Bronze, an alloy of copper and other elements like tin, aluminum, nickel, or zinc, boasts exceptional qualities such as strength, corrosion resistance, and a rich, warm appearance. This material finds extensive applications in art, sculpture, marine components, machinery parts, and more due to its unique blend of properties.
CNC machining has revolutionized manufacturing across industries, enabling precise and efficient production of parts and components. When it comes to working with bronze, a versatile and durable metal alloy, CNC machining techniques play a pivotal role in shaping intricate designs and achieving high-quality end products. This article delves into the nuances of CNC machining for bronze, offering essential tips and considerations to optimize the process.
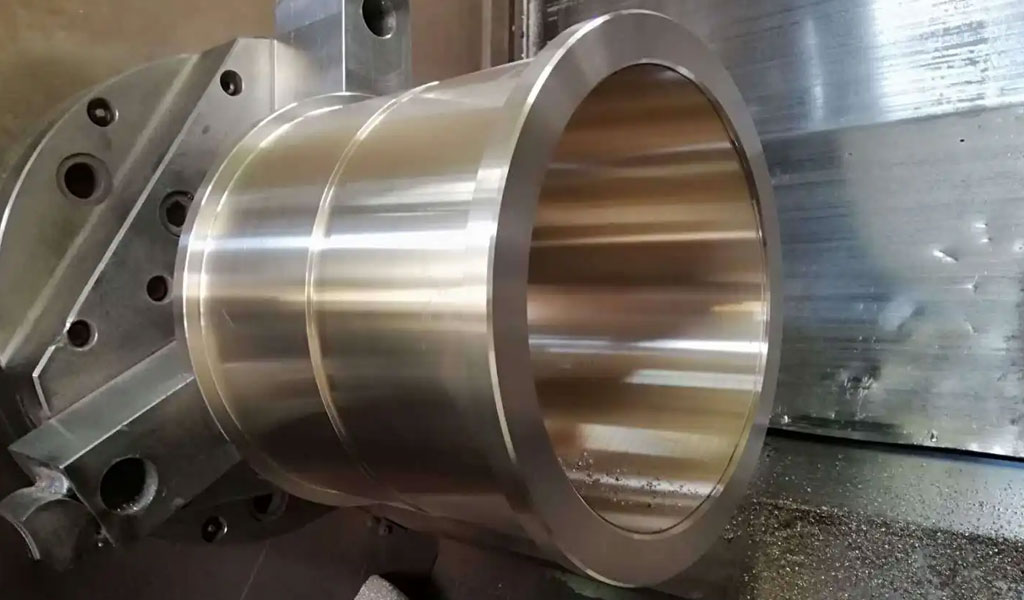

What Is Bronze
Bronze is an alloy, primarily consisting of copper and usually containing tin as the main additional element, though other metals like aluminum, manganese, nickel, or zinc can also be part of the alloy composition. Its history dates back to ancient times, making it one of the earliest alloys used by humans.The composition of bronze can vary significantly, affecting its properties. Commonly, bronze consists of about 88% copper and 12% tin, but this proportion can change based on the desired characteristics. Different compositions yield alloys with varying strengths, colors, and corrosion resistance.
Bronze has desirable material properties, and it is also relatively easy to work with. It is weldable (in an inert atmosphere) and it can be CNC machined like stainless steel. It is also conducive to virtually all surface finishing processes: bead blasting, powder coating, and electrophoresis all produce good results when applied on titanium. Of course, there are metals with a higher degree of machinability than bronze, but bronze offers a good combination of formability and mechanical performance.
Properties
Bronze possesses several advantageous properties:
- Strength: Bronze is stronger and harder than copper, making it suitable for various applications requiring durable materials.
- Malleability: Despite its strength, bronze remains relatively malleable, allowing it to be easily shaped and molded into intricate designs.
- Corrosion Resistance: Bronze has excellent resistance to corrosion, particularly in marine environments, which makes it ideal for ship fittings and other submerged applications.
- Low Friction: Bronze alloys, such as phosphor bronze, exhibit low friction properties, making them suitable for bearings and bushings.
- Appearance: Bronze has a warm, attractive appearance that lends itself well to artistic and decorative purposes.
