturing also enables the production of limited-edition and haute couture garments with unique shapes and textures.
- Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing: 3D printing offers sustainable alternatives to traditional jewelry manufacturing processes, such as casting and machining. Additive manufacturing enables the use of recycled metals, biodegradable polymers, and eco-friendly resins, reducing waste and environmental impact.
G. Commercial 3D Printing For Food Industry
In the food industry, 3D printing is revolutionizing culinary arts, food customization, and personalized nutrition. Additive manufacturing enables chefs, food technologists, and nutritionists to create unique shapes, textures, and flavors with precision and consistency.
- Customized Food Products: 3D printing allows for the creation of custom-shaped food items, such as chocolates, candies, and confections, tailored to individual preferences. Additive manufacturing enables chefs and chocolatiers to experiment with intricate designs and decorative patterns.
- Nutritional Supplements and Functional Foods: 3D printing is being explored for the production of personalized nutritional supplements and functional foods tailored to specific dietary requirements and health goals. Additive manufacturing enables the precise deposition of bioactive ingredients and vitamins, ensuring uniform dosage and efficacy.
- Food Texture Modification: Chefs and food scientists use 3D printing to modify the texture and structure of food items, creating novel culinary experiences and sensory perceptions. Additive manufacturing enables the control of porosity, density, and elasticity in food products, enhancing taste, mouthfeel, and digestibility.
H. Commercial 3D Printing For Defense and Military Applications
In the defense and military sectors, 3D printing is driving innovation in weapon systems, equipment maintenance, and logistics support. Additive manufacturing offers the ability to rapidly produce spare parts, prototypes, and customized components on-demand, enhancing readiness and operational capability.
- Spare Parts Manufacturing: Military organizations use 3D printing to produce spare parts and components for weapons, vehicles, and aircraft, reducing reliance on traditional supply chains and logistics networks. Additive manufacturing enables the production of obsolete and hard-to-find parts with minimal lead time.
- Prototyping and Weapon Development: Defense contractors utilize 3D printing to prototype and iterate on new weapon systems, munitions, and protective gear. Additive manufacturing enables rapid design validation and testing, accelerating the development cycle and reducing development costs.
- Customized Equipment and Gear: Soldiers and tactical units benefit from 3D-printed equipment and gear customized to their individual requirements and mission objectives. Additive manufacturing allows for the production of lightweight, ergonomic, and high-performance components, enhancing mobility and operational effectiveness.
Market Analysis
Commercial 3D printing manufacturer offer the ability to design, create prototypes, and produce prints when you need them.
Current Market Size and Growth Trends
The commercial 3D printing market has experienced exponential growth over the past decade, driven by advancements in technology, increased adoption across industries, and growing demand for customized, on-demand manufacturing solutions. According to research reports, the global 3D printing market was valued at around $13 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach over $50 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20%.
Several factors contribute to this robust growth trajectory. Firstly, the declining cost of 3D printing hardware and materials has made the technology more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and individual consumers. Additionally, advancements in materials science, such as the development of high-performance polymers, metals, and ceramics, have expanded the range of applications for 3D printing across industries. Moreover, the ability of 3D printing to enable rapid prototyping, mass customization, and decentralized manufacturing has garnered significant interest from various sectors.
Major Players in the Commercial 3D Printing Industry
The commercial 3D printing industry is characterized by a diverse ecosystem of players, including technology providers, materials suppliers, software developers, service bureaus, and end-users. Some of the leading companies in the market include:
- Stratasys Ltd.
- 3D Systems Corporation
- EOS GmbH
- General Electric (GE) Additive
- HP Inc.
- Materialise NV
- Renishaw plc
- SLM Solutions Group AG
- ExOne Company
- Desktop Metal, Inc.
These companies offer a wide range of 3D printing technologies, materials, and software solutions tailored to the specific needs of different industries. They also play a crucial role in driving innovation, conducting research and development, and collaborating with industry partners to expand the capabilities of 3D printing technology.
Regional Market Dynamics and Emerging Markets
The commercial 3D printing market exhibits varying dynamics across different regions, influenced by factors such as technological infrastructure, regulatory environment, industry focus, and economic conditions. While North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for 3D printing, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key growth region, driven by rapid industrialization, government initiatives, and increasing investments in research and development.
In North America, the United States dominates the commercial 3D printing market, fueled by a strong presence of technology companies, robust manufacturing sector, and growing adoption in aerospace, automotive, and healthcare industries. Europe, particularly Germany, France, and the United Kingdom, also boasts a thriving 3D printing ecosystem, supported by government funding, academic research, and a highly skilled workforce.
In Asia-Pacific, countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing significant investments in additive manufacturing infrastructure, driven by initiatives to promote advanced manufacturing technologies, enhance domestic industrial capabilities, and foster innovation. Moreover, emerging markets in Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America present untapped opportunities for growth, fueled by increasing industrialization, urbanization, and demand for localized production.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the promising growth prospects, the commercial 3D printing market faces several challenges that need to be addressed to unlock its full potential. These challenges include:
- Cost of Adoption: The initial investment required for 3D printing equipment, materials, and software can be prohibitive for small businesses and startups, limiting widespread adoption.
- Material Limitations: While the range of available 3D printing materials has expanded in recent years, certain materials still pose challenges in terms of mechanical properties, surface finish, and compatibility with specific printing technologies.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring consistency, accuracy, and reliability in 3D printed parts remains a challenge, particularly in industries with stringent quality standards such as aerospace and healthcare.
- Intellectual Property Concerns: The digital nature of 3D printing raises concerns related to intellectual property rights, piracy, and unauthorized replication of proprietary designs.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Regulatory frameworks governing the use of 3D printing in industries like healthcare and aerospace are still evolving, posing compliance challenges for manufacturers and service providers.
The commercial 3D printing market is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by technological advancements, expanding applications, and evolving market dynamics. While challenges persist, the transformative potential of additive manufacturing presents exciting opportunities for businesses, industries, and society as a whole. By addressing key barriers and embracing collaboration, stakeholders can harness the power of 3D printing to drive economic prosperity, sustainability, and social impact on a global scale.











