In the realm of medical advancements, one innovation that has significantly impacted cardiovascular treatments is the Valve Stent. Originally designed to address specific cardiac conditions, Valve Stent technology has evolved over the years, offering novel solutions for patients suffering from various heart-related issues. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of Valve Stent technology, exploring its inception, functioning, applications, recent advancements, and its potential future developments.
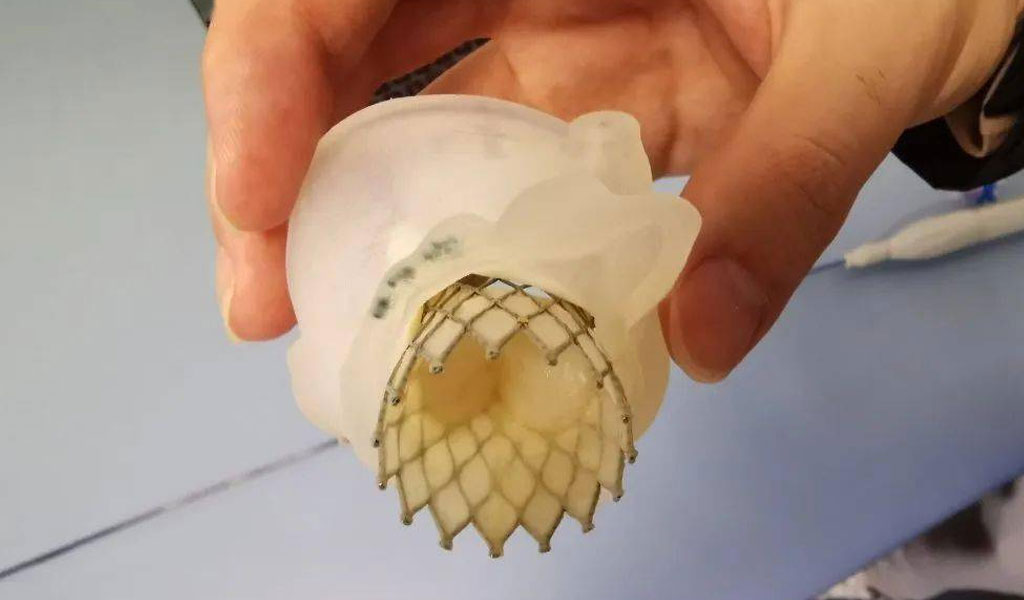
Basics Of Valve Stents
Valve Stents, also referred to as transcatheter heart valves or stent valves, are medical devices designed and micro cutting to treat heart valve diseases. These devices are prosthetic valves that can be implanted via minimally invasive procedures, eliminating the necessity for open-heart surgery. They are constructed using biocompatible materials like metal alloys or polymers and are tailored to simulate the functionality of natural heart valves.
Evolution and Development
The evolution of Valve Stents spans several decades, originating from the need to address specific cardiac conditions. Early designs primarily focused on aortic valve diseases. The initial successful implantation of a transcatheter aortic valve in the early 2000s marked a pivotal moment in interventional cardiology. Subsequent advancements and extensive research efforts have led to diverse types of Valve Stents catering to various heart valves and conditions.
Over time, Valve Stent technology has undergone iterative improvements in terms of design, materials, delivery methods, and compatibility. These enhancements aim to enhance efficacy, durability, and safety while broadening the range of treatable conditions.
How Valve Stents Work
Valve Stents are inserted into the heart through catheter-based procedures. Rather than employing traditional open-heart surgery, these devices are delivered to the intended site through blood vessels. This minimally invasive approach is guided by imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy.
Once the Valve Stent is accurately positioned, it is deployed or expanded at the targeted location within the heart. The expansion mechanism displaces the diseased valve, effectively restoring proper blood flow. The Valve Stent assumes the role of the dysfunctional or narrowed valve, allowing for improved circulation and alleviation of symptoms associated with the heart condition.
The process involves careful placement and deployment of the Valve Stent, ensuring it fits securely and functions effectively within the patient’s anatomy. The objective is to restore normal blood flow through the heart, thereby mitigating the symptoms caused by valve-related issues.
This procedure reduces recovery times, minimizes complications associated with open-heart surgery, and offers a viable treatment option for patients who may not be suitable candidates for traditional surgical interventions.
