In the world of modern engineering, the choice of materials plays a pivotal role in shaping the performance and characteristics of various products. Among the multitude of materials available, carbon fiber and aluminum alloy stand out as two of the most versatile and commonly employed options. Each material possesses its unique strengths and weaknesses, making them ideal choices for specific applications. In this comprehensive comparison, we will delve into the properties, manufacturing processes, applications, and environmental impacts of carbon fiber and aluminum alloy to understand their performance in various contexts.
View More New Articles:

Properties of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a composite material renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity. It is composed of thin, strong crystalline filaments made primarily from carbon atoms.
These fibers are combined with a polymer matrix, typically epoxy resin, to create a composite material that inherits the strengths of both components.
- Strength and Stiffness: Carbon fiber exhibits remarkable tensile strength, making it stronger than steel while being significantly lighter. Its stiffness is also noteworthy, providing superior resistance to deformation under load.
- Weight: One of the most remarkable aspects of carbon fiber is its low density. This characteristic contributes to the material’s lightweight nature, making it an ideal choice for applications where weight reduction is critical.
- Corrosion Resistance: Carbon fiber is highly resistant to corrosion, a quality that sets it apart from metals like aluminum. This feature makes it suitable for use in harsh environments and industries where exposure to corrosive elements is common.
- Electrical Conductivity: Carbon fiber is an electrical insulator, which can be an advantage in applications where electrical interference or conductivity needs to be minimized.
Properties of Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are a family of materials composed primarily of aluminum, with various alloying elements added to enhance specific properties. Aluminum alloys are renowned for their versatility, making them a staple in industries ranging from aerospace to construction.
- Strength: Aluminum alloys offer good strength-to-weight ratios, although not as impressive as carbon fiber’s. These alloys can be tailored to exhibit various levels of strength based on the alloying elements used and the manufacturing process.
- Ductility and Formability: Aluminum alloys are highly ductile and can be easily formed into intricate shapes. This property makes them suitable for applications that require complex geometries.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum alloys possess excellent thermal conductivity, making them invaluable in heat transfer applications such as heat sinks for electronic devices.
- Corrosion Resistance: While aluminum does corrode, the formation of a protective oxide layer on its surface provides a degree of corrosion resistance. However, in corrosive environments, additional protective coatings or treatments may be necessary.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes for carbon fiber and aluminum alloy differ significantly due to their distinct properties and structures.
- Carbon Fiber: The production of carbon fiber involves several intricate steps. It starts with the precursor material, usually polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber, which undergoes oxidation, carbonization, and graphitization processes. These stages transform the precursor into a high-strength carbon fiber material. The carbon fibers are then combined with a polymer matrix in a process called “layup,” followed by curing to create the final composite.
- Aluminum Alloy: Aluminum alloys are typically produced through casting or extrusion processes. In casting, molten alloy is poured into molds to create desired shapes, which are then cooled and solidified. Extrusion involves forcing heated aluminum through a shaped die to create profiles with consistent cross-sections. Further processes like machining, rolling, and forging can refine the material’s properties and shape.
