Vibration is a common form of mechanical motion that refers to the reciprocating motion of an object over time near an equilibrium position. Vibration also has a harmful side. During turning, vibration will increase the surface roughness of the workpiece to be processed, and sometimes texture will appear, which cannot meet the processing requirements.
At the same time, generally with the generation of the first vibration, the subsequent processing will also be accompanied by continuous vibration, so that errors will occur in each process of the entire processing process, and the accumulation of errors will even lead to the scrapping of the workpiece.
Moreover, vibration not only affects the machining accuracy and machining quality, but also causes wear and tear on the machine and the tool. Once this happens, the entire turning machine and tool will be damaged. Workers with rich experience in the machining field are fully aware of In the case of machine tools, the vibration generated during machining is suppressed by sacrificing the machining efficiency of the machine tool and reducing the amount of machining of parts to be cut.
Another kind of vibration generated in turning is mainly the vibration of the tool. The vibration of the tool is easy to observe. The vibration of the tool is a kind of high-frequency vibration. The noise generated during cutting will be very loud and harsh, mainly because the tool is processing. During the process, the wear and tear between the workpiece and the workpiece accumulates, which increases the surface friction force. Under the action of the friction force, the workpiece and the tool will be damaged, and fine and dense traces will be drawn on the surface of the workpiece.
01 How to eliminate vibration
To control the generation of vibration in the CNC turning process, it is necessary to consider both the machine tool and the tool. On the basis of eliminating the internal vibration of the machine tool, it is necessary to reduce the human error in the processing process and the wrong use of the workpiece tool to ensure that the vibration will not cause serious harm. To effectively reduce or eliminate vibration, you can take the following measures.
- For hard-turned parts, you need to choose a machine tool with better rigidity, a Japanese or European machine tool.
- When clamping the tool, the processing sequence of the workpiece should be fully considered, and the most suitable surface should be clamped to ensure the uniform force on the tool, to avoid the unbalanced force during the machining process and the increase of the bending moment, and the tool should be clamped well. , to avoid vibration or even tool flying off during processing.
- Reasonably select the material and type of the tool, and select the appropriate tool according to the material of the workpiece and the machining accuracy requirements. It is strictly forbidden to “cut hard with a soft knife”, which will not only damage the tool, but also increase the hazard of vibration during processing.
- Appropriately increase the stiffness of the tool holder, which can reduce the impact of friction.
- Control the overhang length of the tool. The extended length of the tool is too long, which is not conducive to processing, and is prone to shaking during processing, which will also cause damage to the operator.
- Sharpen or replace the tools that have been used for a long time in time.
- Use anti-vibration shank or carbide shank.
02 Analysis of cutting force
Tangential cutting force, Ft
- 1) Press the tool down, away from the centerline.
- 2) The secondary relief angle is reduced.
Radial cutting force, Fr
- 1) Change the cutting depth and cutting thickness.
- 2) Causes dimension out of tolerance and vibration risk.
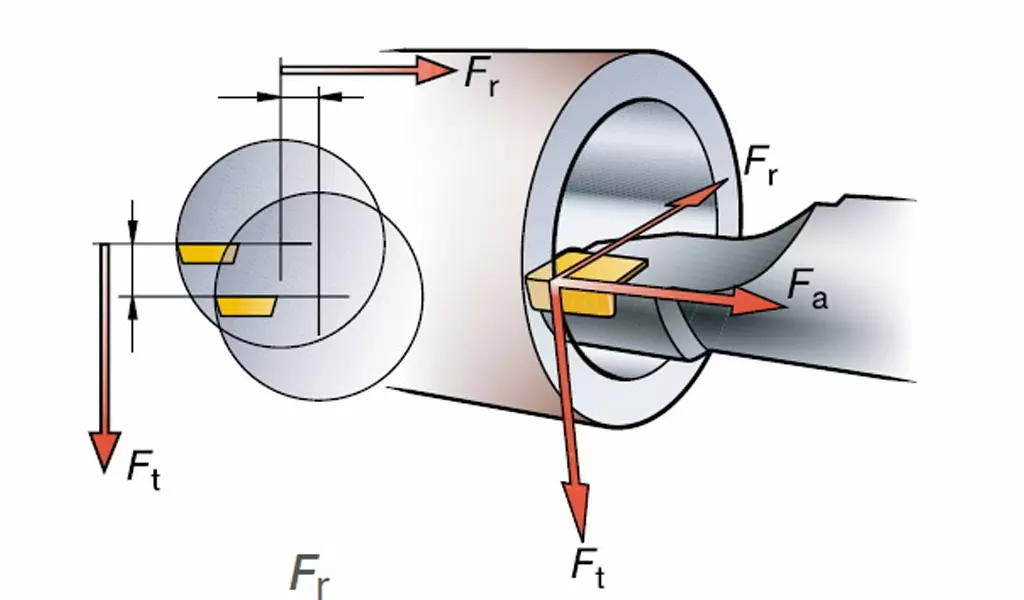
Feed force, Fa
Allocation along the tool feed direction.
Choose the right main deviation (cut in) angle
Select entering (entry) angle and cutting force

Choose a entering angle close to 90° (closer to a 0° cut-in angle).

The most common internal turning operations
- The commonly used rhombus C-type 80° blade.
- Commonly used are boring bars with 95° (-5°) and 93° (-3°) leading deflection (cut-in) angles.
- D-type 55°, W-type 80° and T-type 60° blade shapes are also commonly used.
03 Cases
Processing inside the output shaft pressing plate: the material is 20CrMnTi, and the surface finish is required to be within Ra0.6. The pressing plate is a thin-walled part, and there are often vibration marks on the surface. Using an imported brand blade, the processing life is only 50 pieces of forced tool change.
In the early stage of designing the insert, considering the lack of rigidity of the actual application site machine tool and the workpiece, a design with small chamfers and a wiper edge is adopted, which can reduce the cutting force and reduce the vibration pattern, and can obtain a good finish to meet the needs of According to the requirements of the customer, reasonable cutting parameters were selected for testing. At the end of the test, the cutting force increased due to the wear of the blade edge, resulting in vibration lines, which did not achieve the expected effect.
From the analysis of the test data, there is no problem with the blade material and the cutting edge processing angle. The main factor causing the vibration is the lack of rigidity of the machine tool and the tool holder. The original tool holder uses a steel base tool holder, and the overhang is too long. , is one of the main factors that cause the processing vibration pattern.