Valve Stents have shown promising results in various clinical scenarios, particularly for patients with severe valvular diseases, providing a less invasive alternative with favorable outcomes and improved quality of life.
The continuous refinement and advancements in Valve Stent technology aim to address existing limitations, enhance patient outcomes, and broaden the scope of treatable cardiac conditions.
This overview offers insight into the fundamental aspects of Valve Stents, tracing their evolution, and outlining the mechanism by which they operate to alleviate heart valve diseases.
Applications of Valve Stents
Valve Stents, or transcatheter heart valves, have expanded their applications beyond their initial use for aortic valve replacement. Here are various applications of Valve Stents:
1. Aortic Valve Replacement:
The primary and most established application of Valve Stents is in aortic valve replacement (TAVR – Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement). Aortic stenosis, a condition characterized by the narrowing of the aortic valve opening, is a common indication for this procedure. Valve Stents provide a less invasive alternative to open-heart surgery, particularly for patients deemed high-risk or ineligible for traditional surgical interventions due to various health concerns.
2. Mitral Valve Repair and Replacement:
Valve Stents have been undergoing extensive research and development for the treatment of mitral valve diseases. While the anatomy and functionality of the mitral valve present challenges in design and placement compared to the aortic valve, there are ongoing efforts to develop transcatheter solutions for mitral valve repair and replacement. These innovations aim to provide less invasive treatment options for conditions like mitral regurgitation or mitral stenosis.
3. Pulmonary Valve Interventions:
Pulmonary valve diseases, such as pulmonary stenosis or pulmonary regurgitation, can also benefit from Valve Stent technology. Although interventions involving the pulmonary valve are less common compared to the aortic and mitral valves, transcatheter techniques are being explored and developed for treating pulmonary valve disorders, especially in pediatric populations with congenital heart defects.
4. Tricuspid Valve Repair:
The tricuspid valve, situated between the right atrium and the right ventricle, can develop diseases like tricuspid regurgitation or stenosis. While the tricuspid valve has presented challenges due to its complex anatomy and location, researchers are investigating transcatheter approaches for tricuspid valve repair or replacement using Valve Stents.
5. High-risk and Inoperable Patients:
Valve Stents offer a critical advantage for patients considered high-risk or inoperable for traditional open-heart surgery due to age, frailty, or other underlying health conditions. The minimally invasive nature of Valve Stent procedures reduces recovery times and lowers the risk of complications, providing feasible treatment options for these patients.
6. Valve-in-Valve Procedures:
Valve-in-valve procedures involve placing a new Valve Stent within a previously implanted bioprosthetic valve. This technique serves as an alternative for patients requiring a second valve replacement without undergoing another open-heart surgery. It enables the restoration of valve function without the need to remove the existing valve, reducing procedural risks.
7. Emerging Applications:
Continued research aims to explore Valve Stent applications in various other valve-related disorders, including bicuspid aortic valves, valve diseases in pediatric populations, and addressing structural valve degeneration in previously implanted bioprosthetic valves. These emerging applications signify the potential expansion and versatility of Valve Stent technology.
The diverse applications of Valve Stents showcase their potential to revolutionize the treatment landscape for a wide range of heart valve diseases. Ongoing research and advancements aim to further refine these applications and expand the scope of Valve Stent interventions.
Advancements in Valve Stent Technology
Advancements in Valve Stent technology have been pivotal in enhancing their effectiveness, safety, and applicability across a broader spectrum of patients and conditions. Here are some notable advancements in Valve Stent technology:
1. Enhanced Durability and Biocompatibility:
Improvements in materials science have led to the development of more durable and biocompatible Valve Stents. Innovations in biomaterials and surface coatings aim to minimize the risk of complications such as thrombosis, tissue overgrowth, or calcification. These enhancements contribute to longer-lasting Valve Stents and reduce the need for re-interventions.
2. Customization and Patient-specific Designs:
Advancements in imaging techniques, such as 3D imaging and computational modeling, allow for the creation of patient-specific Valve Stents. Customization ensures an optimal fit within individual anatomies, reducing the risk of complications and improving the overall efficacy of the intervention. Tailored Valve Stents offer a more precise and personalized approach to treatment.