Applications
Bronze’s versatility has led to its use in various industries and applications:
- Art and Sculpture: Renowned for its aesthetic appeal and workability, bronze has been a preferred medium for sculptors throughout history.
- Marine Components: Due to its resistance to corrosion, bronze is utilized in marine applications like propellers, fittings, and ship components.
- Bearings and Bushings: Its low friction properties make certain bronze alloys ideal for manufacturing bearings, bushings, and other machine components.
- Musical Instruments: Some musical instruments, particularly those requiring good resonance and durability, are crafted from bronze or bronze alloys.
- Industrial Machinery: Bronze is used in the construction of gears, valves, and other machine parts due to its strength and wear resistance.
History
Bronze holds significant historical importance. The Bronze Age marked a pivotal period in human civilization when bronze tools, weapons, and artifacts revolutionized various aspects of life, from agriculture to warfare.
Bronze is an alloy renowned for its blend of strength, malleability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Its wide-ranging applications across industries and its historical significance make bronze a cherished material in both artistic and industrial realms. Its properties and versatility have cemented its place as a valued material in the world of manufacturing and craftsmanship.
Why Use Bronze For CNC Machining?
Bronze is a popular choice for CNC machining due to several advantageous properties that make it suitable for various applications and machining processes. Here are some reasons why bronze is favored for CNC machining:
1. Machinability:
Bronze alloys are generally more machinable compared to many other metals. Their composition allows for easier cutting, shaping, and finishing, making them well-suited for CNC machining processes. This ease of machinability reduces production time and costs associated with machining operations.
2. Wear Resistance:
Certain bronze alloys, such as phosphor bronze, exhibit excellent wear resistance. This property is particularly beneficial for manufacturing components like bearings, bushings, gears, and other machine parts that experience friction and wear during operation.
3. Corrosion Resistance:
Bronze possesses good corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments and when exposed to various weather conditions. This makes it a preferred choice for components subjected to moisture or corrosive elements, reducing maintenance and extending the lifespan of parts.
4. Thermal Conductivity:
Bronze has moderate thermal conductivity, which can be advantageous in dissipating heat during machining operations. Efficient heat dissipation helps prevent overheating of tools and workpieces, reducing the risk of thermal damage and ensuring consistent machining performance.
5. Aesthetic Appeal:
Apart from its mechanical properties, bronze is valued for its attractive appearance and warm, golden hue. This aesthetic appeal makes it a preferred material for artistic and decorative applications, where CNC machining allows for intricate and precise designs.
6. Versatility:
Bronze alloys can be tailored to specific requirements by adjusting their composition. Different combinations of metals can yield variations in strength, hardness, and other properties, allowing for versatility in meeting diverse application needs.
7. Ductility and Formability:
Bronze alloys possess a degree of ductility and formability, enabling them to be shaped into complex designs without sacrificing strength. This characteristic is advantageous for creating intricate parts or components requiring precise shapes and dimensions.
The combination of favorable properties such as machinability, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, aesthetics, and versatility makes bronze an excellent choice for CNC machining. Its use spans across various industries, from manufacturing industrial components to crafting intricate artistic pieces, showcasing the adaptability and utility of this versatile alloy in CNC machining processes.
Which Bronze Grade For CNC Machining
The selection of bronze grade for CNC machining depends on the specific requirements of the application, considering factors such as machinability, strength, corrosion resistance, and other properties. Here are some common bronze grades suitable for CNC machining:
1. Aluminum Bronze (Copper-Aluminum Alloys):
- Composition: Typically contains copper with aluminum as the primary alloying element, along with other elements like iron, nickel, and manganese.
- Properties: Offers excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. Exhibits good machinability, making it suitable for various CNC machining applications.
- Applications: Widely used in marine, aerospace, and industrial applications requiring high strength, corrosion resistance, and wear properties.
2. Phosphor Bronze:
- Composition: Contains copper with tin as the primary alloying element and phosphorus in smaller amounts.
- Properties: Exhibits good strength, excellent wear resistance, and self-lubricating properties. It’s known for its high machinability and good corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Commonly used in bushings, bearings, electrical components, and gears due to its wear resistance and machinability.
3. Silicon Bronze:
- Composition: Consists of copper with silicon as the primary alloying element, along with small amounts of other elements like zinc and tin.