Applications
The choice between carbon fiber and aluminum alloy hinges on the specific requirements of the application.
- Carbon Fiber Applications: Carbon fiber’s exceptional strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for industries where weight reduction is paramount. It is commonly used in aerospace for aircraft components like wings, fuselage sections, and structural elements. Additionally, it finds applications in high-performance sports equipment, automotive parts, wind turbine blades, and even medical devices.
- Aluminum Alloy Applications: Aluminum alloys’ versatility and relatively lower cost make them suitable for a wide range of applications. In aerospace, aluminum alloys are used for components like aircraft frames and panels. They are also extensively employed in automotive manufacturing, construction of buildings and infrastructure, marine structures, and consumer electronics due to their excellent conductivity.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of materials is a crucial factor in today’s world, as sustainability takes center stage in design and manufacturing decisions.
- Carbon Fiber: The production of carbon fiber involves energy-intensive processes, and the precursor materials often require significant resources. Additionally, the disposal of carbon fiber composites can be challenging, as they are not easily recyclable. Efforts are being made to develop more sustainable precursor materials and recycling methods.
- Aluminum Alloy: Aluminum is highly recyclable, requiring significantly less energy compared to primary production. Recycled aluminum retains most of its original properties, making recycling a key factor in reducing the environmental footprint of aluminum alloys.
Conclusion
In the dynamic realm of material selection, the choice between carbon fiber and aluminum alloy involves a careful consideration of the specific requirements of the application. Carbon fiber excels in applications where maximum strength and minimal weight are essential, often in aerospace and high-performance sports equipment. On the other hand, aluminum alloys offer versatility, cost-effectiveness, and a broad spectrum of applications ranging from aerospace to everyday consumer goods.
As technology and manufacturing processes continue to evolve, the boundaries between these materials’ capabilities might shift, and innovations in sustainability could alleviate some of the environmental concerns associated with their production. Ultimately, the optimal choice between carbon fiber and aluminum alloy hinges on a thorough understanding of the desired properties, performance demands, and long-term environmental impact.
ISO 9001 certified. BE-CU Prototype Offering CNC machining carbon fiber and other manufacturing services for carbon fiber marterial. Various capabilities include notching, labeling, drilling carbon fiber, grinding, laser cutting carbon fiber, finishing, plating, marking, CNC milling carbon fiber and turning carbon fiber.We stock high quality 3k carbon fiber sheet in a variety of thickness, types and finish. Its a great material used in applications where light weight and strength are needed such as drones. Unlike other workshops, we have no min order and are often filling orders with a single part. We also don’t make you pay for the full sheet and you only get charged for what is used. With a large selection of material, you should find everything you need to make your project come to life. We are also able to handle larger production runs and provide a competitive pricing. If we don’t have the material or finish you require, we are more the willing to look at bringing it in for you.
What Is Carbon Fiber?Carbon fiber is made of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) (or pitch, viscose) and other organic fibers by carbonization (removal of most elements except carbon) by pyrolysis method under inert gas at high temperature above 1,000 °C. Inorganic polymer fibers with a carbon content of more than 90%.
-
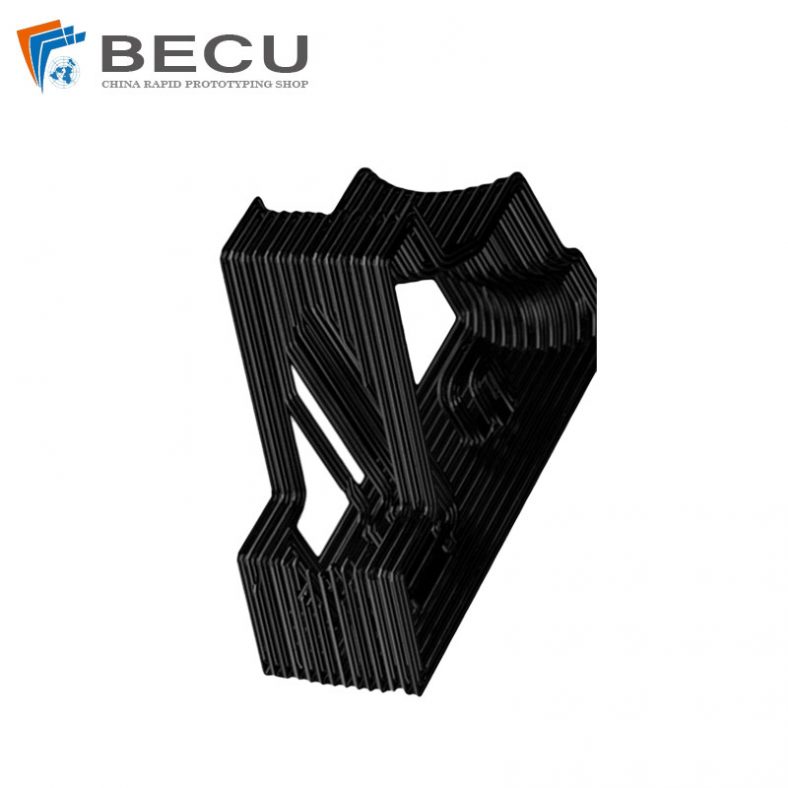

