Fasteners are integral components of any aircraft, holding together critical structures and ensuring the safety and functionality of aerospace systems. These small, often-overlooked components play a crucial role in the design, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft. In the fast-paced world of aerospace machining and engineering, where innovation and precision are paramount, understanding the various types, materials, and characteristics of aircraft fasteners is essential. This comprehensive article delves deep into the world of aerospace fasteners, exploring their role, importance, and the evolving technologies that drive advancements in the field.
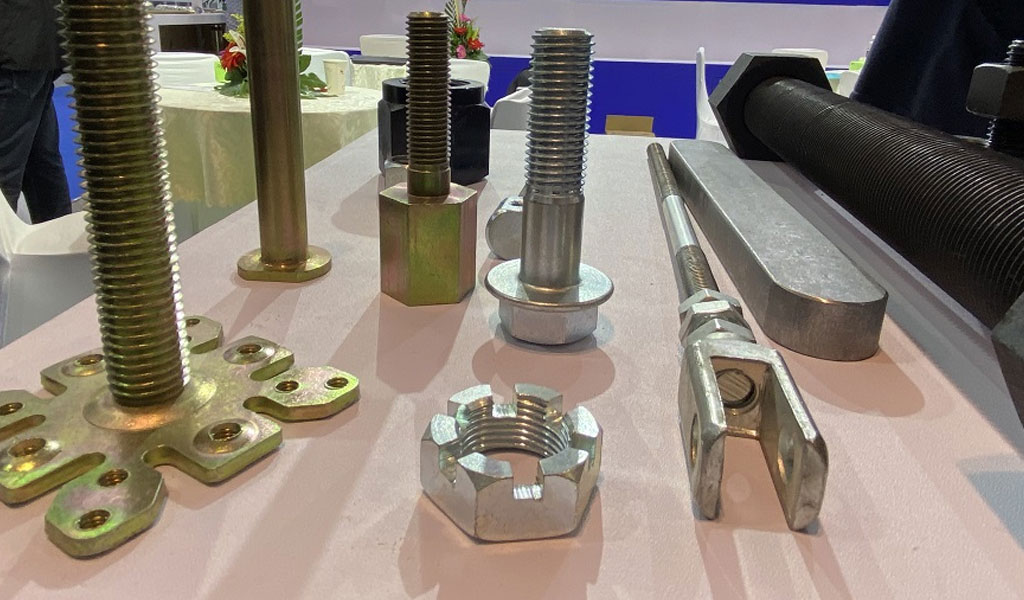

Fasteners Used in Aerospace and Aircraft Industry
Fasteners used in the aerospace industry are highly specialized components designed to meet the rigorous demands of aviation and space travel.
These fasteners play a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity, safety, and functionality of aircraft and spacecraft. They must withstand extreme conditions, including temperature fluctuations, high stress, and corrosive environments.
These fasteners are engineered to meet stringent aerospace industry standards and are subject to rigorous quality control and testing to ensure their reliability and performance in aircraft and spacecraft. Aerospace fasteners are vital for maintaining the structural integrity and safety of aerospace systems, making them an essential component of the industry.
Aircraft Fasteners Characteristics and Quality Standards
Aircraft fasteners must meet specific characteristics and adhere to stringent quality standards to ensure the safety and reliability of aerospace systems. These characteristics and standards are critical in the aerospace industry due to the extreme conditions and high-stress environments in which aircraft and spacecraft operate.
Here are the key characteristics and quality standards for aircraft fasteners:
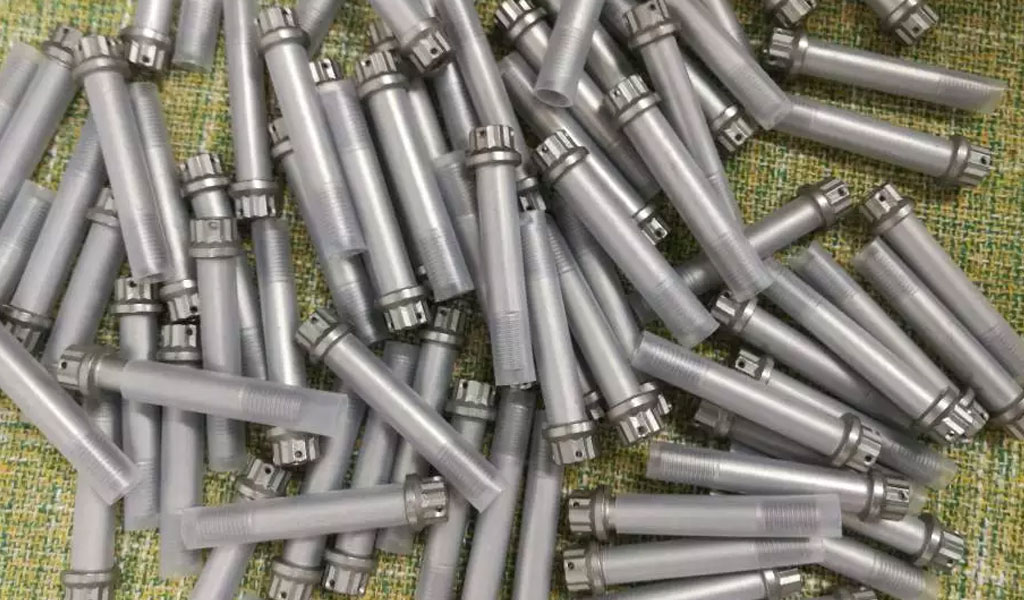

Characteristics of Aircraft Fasteners:
- Strength and Load Capacity:Aircraft fasteners must be capable of withstanding the high stress and load requirements in an aircraft’s structure. They are engineered to meet specified strength criteria to ensure the structural integrity of the aircraft.