- Properties: Offers good strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and weldability. It has moderate machinability compared to other bronze alloys.
- Applications: Used in architectural applications, sculptures, and welding due to its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appearance.
4. Manganese Bronze:
- Composition: Contains copper with manganese as the primary alloying element, along with small amounts of aluminum, iron, and zinc.
- Properties: Provides good strength, wear resistance, and high-load bearing capabilities. It has moderate machinability.
- Applications: Commonly used in heavy-load and high-wear applications such as gears, bushings, and valve components.
5. Tin Bronze:
- Composition: Typically consists of copper with tin as the primary alloying element, sometimes with small amounts of other elements like phosphorus or zinc.
- Properties: Offers good strength, wear resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance. It has moderate machinability.
- Applications: Suitable for applications requiring corrosion resistance and high mechanical strength, including marine components and machine parts.
The choice of bronze grade for CNC machining depends on the specific requirements of the application in terms of strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Understanding the properties and characteristics of each bronze grade is crucial in selecting the most suitable alloy for a particular CNC machining project. It’s advisable to consult with material experts or suppliers to determine the best bronze grade that meets the specific needs of the machining project.
Things To Consider When Machining Bronze
When machining bronze, several crucial factors should be considered to achieve optimal results and prevent issues during the CNC machining process. Here are key considerations:
1. Selection of Bronze Alloy:
Composition Variation: Different bronze alloys possess unique properties. Choose the appropriate alloy based on required characteristics like strength, machinability, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity.
2. Machining Parameters:
- Feeds and Speeds: Experiment with cutting speeds and feed rates to optimize performance. Lower cutting speeds with higher feed rates often work well to reduce heat buildup and improve surface finish.
- Tool Selection: Use sharp tools with proper geometries suited for non-ferrous materials like bronze. Carbide or high-speed steel (HSS) tools are often recommended for machining bronze.
3. Cooling and Lubrication:
- Coolant Compatibility: Some bronze alloys may react adversely to certain coolants. Conduct compatibility testing to ensure the coolant used is suitable and aids in dissipating heat without affecting the material.
- Lubrication: Employ suitable lubrication to reduce friction and heat generation, improving tool life and surface finish.
4. Chip Control:
Chip Formation: Bronze often produces long, stringy chips that can interfere with machining. Implement chip control measures, such as optimized tool paths or chip breakers, to manage chip formation and avoid tool damage.
5. Workholding and Fixturing:
Secure Clamping: Properly secure the bronze workpiece to prevent movement or vibrations during machining. Effective fixturing ensures accuracy and consistency in the final product.
6. Tool Maintenance:
Regular Inspection: Check cutting tools frequently for signs of wear or damage. Blunt or damaged tools can negatively impact surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
7. Quality Control:
Continuous Monitoring: Conduct periodic quality checks during the machining process to ensure dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and material integrity, adhering to specified tolerances and standards.
8. Consideration of Bronze Properties:
Softness and Galling: Bronze is softer than many other metals, and galling or smearing can occur during cutting. Adjust machining techniques to accommodate these characteristics.
9. Toolpath Optimization:
Optimized Toolpaths: Utilize CNC programming to create optimized toolpaths that minimize tool engagement and reduce heat generation while achieving required precision.
Machining bronze requires a nuanced approach considering its unique properties and challenges. By carefully selecting the alloy, optimizing machining parameters, employing proper tooling and fixturing, managing chips, and ensuring quality control, manufacturers can leverage CNC machining to produce high-quality bronze components across various industries. These considerations are crucial for enhancing efficiency, minimizing tool wear, and achieving precise results when working with bronze materials.
Surface Finishes For Machined Bronze Parts
Surface finishes for machined bronze parts can be varied to achieve different aesthetics, functionalities, and performance characteristics. The choice of surface finish depends on the application requirements and desired appearance. Here are several common surface finishes used for machined bronze parts:
1. Smooth Finish:
As-Machined Finish: This finish is achieved directly from the CNC machining process. It provides a smooth surface with visible tool marks. Depending on the tooling and machining parameters, the surface can vary in roughness.
2. Polished Finishes:
- Polished Finish: Achieved by using abrasives or polishing compounds, this finish results in a high-gloss surface. It enhances the aesthetic appeal and removes machining marks, providing a reflective and smooth surface.