3D Printing Continuous Fibres
-
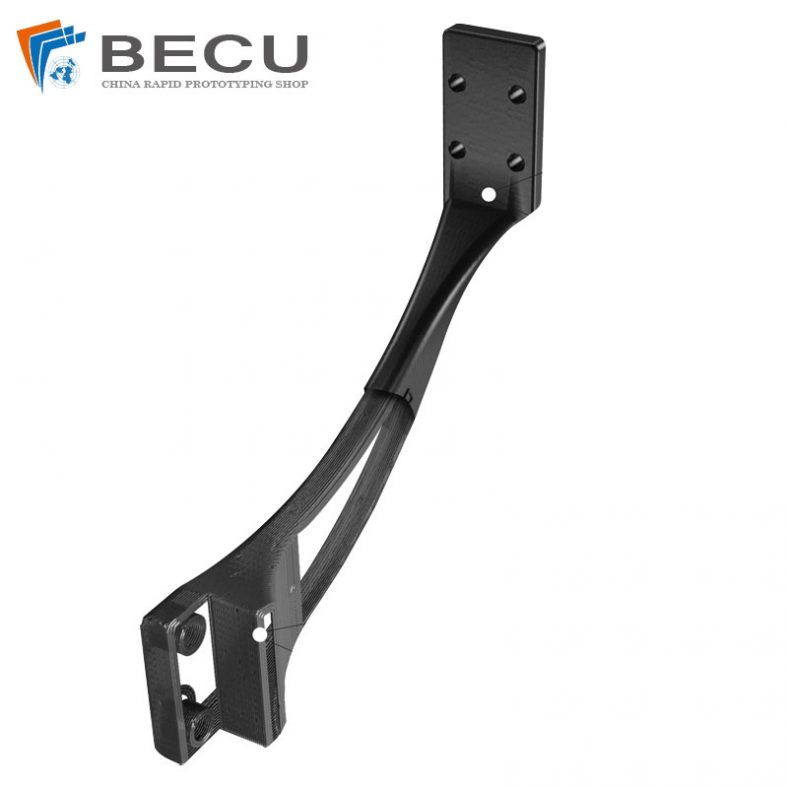

3D Printing Short Fibre Filled Wires
-
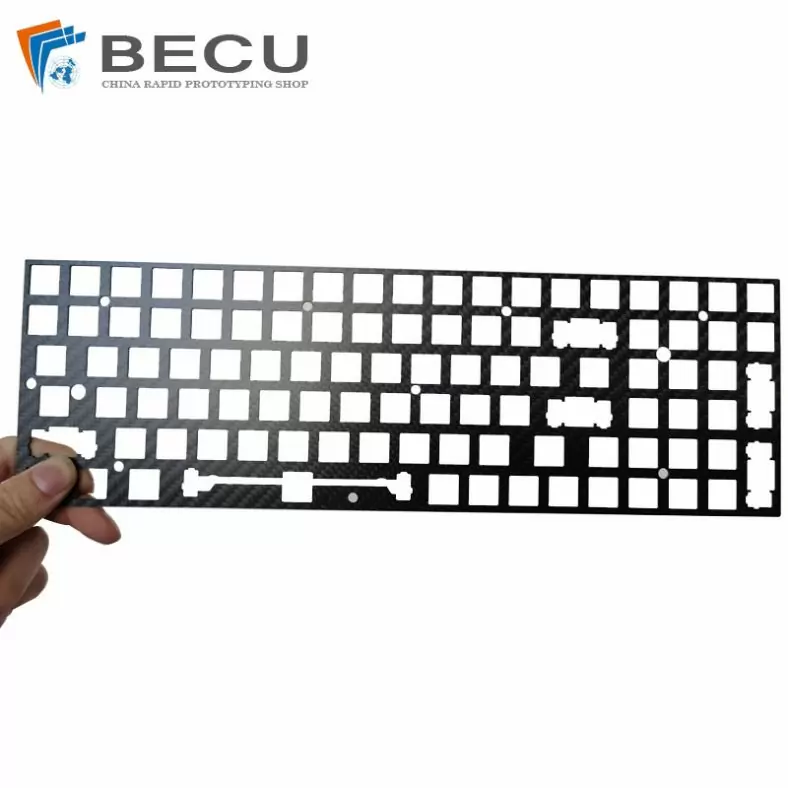

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Positioning Keyboard
-
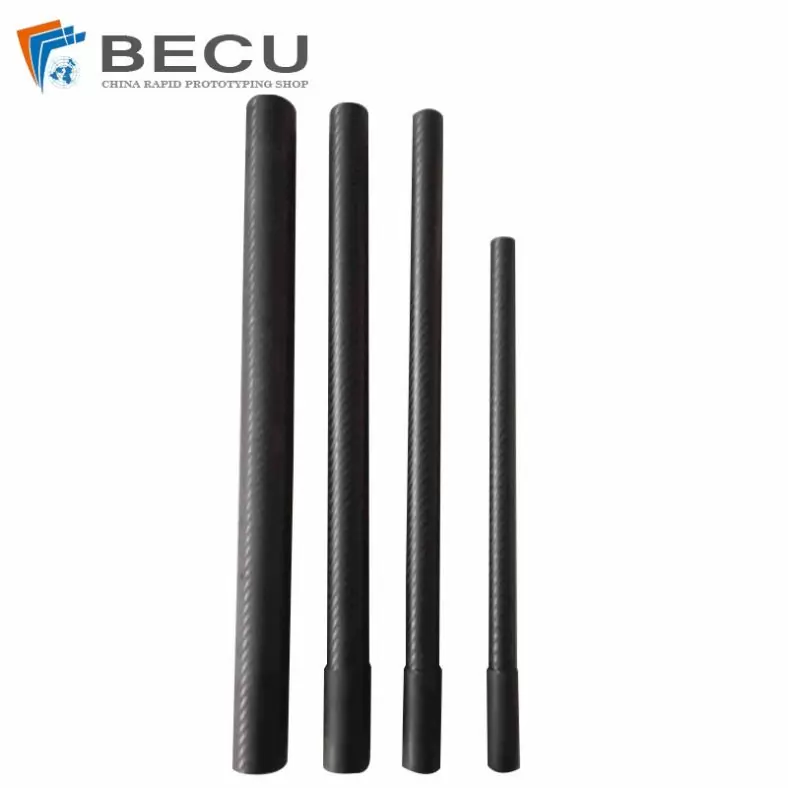

Cnc Turning Industrial Copper-Aluminum Clad Carbon Fiber Machinery Parts
-

Carbon Fiber Luggage Tag Ornaments
-

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Guitar Shape Crafts
-

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Drone Rack
-

Cnc Milling Carbon Fiber Finger Buckle
