Carbon fiber has revolutionized various industries due to its exceptional strength, lightweight nature, and versatility. It has found applications in fields ranging from aerospace and automotive to sports equipment and construction. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of carbon fiber, exploring its different types and their diverse uses.
View More Posts:

1. Introduction to Carbon Fiber
Definition and Composition
Carbon fiber is a high-strength, lightweight material composed of thin fibers made mostly from carbon atoms. These fibers are tightly bound together by a polymer matrix, usually epoxy, which enhances their overall strength and durability. The resulting composite material offers an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, making it an attractive choice for various applications where weight reduction and high-performance are crucial.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of carbon fiber involves several intricate steps. It typically starts with a precursor material, which is a substance rich in carbon, such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, or pitch. The precursor undergoes processes like oxidation, carbonization, and graphitization, during which volatile elements are removed, leaving behind the carbonized fiber structure. These fibers are then woven together to form sheets or fabrics, which are impregnated with a polymer resin. The resulting composite is cured under heat and pressure to achieve its final strength and rigidity.
2. Types of Carbon Fiber
There are various types of carbon fiber available, each with unique properties suited for specific applications. Let’s explore some of the prominent types:
Standard Modulus Carbon Fiber
Standard modulus carbon fiber, often referred to as “IM” (intermediate modulus), strikes a balance between strength and flexibility. It finds use in applications requiring moderate strength and stiffness, such as sporting goods and industrial equipment.
Intermediate Modulus Carbon Fiber
Intermediate modulus carbon fiber boasts enhanced stiffness compared to the standard modulus variety. This type is commonly used in aerospace and automotive components where increased strength is essential.
High Modulus Carbon Fiber
High modulus carbon fiber offers exceptional stiffness and strength, making it ideal for demanding applications in the aerospace and defense sectors, where structural integrity is of utmost importance.
Ultra-High Modulus Carbon Fiber
Ultra-high modulus carbon fiber takes stiffness to the next level, making it suitable for advanced aerospace and industrial applications. Its impressive rigidity comes with trade-offs in terms of flexibility.
High-Strength High-Strain Carbon Fiber
High-strength high-strain carbon fiber, also known as “toughened” carbon fiber, is engineered to withstand high impact and strain. This type finds use in sports equipment like tennis rackets and bicycle frames.
Pitch-Based Carbon Fiber
Derived from coal tar or petroleum pitch, pitch-based carbon fiber possesses excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It finds applications in high-temperature environments and electromagnetic shielding.
PAN-Based Carbon Fiber
PAN-based carbon fiber is produced from polyacrylonitrile and is the most common type used due to its versatile properties. It is used in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and sports.
Rayon-Based Carbon Fiber
Rayon-based carbon fiber, though less common, offers good heat resistance and mechanical properties. It is used in applications requiring thermal stability, such as rocket nozzles and brake components.
3. Applications of Carbon Fiber
Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace industry extensively relies on carbon fiber for its lightweight yet robust properties. Carbon fiber-reinforced composites are used in aircraft components like wings, fuselage sections, and interior panels. These materials contribute to fuel efficiency and overall performance.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, carbon fiber plays a pivotal role in reducing vehicle weight, thereby enhancing fuel efficiency and handling. High-performance vehicles utilize carbon fiber in body panels, chassis components, and interiors, striking a balance between strength and weight.
Sports and Recreation
Carbon fiber has transformed the sports equipment landscape, enabling the creation of lighter and more durable products. Tennis rackets, golf clubs, bicycle frames, and even helmets benefit from carbon fiber’s strength-to-weight ratio, improving athletes’ performance and safety.
Civil Engineering and Construction
The construction industry leverages carbon fiber’s strength in retrofitting and reinforcing structures like bridges and buildings. Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP) are used to enhance load-bearing capacities and extend the lifespan of existing structures.
Renewable Energy Sector
Wind turbine blades, often subjected to high stresses and harsh environmental conditions, benefit from the durability of carbon fiber composites. The material’s corrosion resistance and high strength make it suitable for large-scale renewable energy applications.
