Carbon fiber pultrusion is a highly advanced and versatile manufacturing process that plays a pivotal role in the production of lightweight and high-strength composite materials. This article provides an in-depth overview of carbon fiber pultrusion, covering its principles, benefits, applications, challenges, and future prospects. With a focus on the engineering aspects, we delve into the intricate details of the pultrusion process, discussing its steps, materials, equipment, and key factors that influence product quality. Moreover, we explore the wide-ranging applications of carbon fiber pultrusion across industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, sports, and more. The article concludes by highlighting the challenges faced by this technology and the potential avenues for further innovation.

Introduction
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites have revolutionized various industries by offering exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. Among the different methods to manufacture CFRP composites, carbon fiber pultrusion stands out as an efficient and precise process. Pultrusion involves the continuous pulling of reinforcing fibers through a resin bath and a heated die, resulting in a composite material with consistent mechanical properties.
The Pultrusion Process
Carbon fiber pultrusion is a highly controlled manufacturing process that combines fibers and resin to produce composite profiles of varying shapes and sizes. The process typically involves the following steps:
Fiber Preprocessing
The raw carbon fibers are initially treated to enhance their bonding characteristics with the polymer matrix. This may involve sizing, coating, and other surface treatments to optimize adhesion and overall performance.
Resin Impregnation
The treated carbon fibers are drawn through a resin bath, where they are thoroughly impregnated with the polymer matrix material. The resin ensures the fibers are encapsulated and bonded together.
Forming and Shaping
The resin-impregnated fibers are then passed through a forming die, which gives the composite its desired shape. This die is often heated to facilitate curing and proper consolidation of the composite.
Curing
After shaping, the composite material enters a heated die that promotes resin curing. The curing process involves the application of heat and pressure to solidify the polymer matrix, resulting in a strong and durable composite structure.
Pulling and Cutting
As the cured composite exits the die, it is continuously pulled by a set of caterpillar tracks. This pulling mechanism ensures uniform cross-sectional shape and dimensions. Finally, the composite is cut into desired lengths.
Materials and Equipment
Carbon Fibers
Carbon fibers are the backbone of the pultrusion process, providing exceptional strength and stiffness. The choice of carbon fiber type, arrangement, and orientation significantly influences the final composite’s mechanical properties.
Polymer Matrix
The polymer matrix, typically a thermosetting resin like epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester, binds the carbon fibers together and transfers loads between them. The selection of the polymer matrix depends on the specific application’s requirements.
Pultrusion Machine
A pultrusion machine consists of various components, including resin baths, forming dies, heating elements, pulling mechanisms, and cutting devices. These components work together to ensure a continuous and controlled manufacturing process.
Benefits and Advantages
Carbon fiber pultrusion offers several compelling benefits that contribute to its popularity in various industries:
Lightweight and High Strength
CFRP composites produced through pultrusion are exceptionally lightweight while maintaining impressive mechanical strength. This property is particularly advantageous in applications where weight reduction is critical.
Design Flexibility
The pultrusion process allows for the creation of complex profiles and shapes with precise dimensional control. This design flexibility enables engineers to tailor composite structures to specific requirements.
Corrosion Resistance
CFRP composites are inherently corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as marine and chemical industries.
Fatigue Resistance
The excellent fatigue resistance of carbon fiber pultruded composites ensures prolonged durability, even under cyclic loading conditions.
Electric and Thermal Insulation
Carbon fibers are non-conductive and have low thermal conductivity, making pultruded composites suitable for applications where electrical or thermal insulation is necessary.
Applications
Carbon fiber pultrusion finds diverse applications across various industries:
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, pultruded carbon fiber components are used for aircraft interiors, structural elements, and rotor blades in helicopters, offering weight savings without compromising performance.
Automotive
Pultruded carbon fiber profiles are employed in automotive components such as chassis reinforcements, interior panels, and body parts, contributing to enhanced fuel efficiency and crash safety.