- Buffed Finish: Similar to polishing, buffing involves using a softer material, like cloth or felt, with polishing compounds to achieve a high shine. It can remove minor imperfections and create a lustrous surface.
3. Textured Finishes:
- Brushed Finish: Created by brushing the surface with abrasive materials, a brushed finish results in fine parallel lines or a satin-like texture. It’s often used for decorative purposes and to mask scratches or imperfections.
- Sandblasted Finish: Achieved by propelling abrasive particles at the surface under high pressure, sandblasting creates a textured surface. It provides a matte appearance and is useful for creating a non-reflective finish or for enhancing adhesion in certain applications.
4. Coated or Treated Finishes:
- Anodized Finish: While primarily used for aluminum, anodizing can also be applied to certain bronze alloys. It creates a durable, corrosion-resistant, and sometimes colored surface layer through an electrochemical process.
- Chemical Patina: Chemical treatments can be applied to bronze to induce patina, which forms a protective layer on the surface. This process can produce various colors and textures, offering both aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
5. Functional Finishes:
Lubricious Finish: A finish that incorporates lubricating agents or coatings to reduce friction and wear in moving parts, particularly useful for bearings or components requiring low friction.
The selection of a specific surface finish for machined bronze parts depends on the intended application, functional requirements, aesthetic preferences, and the properties of the bronze alloy used.
Experimentation and testing may be necessary to achieve the desired surface finish while ensuring that the final part meets the required specifications and performance standards. Consulting with surface finishing specialists or experienced machinists can provide valuable insights into selecting the most appropriate finish for a particular machined bronze component.
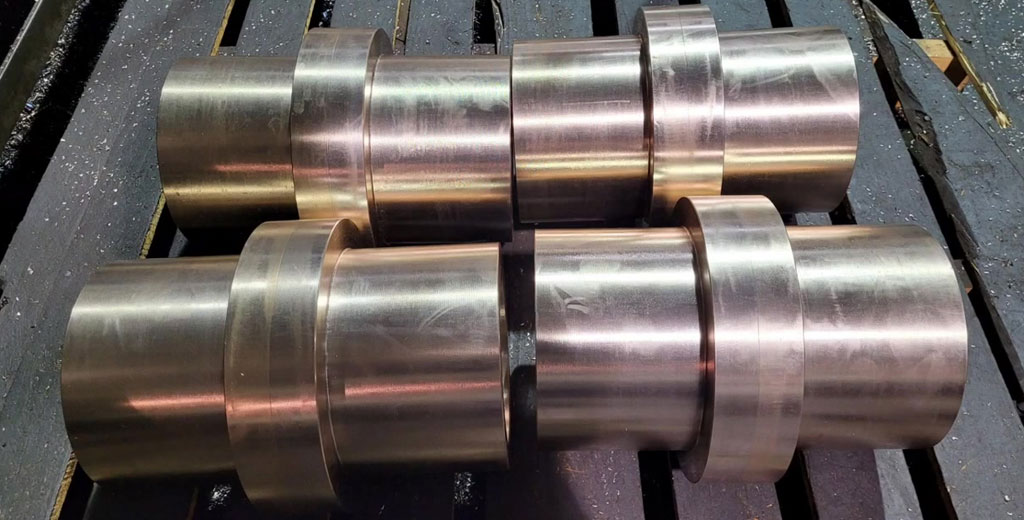

Online Cooperate with China Top Bronze CNC Machining Company
Be-Cu.com is a respected provider of bronze/beryllium copper machining service and parts and is highly experienced in the production of bronze parts and prototypes. Get a free quote now.