Medical Field
Carbon fiber’s radiolucency (ability to allow X-rays to pass through) makes it valuable in medical imaging and equipment. Carbon fiber-reinforced materials are used in devices like X-ray tables, surgical instruments, and orthopedic implants.
4. Future Trends and Innovations
Carbon Fiber Composites
The ongoing research and development of advanced carbon fiber composites aim to push the boundaries of material performance. By tailoring fiber orientations and resin matrices, engineers can optimize strength, flexibility, and other attributes for specific applications.
Nanotechnology Integration
Integrating nanomaterials with carbon fiber composites introduces new possibilities for enhancing mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. Carbon nanotubes, for instance, can reinforce the fiber matrix, resulting in composites with unprecedented strength and multifunctionality.
Sustainable Production Methods
As environmental concerns grow, the carbon fiber industry is focusing on sustainable production methods. This includes exploring bio-based precursor materials, improving recycling processes, and minimizing energy consumption during manufacturing.
5. Challenges and Considerations
Cost Implications
Carbon fiber’s production involves intricate processes and high material costs, which can limit its adoption in some industries. However, ongoing research is working to develop cost-effective production methods without compromising material quality.
Recycling and Disposal
Carbon fiber’s durability presents challenges in terms of recycling and disposal. Current methods involve breaking down composites into their constituent materials, but a more efficient and widespread recycling infrastructure is needed to manage the increasing volume of carbon fiber waste.
Regulatory and Safety Concerns
Certain applications, such as aviation and medical devices, require rigorous adherence to safety and regulatory standards. Ensuring that carbon fiber materials meet these standards is crucial to maintaining the integrity and reliability of products.
6. Conclusion
Carbon fiber’s unique properties have transformed industries and pushed the boundaries of what is possible in engineering and design. Its diverse types cater to a wide range of applications, from lightweight aircraft components to high-performance sports equipment. As research continues, the future promises even more innovative applications and sustainable production methods, making carbon fiber a cornerstone of modern material science. However, challenges surrounding cost, recycling, and safety must be addressed collaboratively to unlock the full potential of this remarkable material.
Carbon fiber is made of polyacrylonitrile fiber, pitch fiber, viscose fiber pre-oxidized, carbonized, and graphitized at high temperature. It has excellent chemical properties, mechanical properties, and thermal properties. It has strong designability and is often combined with resin matrix. used in composite materials. It has various models and specifications, the specific characteristics of different models, and the fields of use are also different. In this article, the editor will explain to you.
- T300: This is the earliest model, with more than 30 years of production history and more than 20 years of application history, and it is still widely used until now. Its composite material has balanced performance and good quality consistency, and its application fields include sports goods, furniture and building materials, machinery manufacturing, medical equipment, and auto parts. Tow sizes are available in 1k, 3k, 6k and 12k.
- T700S: It is a high-strength standard modulus carbon fiber with excellent processability for filament winding, weaving and pre-impregnation, and is used in a variety of industrial and recreational products requiring high tensile strength, including pressure vessels such as natural gas cylinders, oxygen cylinders ), etc., the tow specifications are 6k, 12k and 24k.
- T700G: Tensile modulus and adhesion properties are better than T700S, and its application range includes aircraft and high-end sports equipment requiring excellent composite performance.
- T800H: High-strength medium-mold carbon fiber, used to meet the weight reduction requirements of aircraft, mainly used in civil aircraft, such as tail drop and horizontal stabilizer, tow specifications are 6k and 12k.