Construction
The construction sector benefits from pultruded composite materials in reinforcing concrete structures, creating lightweight yet robust beams, columns, and façade elements.
Sports and Recreation
Sports equipment like tennis rackets, golf shafts, fishing rods, and bicycle frames utilize pultruded carbon fiber composites for their lightweight and high-performance attributes.
Energy and Infrastructure
Carbon fiber pultrusion is utilized in renewable energy applications such as wind turbine blades, as well as in infrastructure projects involving bridges, cable supports, and corrosion-resistant structures.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Cost
Despite its numerous advantages, the high cost associated with carbon fiber pultrusion equipment, materials, and processing remains a challenge, limiting its widespread adoption in certain industries.
Production Rate
The pultrusion process is inherently continuous, which might not be suitable for certain low-volume or customized production requirements.
Recycling
Efforts to recycle pultruded carbon fiber composites are ongoing, as the complex nature of composite materials presents challenges in terms of separation and material degradation.
Material Variability
Maintaining consistent fiber-resin ratios and cross-sectional shapes can be challenging due to variations in fiber alignment and resin impregnation.
Conclusion
Carbon fiber pultrusion stands as a testament to engineering ingenuity, enabling the creation of lightweight, high-strength, and versatile composite materials. From its carefully controlled manufacturing process to its