-
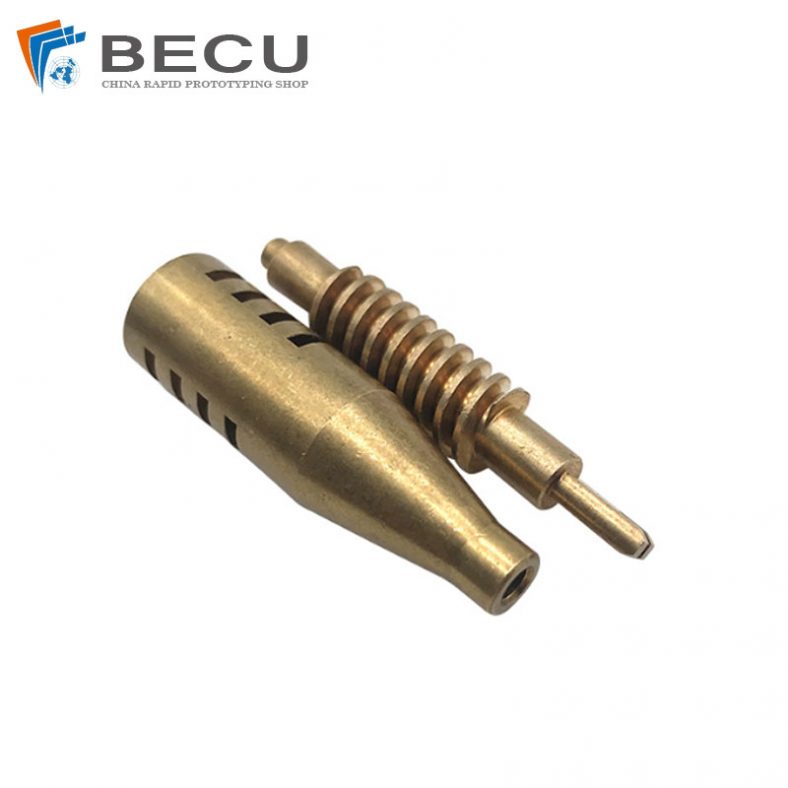

CNC Turning-Milling Machining Copper Facial Massage Roller
-
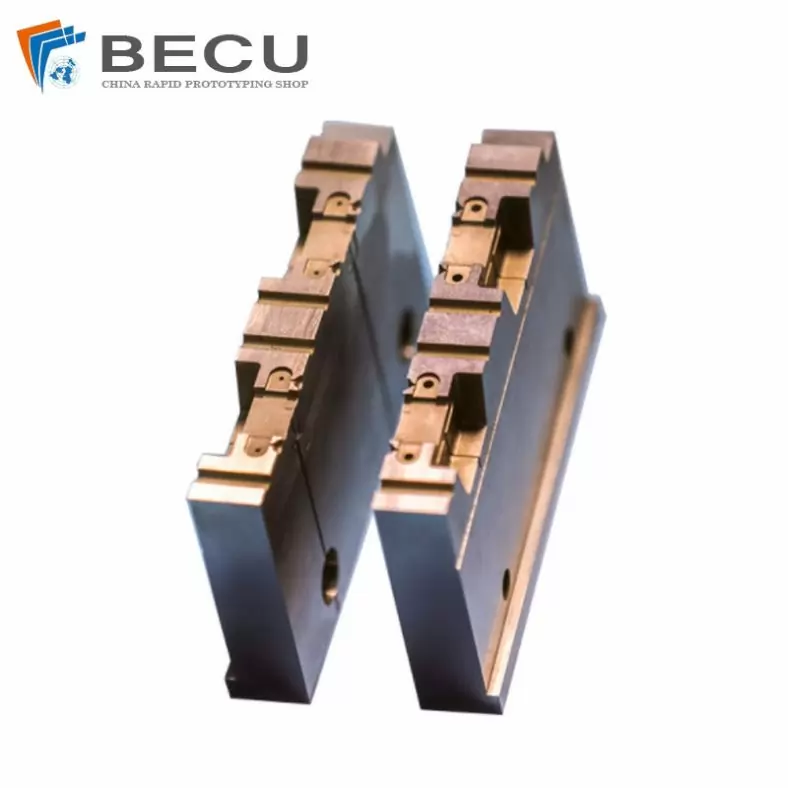

Precision Wire Cutting Plastic Injection Mould Core