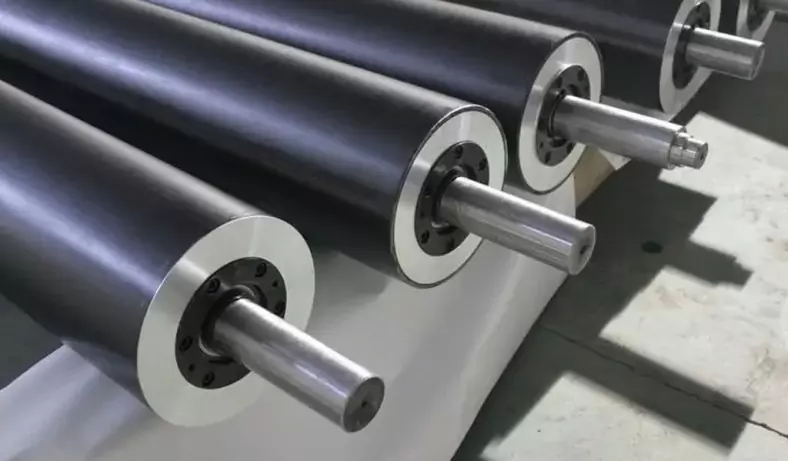
- M40J: Carbon fiber with the highest modulus at present, with particularly good stiffness and thermal expansion coefficient, which can be used in spaceships, advanced sports equipment and industrial rollers.
The carbon fiber material is still being developed, and it is believed that more models will be used in the future. China Be-cu Prototype Material Technology Co., Ltd. selects high-quality carbon fiber and resin, and specializes in machining carbon fiber composite products for customers. It has a leading