diverse applications, pultruded carbon fiber composites continue to shape industries across the spectrum. As challenges are addressed and innovations continue to emerge, the future of carbon fiber pultrusion holds promise for even greater advancements, pushing the boundaries of lightweight design and performance to new heights.
ISO 9001 certified. BE-CU Prototype Offering CNC machining carbon fiber and other manufacturing services for carbon fiber marterial. Various capabilities include notching, labeling, drilling carbon fiber, grinding, laser cutting carbon fiber, finishing, plating, marking, CNC milling carbon fiber and turning carbon fiber.We stock high quality 3k carbon fiber sheet in a variety of thickness, types and finish. Its a great material used in applications where light weight and strength are needed such as drones. Unlike other workshops, we have no min order and are often filling orders with a single part. We also don’t make you pay for the full sheet and you only get charged for what is used. With a large selection of material, you should find everything you need to make your project come to life. We are also able to handle larger production runs and provide a competitive pricing. If we don’t have the material or finish you require, we are more the willing to look at bringing it in for you.
What Is Carbon Fiber?Carbon fiber is made of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) (or pitch, viscose) and other organic fibers by carbonization (removal of most elements except carbon) by pyrolysis method under inert gas at high temperature above 1,000 °C. Inorganic polymer fibers with a carbon content of more than 90%.