-
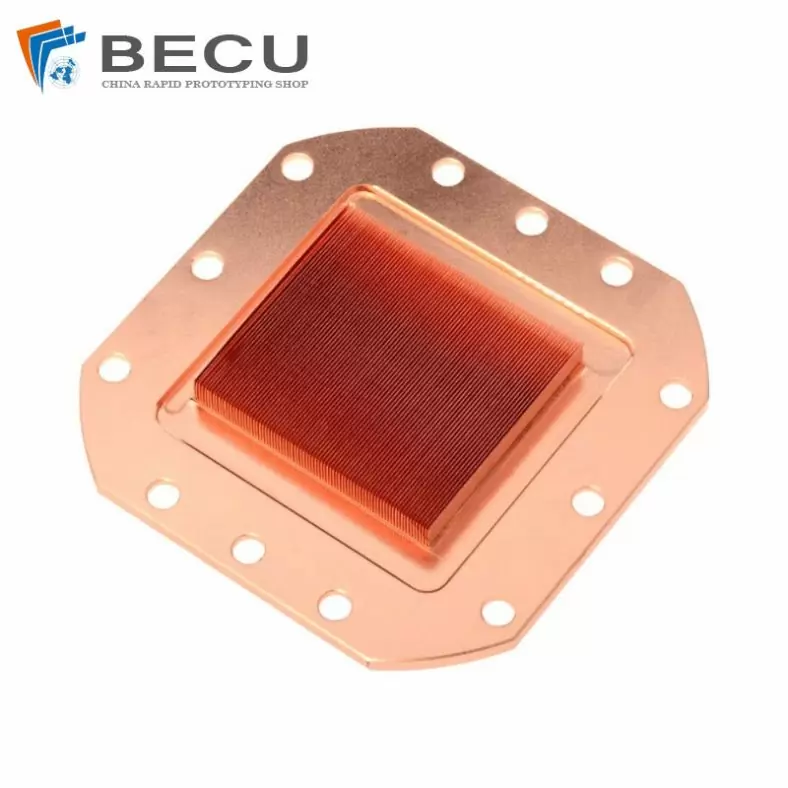
Custom Machining Copper Water Cooling Heat Sink
-
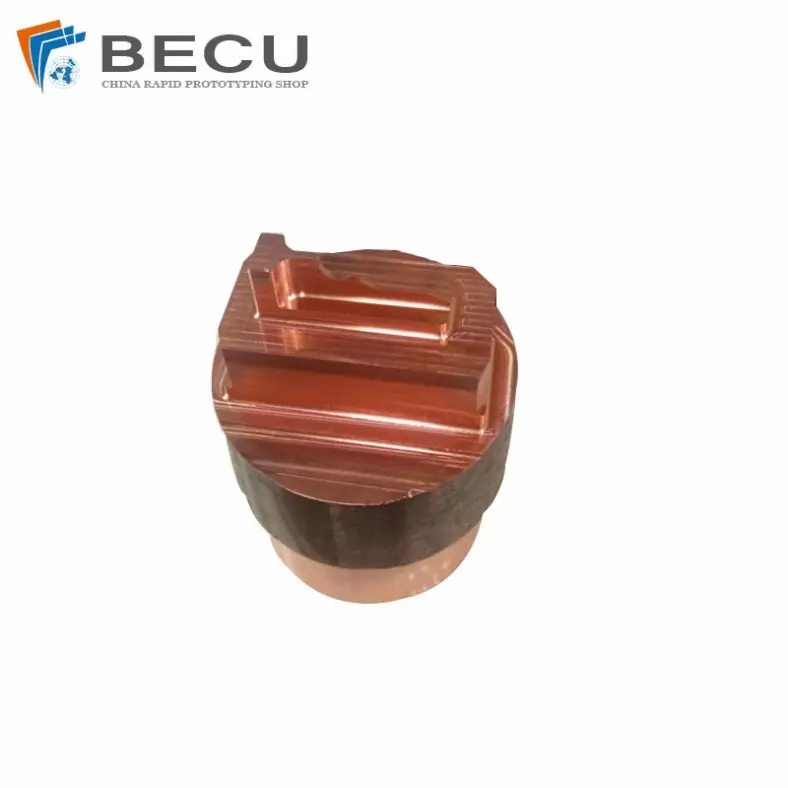

Cnc Carved Machining And Wire Cutting Copper Electrode