- Corrosion Resistance:Given the wide range of environmental conditions aircraft are exposed to, fasteners must have excellent corrosion resistance. They are often coated with protective materials to prevent corrosion, such as cadmium plating or specialized coatings.
- Temperature Resistance:Aircraft operate in extreme temperature variations, from freezing cold at high altitudes to high temperatures during take-off and landing. Fasteners must maintain their integrity under these conditions.
- Fatigue Life:Aircraft components are subjected to thousands of cycles of stress, such as pressurization and depressurization, during their operational life. Fasteners need to have a long fatigue life to prevent catastrophic failures.
- Weight Considerations:Reducing weight is a continuous goal in aerospace engineering. Fasteners are designed to be as lightweight as possible without compromising strength and durability.
- Installation and Removal:Ease of installation and removal is essential for maintenance and repair. Special tools and techniques are often used to ensure fasteners can be installed and removed efficiently.
- Accessibility and Maintenance:Fasteners must be designed to be accessible for maintenance and inspection. Easy access to fasteners is crucial for the timely servicing of aircraft components.
Quality Standards for Aircraft Fasteners:
- AS/EN9100 Quality Management System:This quality management standard is specific to the aerospace industry and is based on ISO 9001. AS/EN9100 certification ensures that the manufacturer has a robust quality management system in place, from design to production and testing.
- NADCAP (National Aerospace and Defense Contractors Accreditation Program):NADCAP is a global accreditation program for aerospace manufacturers and suppliers. It provides a standardized approach to quality assurance, including materials testing and heat treatment processes.
- AMS (Aerospace Material Specifications):AMS specifications set the standards for materials used in aerospace, including materials used for fasteners. These specifications dictate the composition, quality, and manufacturing processes.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials):ASTM standards cover a wide range of materials, including those used in aerospace fasteners. These standards ensure materials meet specific mechanical and chemical requirements.
- Military Standards (MIL-SPEC):Some aerospace fasteners may adhere to military standards, which set requirements for reliability and quality, particularly for defense and military machining applications.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization):ISO standards, particularly ISO 9001, play a role in the quality management systems of aerospace manufacturers, ensuring that processes meet international standards.
- FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) Regulations:Aircraft fasteners used in civil aviation must adhere to FAA regulations, which include strict quality and safety standards. The FAA oversees and approves the use of such fasteners in aircraft.
- European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) Regulations:EASA sets safety and quality standards for aviation in Europe, including the use of fasteners in aircraft construction.
Compliance with these quality standards is essential to ensure that aircraft fasteners meet the rigorous requirements of the aerospace industry, ultimately contributing to the safety and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft. Aerospace manufacturers and suppliers must adhere to these standards to provide components that meet the highest quality and safety levels.
Types of Aerospace and Aircraft Fasteners
Aerospace and aircraft fasteners are crucial components in the construction and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft. These fasteners come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and requirements. Here are some of the key types of aerospace and aircraft fasteners:
Rivets
- Description: Rivets are permanent mechanical fasteners that are commonly used in aircraft construction. They consist of a cylindrical shaft with a head on one end. The rivet is inserted through aligned holes in the components to be joined, and the other end is deformed to create a second head, effectively “locking” the components together.
- Applications: Rivets are used extensively in the aerospace industry, particularly in the assembly of the aircraft’s structural components, such as the fuselage and wings. They provide strong, durable connections that can withstand the stresses of flight.
Bolts
- Description: Bolts are threaded fasteners that consist of a head, a shank, and a threaded portion. They require the use of a nut for assembly. Bolts are versatile and can be easily removed and replaced, making them suitable for components that need to be regularly accessed.
- Applications: Bolts are used in various aircraft systems, including attaching engine components, securing access panels, and joining structural elements. They provide a secure and maintainable connection.
