3d Printed Mushrooms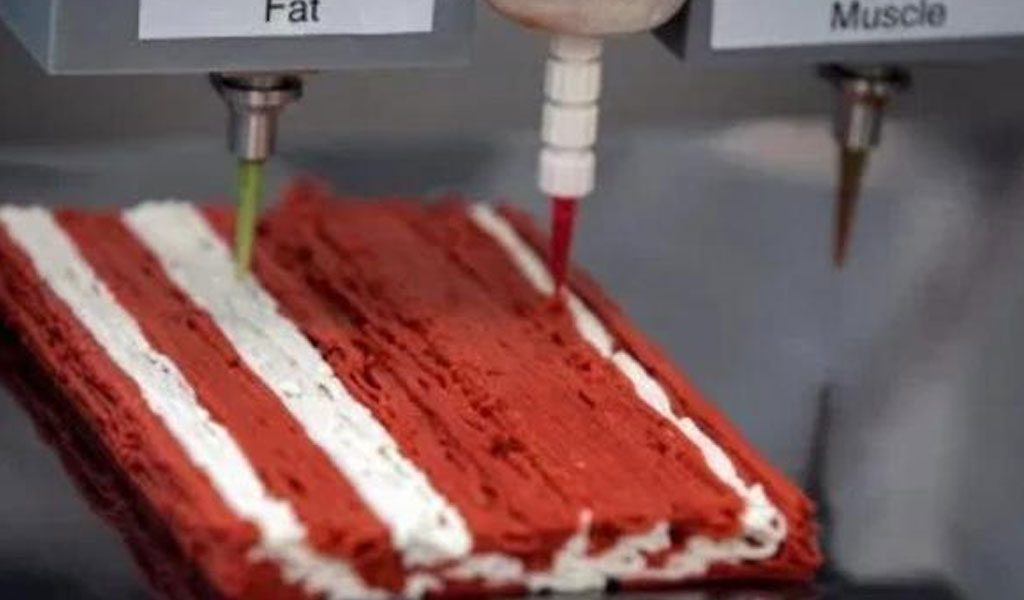 
3d Printed Steak
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has emerged as a groundbreaking technology with the potential to revolutionize various industries. In recent years, it has gained significant traction in the food sector, opening up new possibilities for customized and innovative food production. However, ensuring food safety standards with additive manufacturing is of paramount importance. This article explores the challenges and considerations in achieving food safety with 3D printing, emphasizing the critical aspects that must be addressed to ensure consumer protection and regulatory compliance.
Is additive manufacturing food-safe?
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, can be food-safe when certain conditions are met. The safety of additive manufacturing in the food industry depends on several factors, including the materials used, the manufacturing process, and adherence to food safety standards. Here are some key considerations regarding the food safety of additive manufacturing:
- Material Selection: Choosing food-grade materials is crucial for ensuring the safety of 3D printed food products. Food-safe materials are specifically designed and tested to meet regulatory requirements for contact with food. It is essential to select materials that are free from contaminants and have been approved for use in food applications.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to food safety regulations and standards is paramount. Different countries have specific regulations governing food production and contact materials. Manufacturers must ensure that the materials and processes used in additive manufacturing comply with these regulations. Compliance with standards such as those set by the FDA in the United States or the EFSA in the European Union is essential.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process itself should be designed and controlled to ensure food safety. This includes maintaining a clean and controlled production environment, implementing proper hygiene practices, and regularly cleaning and sanitizing the 3D printing equipment and facilities.
- Quality Control and Testing: Implementing robust quality control measures is essential to monitor the safety and quality of 3D printed food products. Regular testing should be conducted to detect potential risks, such as microbial contamination, chemical hazards, or foreign particles. Comprehensive testing protocols can help identify any potential issues and ensure the safety of the printed food.
- Allergen Management: Managing allergens is crucial when producing 3D printed food products. Cross-contamination between different food materials must be avoided to prevent the transfer of allergens. Clear labeling and communication about the presence of allergens in the printed food products are necessary to protect consumers with allergies.
- Continuous Improvement and Research: Ongoing research and development efforts are essential to improving the food safety of additive manufacturing. It is crucial to stay informed about the latest advancements, best practices, and research in the field to continually enhance food safety standards.
The food safety of additive manufacturing relies on careful implementation of these considerations. By adhering to proper material selection, regulatory compliance, manufacturing processes, quality control, allergen management, and ongoing research, additive manufacturing can be used to produce food products that meet food safety standards.

The Promise of Additive Manufacturing in the Food Industry
Additive manufacturing has reshaped multiple industries by enabling the production of complex and customized objects. In the food sector, 3D printing offers exciting opportunities to create novel food products, personalized nutrition, and improved food accessibility. It allows for intricate designs, precise portion control, and the incorporation of various ingredients in a single print. However, with these opportunities come unique challenges, particularly in guaranteeing food safety standards.
Materials and Regulations
Choosing the appropriate materials for 3D printing food products is crucial. Food-grade materials that comply with regulatory standards and have been tested for safety should be selected. These materials must be free from contaminants, possess suitable mechanical properties for the printing process, and be compatible with food contact.
Regulatory compliance is essential when using additive manufacturing in the food industry. Different countries have specific regulations governing food production and contact materials. Familiarity with these regulations, such as those issued by the FDA in the United States or the EFSA in the European Union, is vital to ensure compliance with food safety standards.
Maintaining a Safe Production Environment
A controlled and hygienic production environment is crucial to prevent contamination and ensure food safety. Regular cleaning and sanitization of the 3D printing equipment and facilities are essential. Personnel involved in the manufacturing process should adhere to strict hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing, proper protective clothing, and compliance with food safety protocols.
Quality Control and Testing
Robust quality control measures are imperative to monitor the safety and quality of 3D printed food products. Testing should be conducted regularly to detect potential risks such as microbial contamination, chemical hazards, or foreign particles. Implementing traceability systems enables the tracking and identification of the materials used in each batch of printed food, facilitating swift and targeted recalls if necessary.
Allergen Management
Managing allergens is a critical aspect of food safety, especially in additive manufacturing. Cross-contamination between different food materials should be avoided to prevent allergen transfer. Clear labeling and communication about the presence of allergens in the printed food products are essential to protect consumers with allergies.
Shelf Life and Storage Considerations
Additive manufacturing may introduce unique factors that influence the shelf life and storage requirements of 3D printed food. Factors such as moisture content, packaging materials, and storage conditions must be carefully considered to maintain the safety and quality of the printed food products over time.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Conducting thorough risk assessments is vital to identify and mitigate potential hazards associated with additive manufacturing. Assessments should consider the entire production process, including material selection, printing, post-processing, and packaging. By identifying risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies, manufacturers can minimize the likelihood of food safety issues.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Collaboration among stakeholders, including food safety experts, regulatory authorities, and industry peers, is crucial for achieving and maintaining high food safety standards. Regular communication and knowledge sharing facilitate the exchange of best practices, emerging research, and insights. This collective effort ensures that the latest advancements in additive manufacturing and food safety are incorporated into production processes.
Additive manufacturing presents exciting possibilities for the food industry, enabling customization, innovation, and improved food accessibility. However, ensuring food safety standards is paramount. Through careful materials selection, maintaining a clean production environment, rigorous quality control, allergen management, and risk assessment, producers can mitigate potential hazards. Compliance with regulatory requirements and collaboration with relevan