technical force in the country and has cooperated with many enterprises.Guess you like: There are several models of carbon fiber
ISO 9001 certified. BE-CU Prototype Offering CNC machining carbon fiber and other manufacturing services for carbon fiber marterial. Various capabilities include notching, labeling, drilling carbon fiber, grinding, laser cutting carbon fiber, finishing, plating, marking, CNC milling carbon fiber and turning carbon fiber.We stock high quality 3k carbon fiber sheet in a variety of thickness, types and finish. Its a great material used in applications where light weight and strength are needed such as drones. Unlike other workshops, we have no min order and are often filling orders with a single part. We also don’t make you pay for the full sheet and you only get charged for what is used. With a large selection of material, you should find everything you need to make your project come to life. We are also able to handle larger production runs and provide a competitive pricing. If we don’t have the material or finish you require, we are more the willing to look at bringing it in for you.
What Is Carbon Fiber?Carbon fiber is made of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) (or pitch, viscose) and other organic fibers by carbonization (removal of most elements except carbon) by pyrolysis method under inert gas at high temperature above 1,000 °C. Inorganic polymer fibers with a carbon content of more than 90%.
-
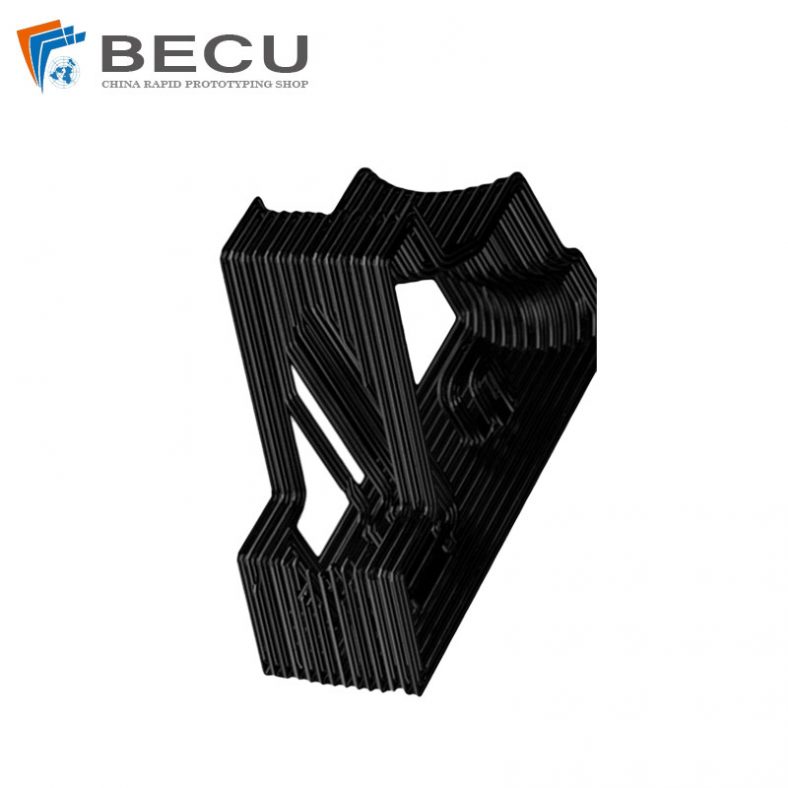

3D Printing Continuous Fibres
-
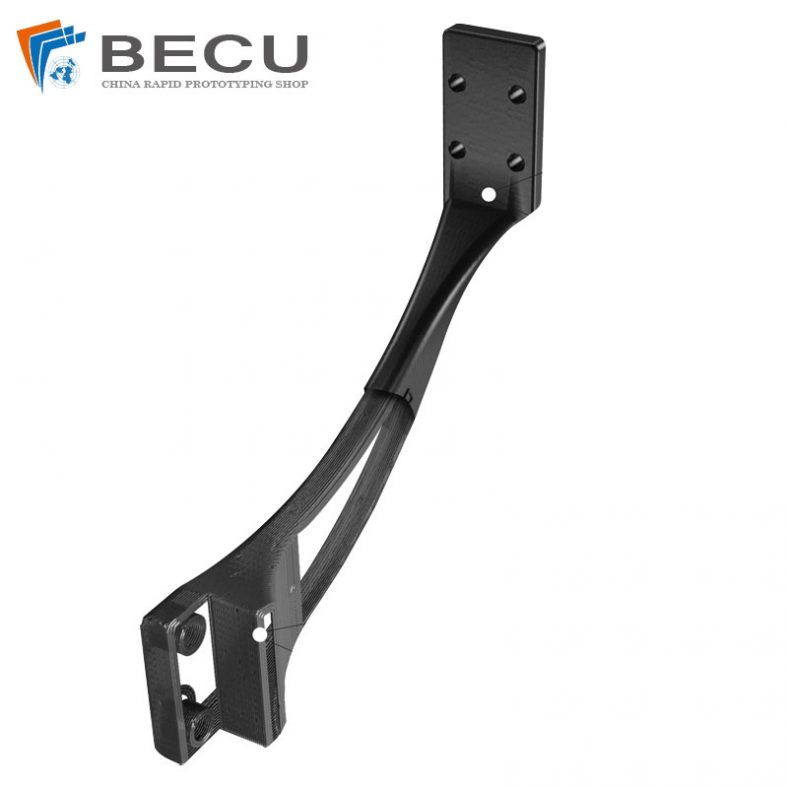

3D Printing Short Fibre Filled Wires
-
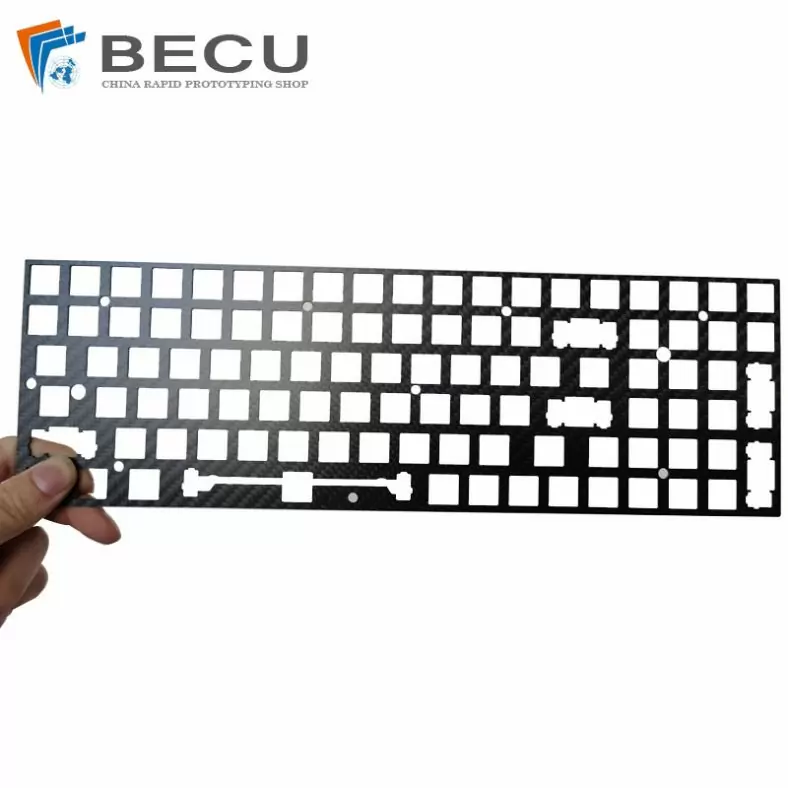