Screws
- Description: Screws are threaded fasteners similar to bolts but typically have a pointed end for self-tapping into materials. They can be used for a wide range of applications, from fastening panels to attaching electrical and avionic components.
- Applications: Screws are used throughout an aircraft for different purposes, including securing interior components, avionics, and smaller access panels. They come in various types, such as machine screws and self-tapping screws.
Nuts
- Description: Nuts are often paired with bolts or screws and are used to secure these fasteners in place. Nuts come in various shapes, such as hexagonal, square, and wing nuts, and can be chosen based on the specific application’s requirements.
- Applications: Nuts are critical for fastening components in an aircraft, providing the necessary counterforce to the bolt or screw. They are used in various systems, including the landing gear, engine components, and control surfaces.
Washers
- Description: Washers are flat, thin plates with a hole in the center. They are placed under the head of a bolt or nut to distribute the load and prevent damage to the surface of the aircraft structure.
- Applications: Washers are used in combination with bolts and nuts to ensure a more even load distribution. They are commonly used in aircraft to protect critical surfaces from damage.
Clamps
- Description: Clamps are used to secure hoses, wires, and other components within an aircraft. They come in various forms, such as hose clamps, cable clamps, and spring clamps, and are designed to provide a secure hold without damaging the components they are securing.
- Applications: Clamps are found throughout an aircraft, ensuring that various systems, such as hydraulic lines, electrical wiring, and tubing, are securely fastened and organized.
Pins
- Description: Pins are cylindrical fasteners with a variety of designs and locking mechanisms. They are used for alignment, securing, or releasing components and often require tools or mechanisms to install or remove.
- Applications: Aircraft pins are used for tasks such as securing landing gear, locking landing gear doors, and providing secure connections in flight control systems.
Latches
- Description: Latches are mechanical devices used to fasten doors, panels, and access points on an aircraft securely. They can vary in complexity and design, from simple sliding bolts to more advanced locking mechanisms.
- Applications: Latches are vital for securing aircraft doors, cargo holds, and panels. They ensure that these access points remain closed during flight.
Blind Fasteners
- Description: Blind fasteners are used in situations where access to the opposite side of the component is limited or impossible. They are designed to be installed from one side of the structure and securely fastened on the other side.
- Applications: Blind fasteners are commonly used in the assembly of aircraft components in confined or hard-to-reach spaces, making them an essential type of fastener for modern aerospace applications.
These various types of fasteners play crucial roles in ensuring the structural integrity, safety, and functionality of aircraft. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications, making them indispensable components in aerospace engineering.
Materials of Aerospace Fasteners – Which Material to Choose for Aircraft
Aerospace and aircraft fasteners are manufactured from various materials, each chosen for its specific properties and suitability for the demanding conditions of aviation and space travel. Here are some of the materials commonly used in aerospace and aircraft fasteners:
Aluminum Alloys:
Description: Aluminum alloys are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making them a popular choice for aerospace applications. They are particularly well-suited for applications where weight reduction is a priority.
Applications: Aluminum alloy fasteners are used in aircraft structures, especially those parts where weight savings are essential, such as the fuselage, wings, and interior components.
Titanium Alloys:
Description: Titanium alloys offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional corrosion resistance, and high-temperature stability. They are favored for their ability to withstand extreme conditions.
Applications: Titanium fasteners are used in critical aerospace components, including the aircraft’s frame, landing gear, and engine components. Their high strength makes them suitable for applications where durability and reliability are paramount.
| Types | Fasteners | Application Introduction |
|---|---|---|
| TA1,TA2 | Rivet, washer | Mainly for welding load-bearing structural parts |
| TA15 | Nut, plug screw | Most used titanium alloy fastener materials |
| TC4 | Bolt | Requiring reduce weight and resist heat |
| TC6 | Bolt, nut | Requiring reduce weight and resist heat |
| TC16 | Bolt, screw, self-locking nut, rivet | The service temperature should be less than 30o ℃ |
| TB2 | Rivet | Requiring strength, and temperature less than 200 ℃ |
| TB3 | Bolt, screw, nut | Requiring oxidation & corrosion resistance, and reduce weight |
Stainless Steel:
Description: Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and durability. It maintains its mechanical properties at a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for aerospace applications.
Applications: Stainless steel fasteners are used in various aircraft systems, including avionics, interior components, and engine components. They provide corrosion resistance and strength.
Inconel:
Description: Inconel is a family of nickel-based superalloys known for their high-temperature resistance and exceptional strength. They are ideal for use in extreme conditions and harsh environments.
Applications: Inconel fasteners are used in critical aerospace components, such as gas turbine engine parts, exhaust systems, and components exposed to high temperatures and corrosive atmospheres.
Superalloys:
Description: Superalloys are a group of high-performance materials, often nickel-based, with exceptional high-temperature and corrosion resistance. They are engineered for demanding aerospace applications.