-
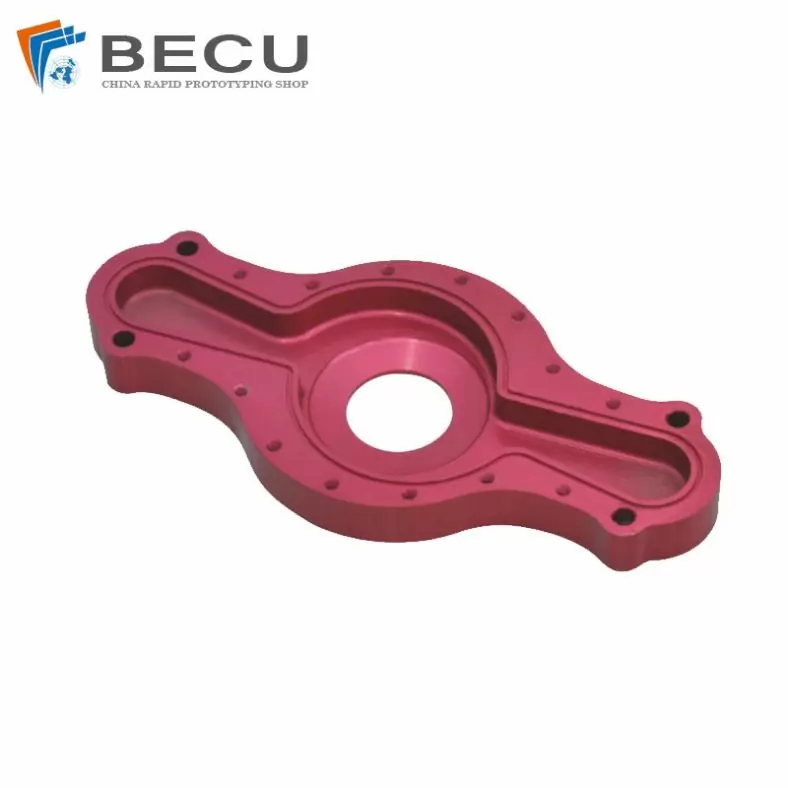

CNC Milling Automotive Audio Amplifier Base
-
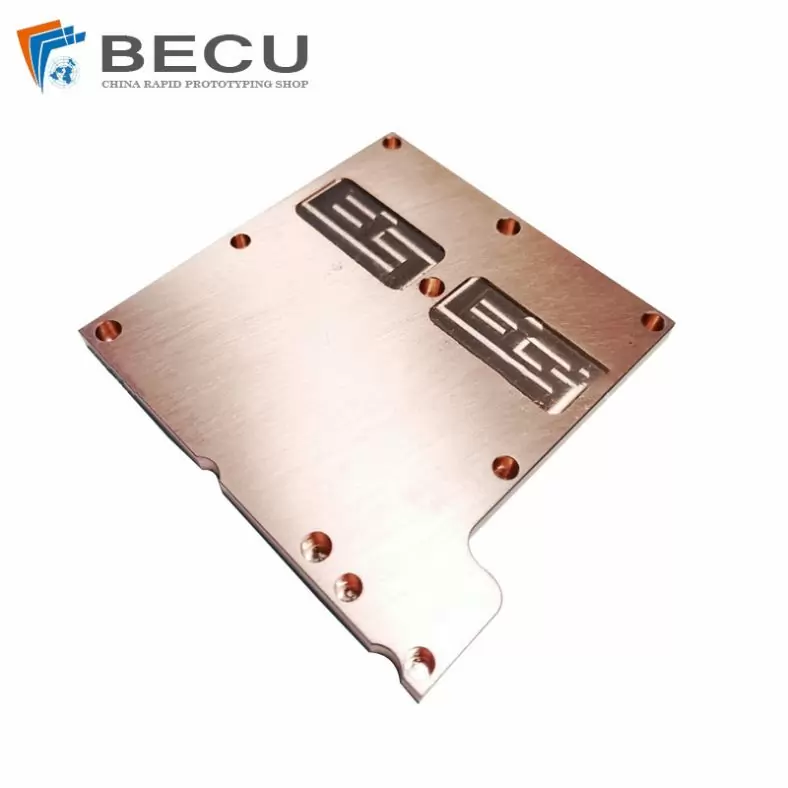

Precision Machining Heatsink Spacer Substrate
-