-
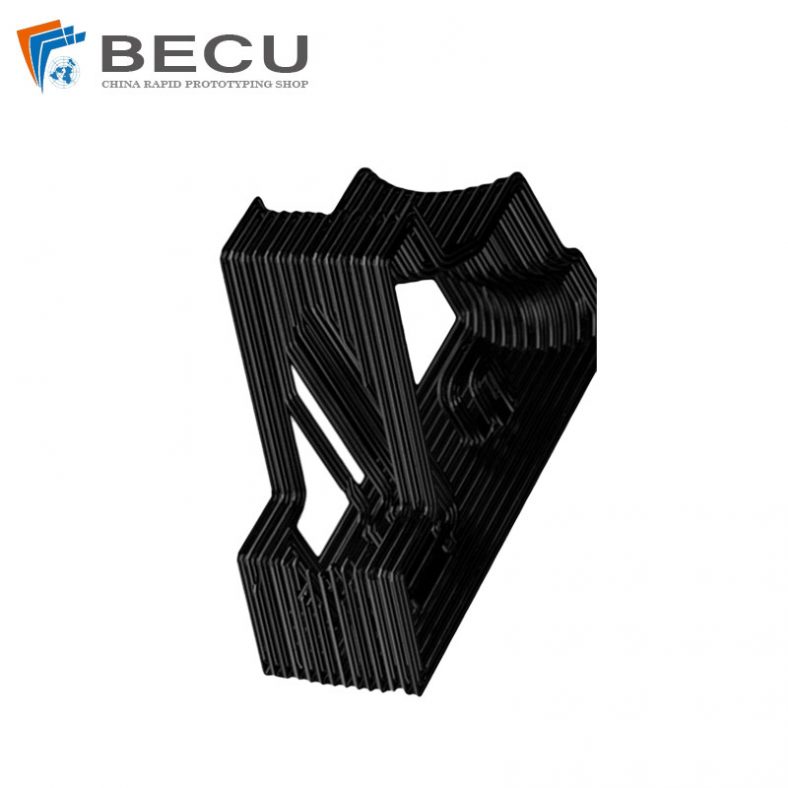

3D Printing Continuous Fibres
-
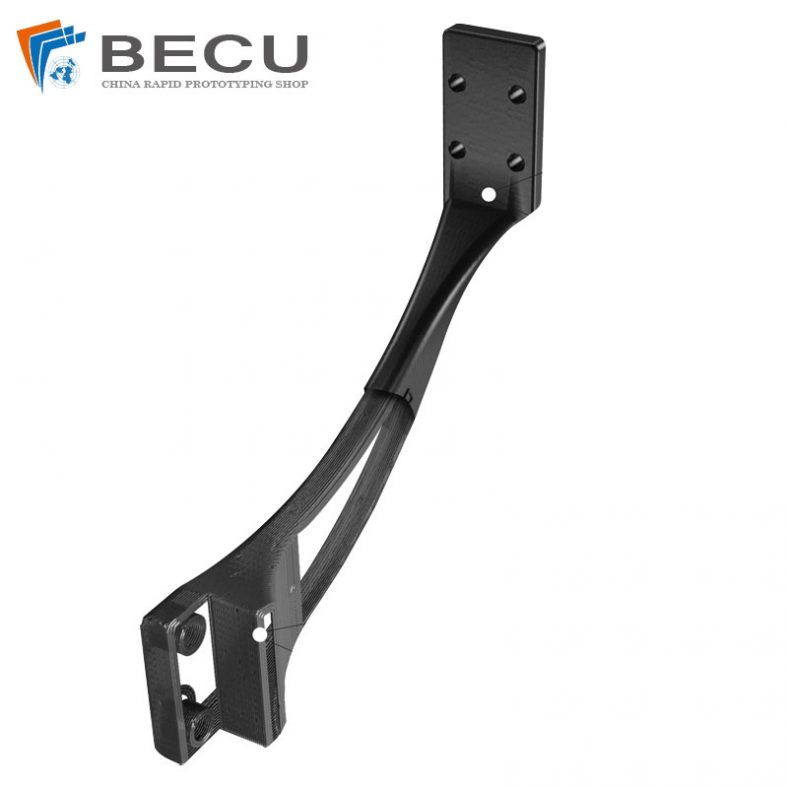

3D Printing Short Fibre Filled Wires
-
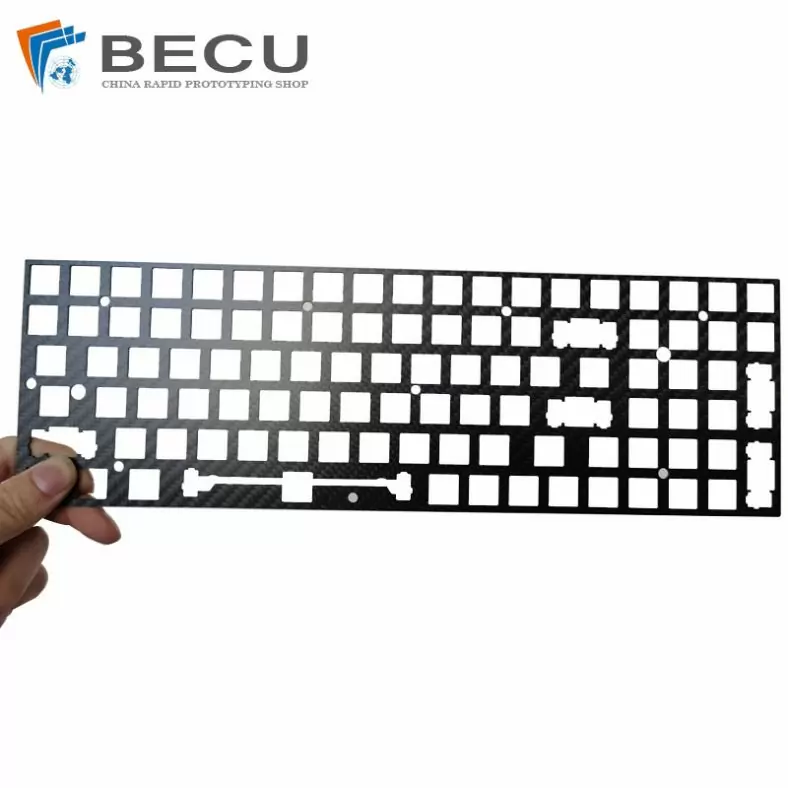

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Positioning Keyboard
-
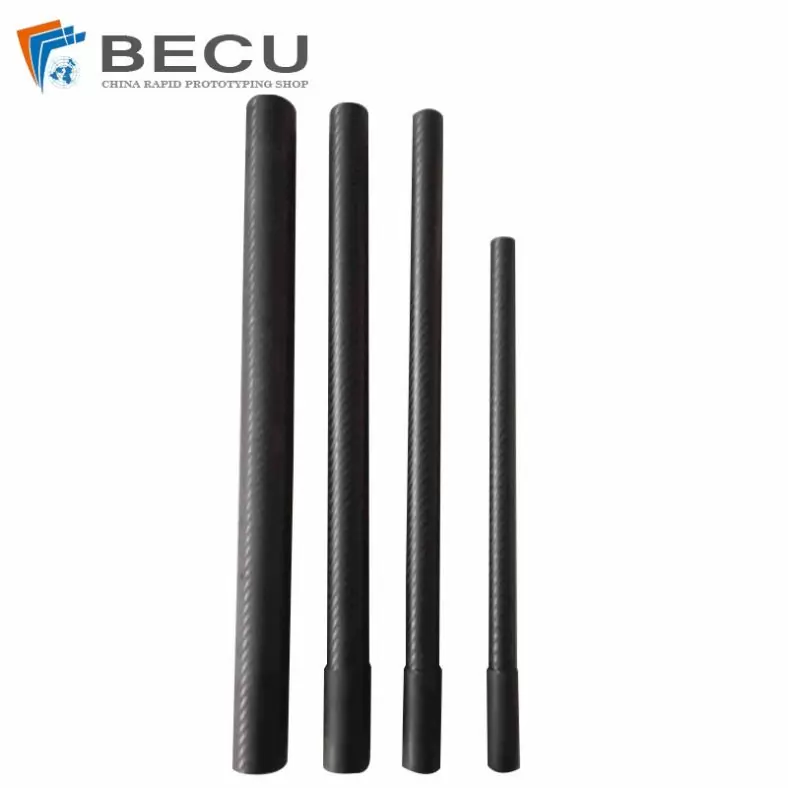

Cnc Turning Industrial Copper-Aluminum Clad Carbon Fiber Machinery Parts
-
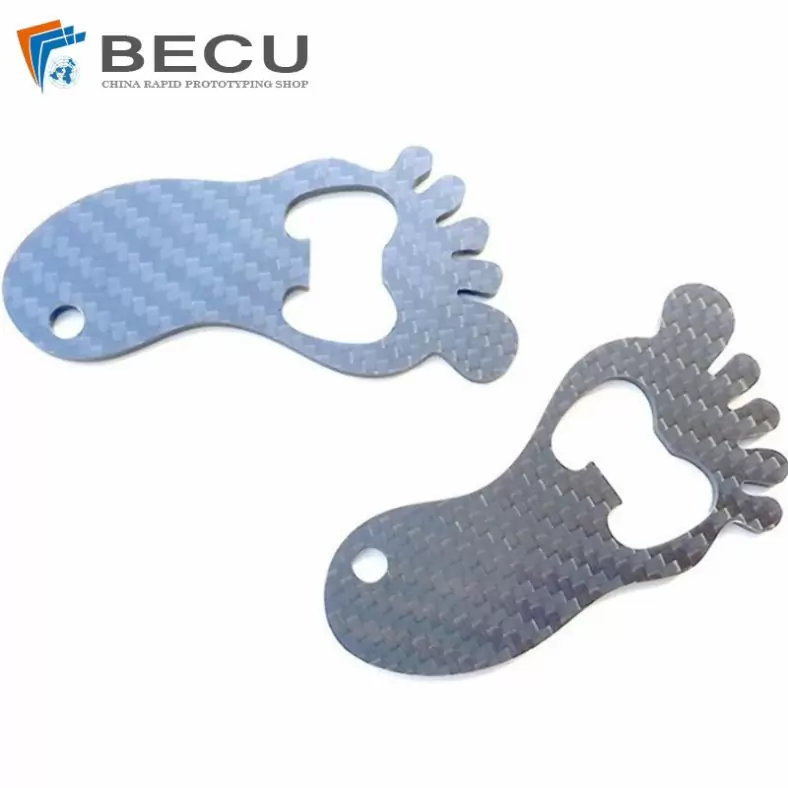

Carbon Fiber Luggage Tag Ornaments
-
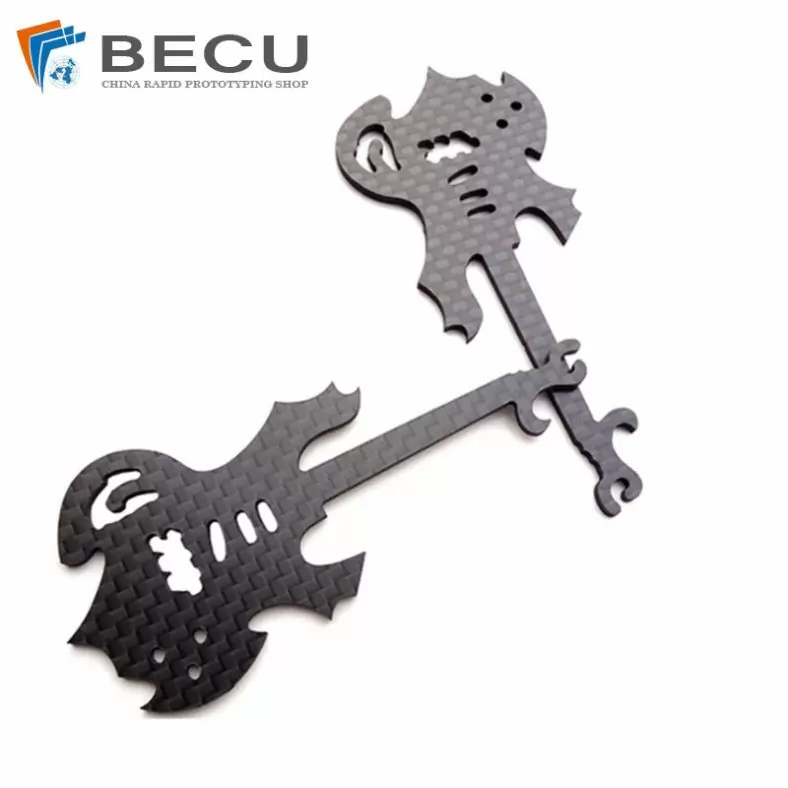

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Guitar Shape Crafts
-
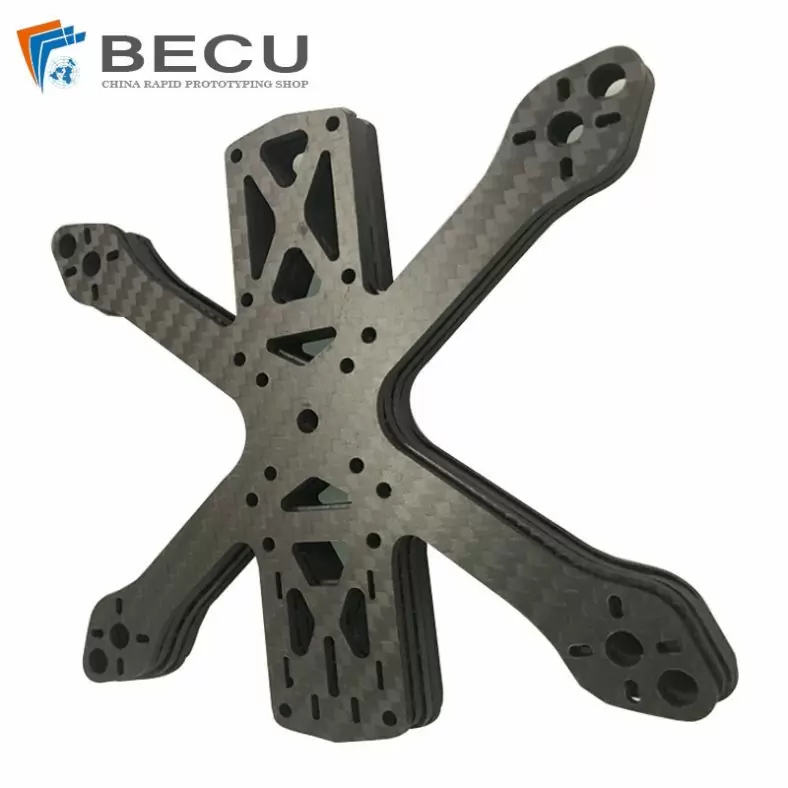

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Drone Rack
-
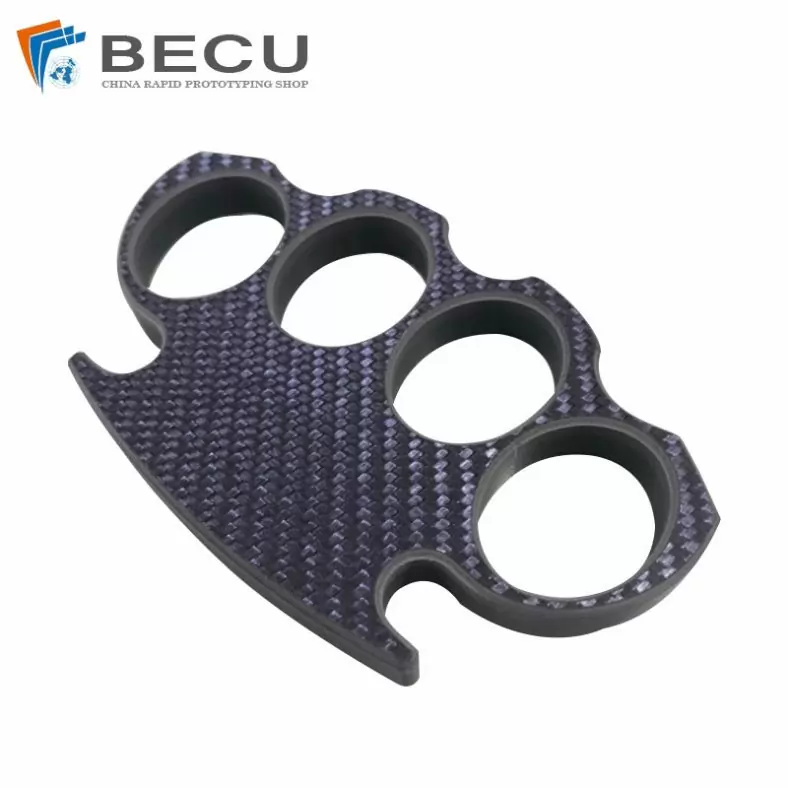

Cnc Milling Carbon Fiber Finger Buckle