Applications: Superalloy fasteners are used in aircraft engines, gas turbine components, and other systems where exposure to extreme temperatures and stress is common. They play a vital role in ensuring engine reliability.
Composite Fasteners:
Description: Composite materials are becoming increasingly popular in aerospace due to their lightweight properties. Composite fasteners are made from composite materials, which combine the strength of various materials with reduced weight.
Applications: Composite fasteners are used in components and structures where weight reduction is a primary consideration. They are often found in modern aircraft interiors, as well as components where reducing the overall weight of the aircraft is a critical design goal.
The choice of material for aerospace and aircraft fasteners depends on various factors, including the specific application, the operating conditions, weight considerations, and the materials’ resistance to corrosion and temperature variations. The correct selection of materials is essential to ensure the performance, safety, and longevity of aerospace and aircraft systems.
Advancements in Aerospace Fasteners
Advancements in aerospace fasteners have been instrumental in enhancing the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of aircraft and spacecraft. These advancements leverage cutting-edge technologies and materials to meet the evolving needs of the aerospace industry. Here are some notable advancements in aerospace fasteners:
3D-Printed Fasteners:
Description: Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has revolutionized the aerospace industry, including fastener production. 3D-printed fasteners are fabricated layer by layer, offering precise control over their design and material composition.
Benefits:
- Complex Geometries: 3D printing allows for the creation of intricate and customized fastener designs that were previously impossible with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Lightweight Design: The ability to optimize the design reduces material waste, resulting in lightweight fasteners that contribute to fuel efficiency.
- On-Demand Production: Fasteners can be produced on-site or as needed, reducing inventory costs and lead times.
Applications: 3D-printed fasteners are used in various aerospace applications, including structural components, interior elements, and customized parts for specific aircraft or spacecraft.
Smart Fasteners:
Description: Smart fasteners are equipped with embedded sensors and data collection capabilities. They allow real-time monitoring of fastener conditions and the surrounding structure.
Benefits:
- Condition Monitoring: Smart fasteners can detect stress, temperature, vibration, and other factors that may affect their integrity and the structure they hold together.
- Predictive Maintenance: By continuously monitoring fasteners, maintenance teams can predict and address issues before they become critical, increasing safety and reducing downtime.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data collected from smart fasteners can inform maintenance and design decisions, enhancing aircraft and spacecraft performance.
Applications: Smart fasteners are used in critical aerospace components, including engine parts, aircraft structures, and spacecraft to ensure early detection of stress or damage.
Eco-Friendly Fasteners:
Description: Eco-friendly fasteners are designed with sustainability in mind. They use materials and manufacturing processes that minimize environmental impact.
Benefits:
- Reduced Environmental Footprint: Eco-friendly fasteners are produced using sustainable materials and processes, reducing waste and energy consumption.
- Recyclability: These fasteners are often designed for easy disassembly and recycling at the end of their service life.
- Lower Toxicity: Eco-friendly materials may be less toxic and harmful to the environment during their production and disposal.
Applications: Eco-friendly fasteners are incorporated into aircraft and spacecraft to align with the aerospace industry’s increasing emphasis on environmental responsibility.
Nanostructured Fasteners:
Description: Nanostructured fasteners are manufactured using advanced nanomaterials and processes. These materials exhibit exceptional strength, lightness, and durability at the nanoscale.
Benefits:
- High Strength: Nanostructured materials offer superior strength and can withstand extreme conditions, contributing to enhanced structural integrity.
- Weight Reduction: Their lightweight nature reduces the overall weight of aircraft and spacecraft, which is crucial for fuel efficiency.
- High-Temperature Stability: Nanostructured fasteners can maintain their properties in high-temperature environments, such as those found near engines.
Applications: Nanostructured fasteners are utilized in aerospace components that require the highest strength and durability, including engine parts, landing gear, and structural elements.
These advancements in aerospace fasteners are driving innovation in the industry, leading to safer, more efficient, and environmentally sustainable aircraft and spacecraft. As technology continues to advance, the aerospace sector can expect further developments in fastener design and production methods.
In Conclusion
Aerospace fasteners are the unsung heroes of aviation and space exploration, playing a critical role in ensuring the structural integrity, safety, and performance of aircraft and spacecraft. As technology continues to advance, the aerospace industry has witnessed remarkable innovations in fastener design and manufacturing.
Our Fasteners Case Studies:
The continuous evolution of aerospace fasteners reflects the industry’s commitment to safety, efficiency, and sustainability. As the aerospace sector faces new challenges and opportunities, fastener advancements will continue to drive innovation, enhancing the capabilities of aircraft and spacecraft. These advancements not only improve the performance and safety of aerospace systems but also contribute to a more environmentally responsible and sustainable future for aviation and space exploration.