3. Navigation and Delivery Systems:
Refinements in delivery systems and navigational tools have significantly improved the precision and ease of Valve Stent deployment. Smaller and more flexible catheters enable smoother navigation through intricate vasculature, enhancing the accuracy of placement and reducing procedural complexities. Advanced delivery systems also contribute to shorter procedure times and improved patient outcomes.
4. Minimizing Paravalvular Leakage:
Paravalvular leakage, where blood leaks around the edges of the implanted Valve Stent, has been a concern. Advancements in Valve Stent design and deployment techniques aim to reduce this complication. Newer iterations of Valve Stents include features intended to minimize or eliminate paravalvular leaks, enhancing their efficacy and patient outcomes.
5. Transcatheter Mitral Valve Repair:
The development of transcatheter devices specifically for mitral valve repair, such as edge-to-edge repair devices, offers minimally invasive solutions for mitral regurgitation. These devices can restore proper valve function without the need for open-heart surgery, providing an alternative for patients who might not be suitable candidates for surgical intervention.
6. Remote Monitoring and Smart Technologies:
Integration of smart technologies within Valve Stents allows for remote monitoring of the device and the patient’s condition. These advancements enable real-time assessment of Valve Stent performance, early detection of potential issues, and timely interventions, improving post-procedural care and patient outcomes.
7. Next-generation Biodegradable Valve Stents:
Research into biodegradable Valve Stents aims to develop devices that gradually degrade over time, leaving behind healthy tissue. This approach eliminates the need for a permanent implant and may reduce long-term complications associated with permanent devices.
8. Expanded Applications and Clinical Trials:
Ongoing clinical trials explore the use of Valve Stents in new applications, including bicuspid aortic valves, younger patient populations, and patients with previously implanted valves. These trials aim to expand the indications and refine the techniques for Valve Stent interventions.
Advancements in Valve Stent technology continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in treating various heart valve conditions. These innovations signify a transformative shift towards safer, more effective, and patient-tailored treatments, marking a promising future for Valve Stent technology in cardiovascular care.
China Best Valve Stent Laser Cutting Manufacturer
Valve Stent technology has emerged as a transformative force in the realm of cardiovascular interventions. Its evolution from aortic valve replacement to a spectrum of applications addressing diverse heart valve conditions reflects its substantial impact on patient care.
The development of Valve Stents has revolutionized treatment paradigms by offering minimally invasive alternatives to conventional open-heart surgeries. This innovation has notably benefited patients considered high-risk or unsuitable candidates for traditional procedures, providing them with viable treatment options and improving their quality of life.
Advancements in materials, customization, navigation, and monitoring systems have propelled Valve Stent technology forward. Enhanced durability, biocompatibility, and personalized designs contribute to improved efficacy and reduced complications, thereby ensuring better long-term outcomes for patients.
Moreover, the expansion of Valve Stent applications, including mitral valve interventions, pulmonary valve treatments, and exploration into emerging areas, signifies the technology’s potential to address a broader range of cardiovascular conditions.
However, challenges such as ensuring long-term durability, reducing costs, and broadening accessibility still need to be addressed to optimize the widespread adoption of Valve Stent technology. Efforts in ongoing research, clinical trials, and technological innovations aim to overcome these challenges and further refine this groundbreaking technology.
As Valve Stent technology continues to evolve, its impact on cardiovascular care remains profound. The future promises continued advancements, including biodegradable devices, expanded indications, and improved patient outcomes, reinforcing the critical role of Valve Stents in reshaping the landscape of heart valve interventions.
No matter if a single prototype or ten thousand market-ready parts are being ordered, having trust in your manufacturer is absolutely essential. Parts that are going through the prototyping stage will likely involve intellectual property and trade secrets that need to be kept away from the public eye, and production parts will need to have a great deal of precision so that they are consistent.
Be-Cu prototype inc having over ten years of experience in the field of Valve Stent Laser Cutting and with over 2 million parts manufactured, our 33,000+ customers continue to use our medical laser cutting service because they know that every part they order will conform to our strict set of capabilities. At the same time, we provide 365-day guarantees on all parts, no matter the order size, meaning that engineers can remain confident in the longevity of their parts.