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Positioning Keyboard
-
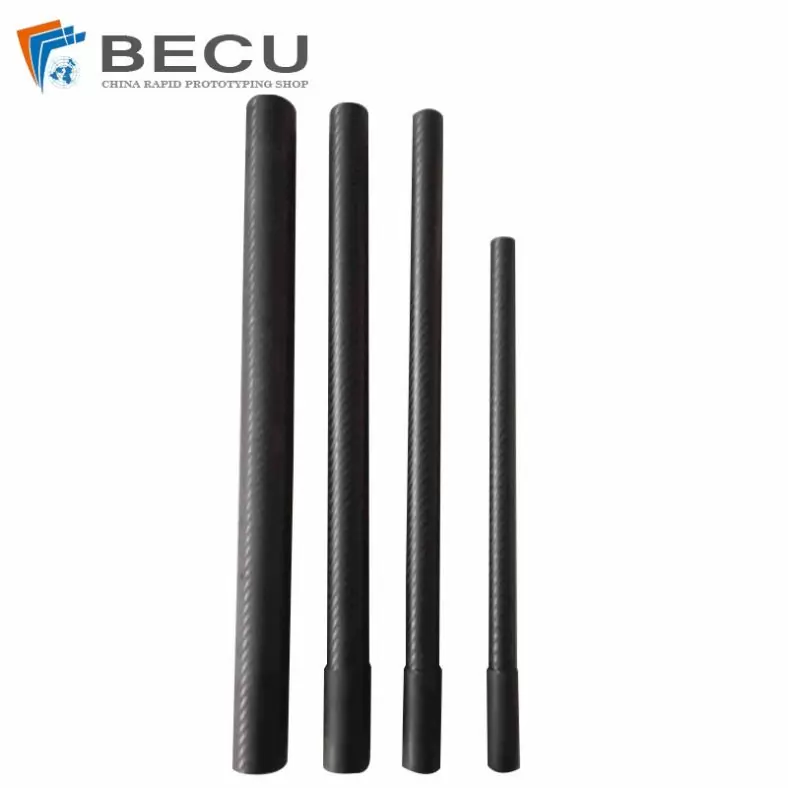

Cnc Turning Industrial Copper-Aluminum Clad Carbon Fiber Machinery Parts
-
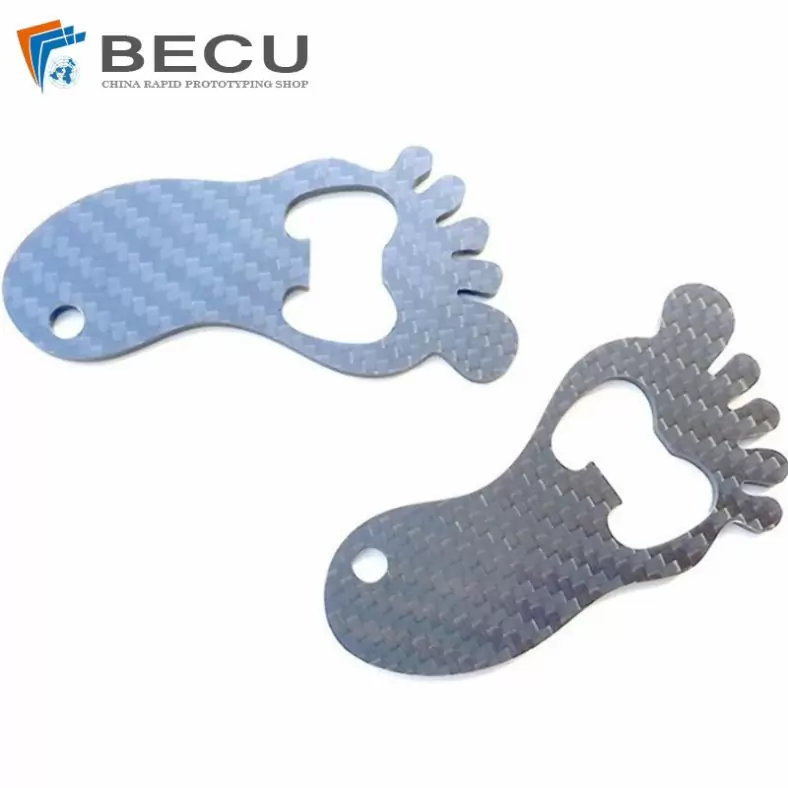

Carbon Fiber Luggage Tag Ornaments
-
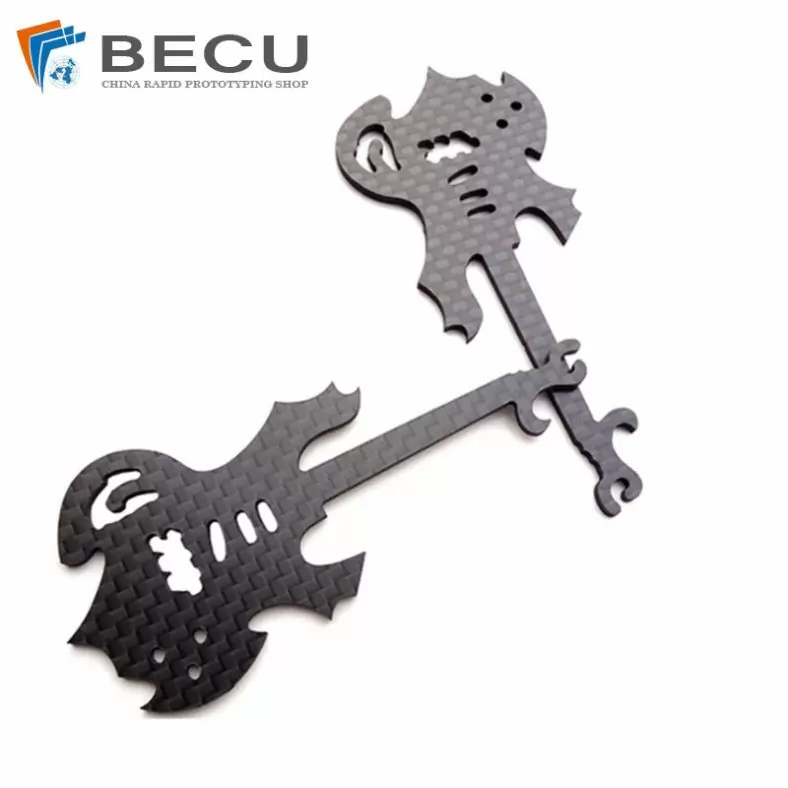

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Guitar Shape Crafts
-
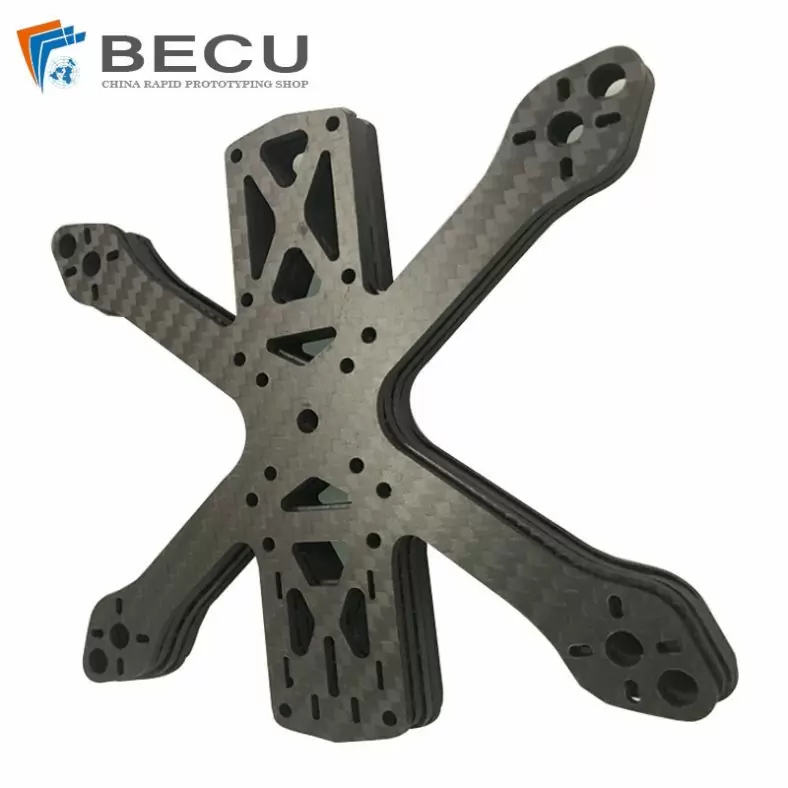

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Drone Rack
-
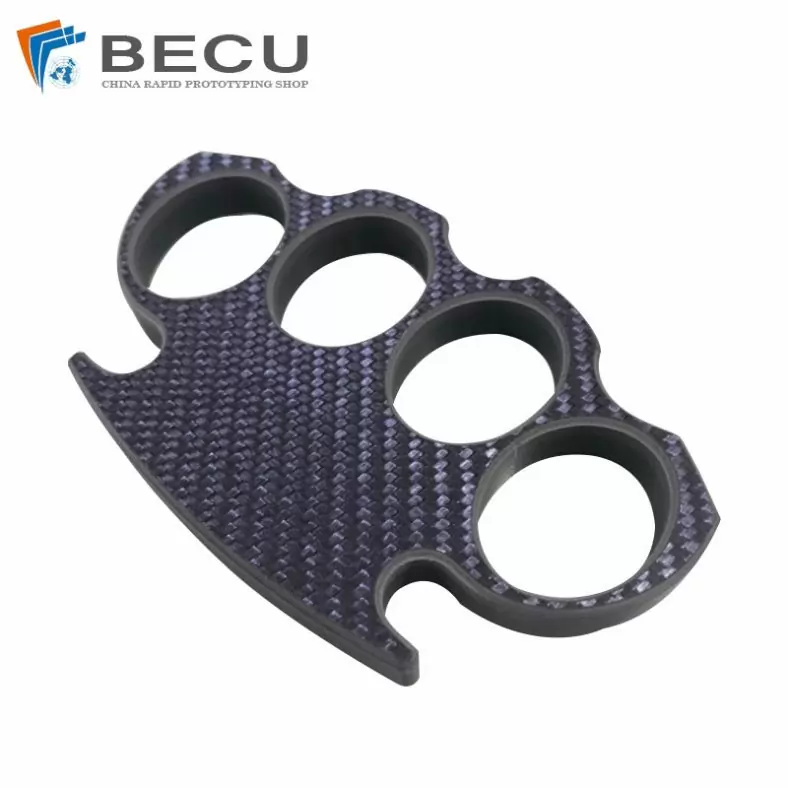

Cnc Milling Carbon Fiber Finger Buckle