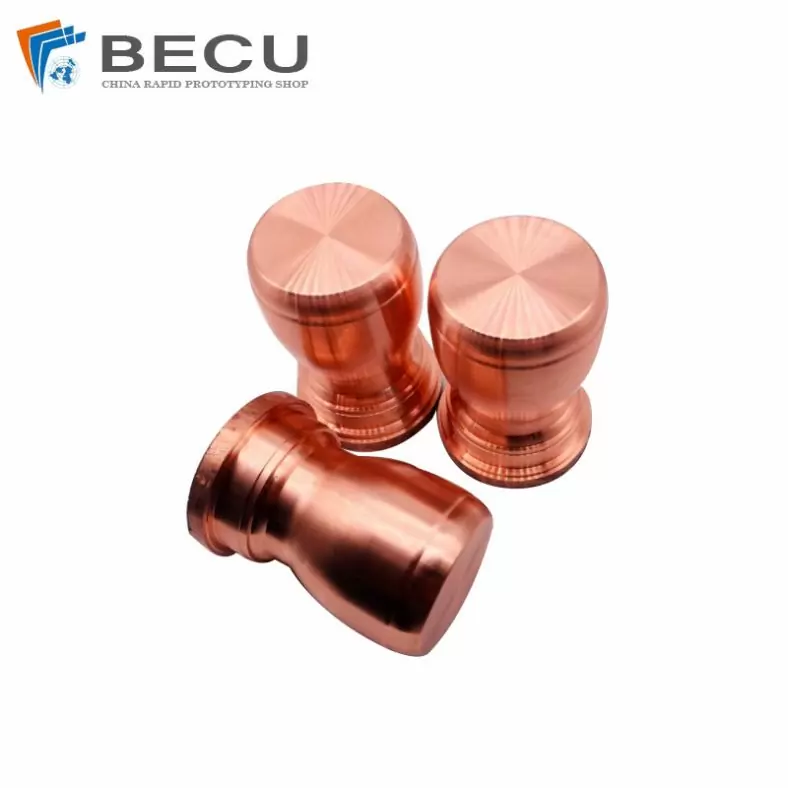

Precision Turning T3 Copper Machinery Parts By Polishing
-
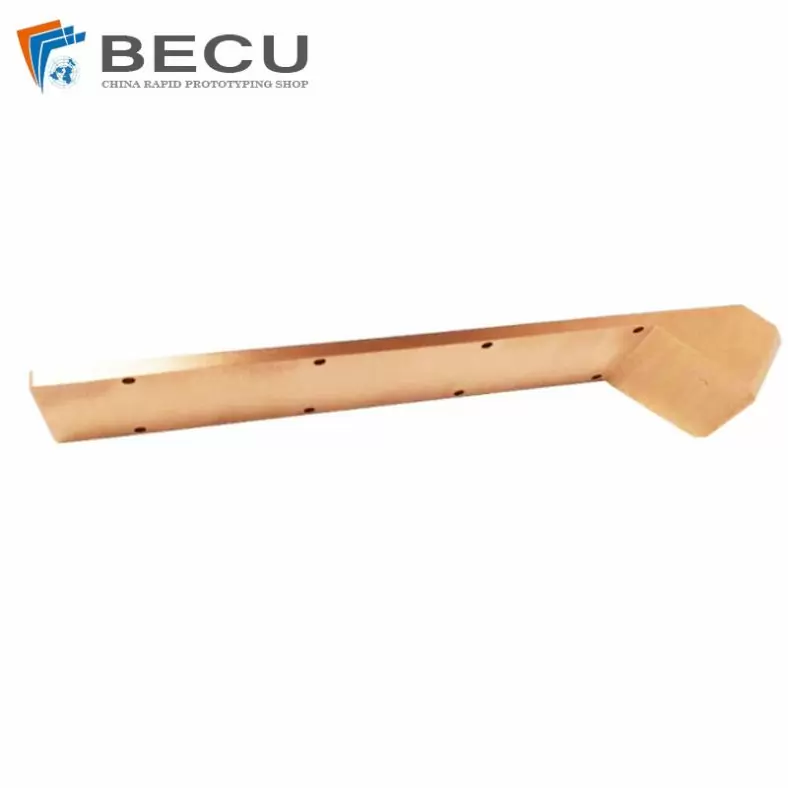

Precision Milling Machining Chrome-Plated Copper Spare Parts
