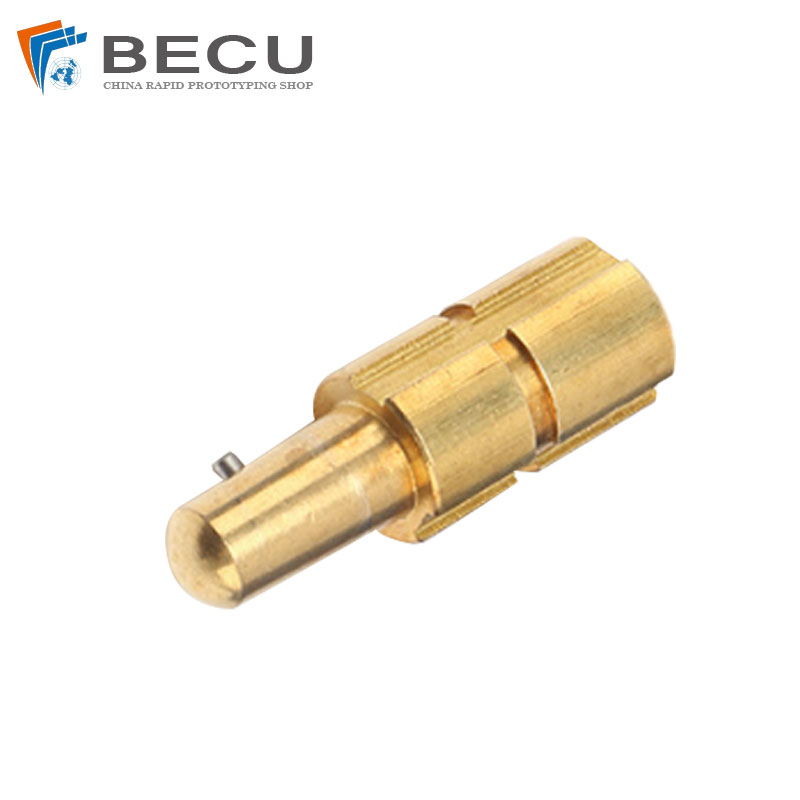
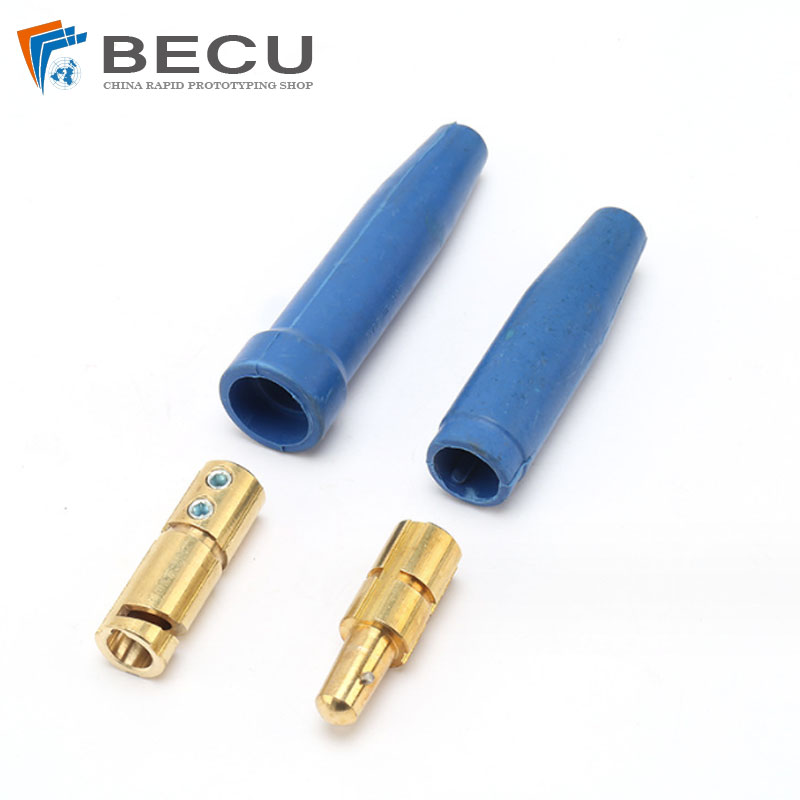
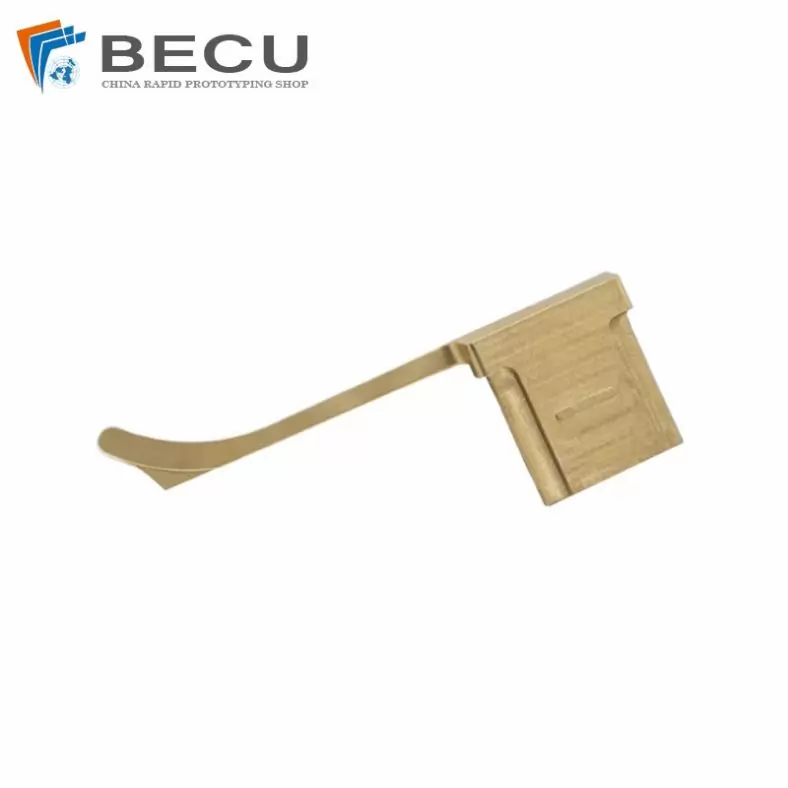
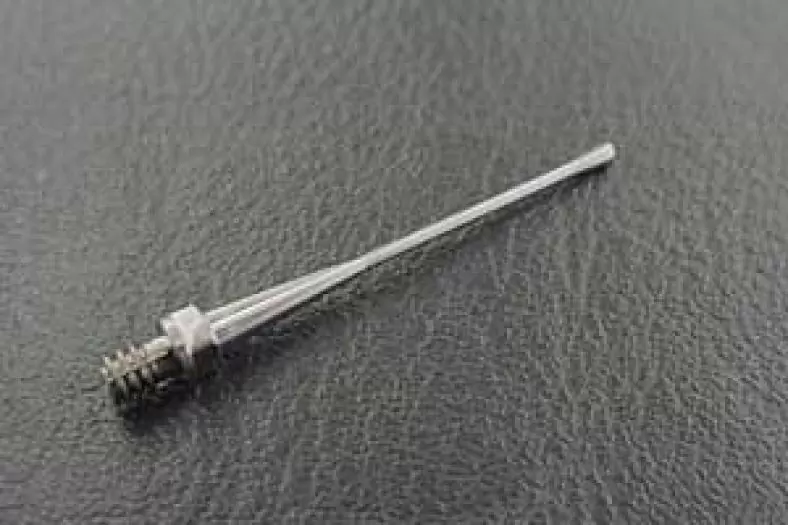
Welding Machine Plug
- No.: Brass 353
- Color: Custom
- Surface Treatment: Oxidation
- Product Material: Brass Alloy
- Proofing Cycle: 7 days(100000 pcs/M)
- Application: Precision Cnc Machining
- machining Factory: Be-cu Rapid Prototyping Companies
- Product Category: Brass CNC Machining
- Production Process: Cnc Turning
- Size: According To Customer’s Drawings
What Is Welding Machine Plug
A welding machine plug is a specialized electrical connector designed for use with welding equipment. Welding machines require a significant amount of power to operate, and as such, they often have specific plug configurations that are different from standard household or industrial plugs. These plugs are designed to handle the high electrical currents and voltages that welding machines typically require.
Welding machine plugs are typically designed to ensure a secure and reliable connection between the welding machine and the power source, while also preventing accidental disconnections that could lead to safety hazards. They are often larger and more robust than regular plugs to accommodate the higher electrical loads involved in welding processes.
There are different types of welding machine plugs and sockets, each with its own specific design and compatibility. Some common types include:
- Twist-Lock Plugs: These plugs require a twisting motion to lock them into the socket, providing a secure connection that is less prone to accidental disconnection. They are commonly used in industrial and heavy-duty applications.
- Dinse Connectors: These are commonly used in TIG and MIG welding machines. They consist of a male and female connector with threaded components that secure them together, ensuring a reliable connection.
- Cam-Lock Connectors: Cam-lock connectors use a cam mechanism to secure the plug into the socket. They are often used in applications where quick and easy connections are required.
- Pin-and-Sleeve Connectors: These connectors use a system of pins and sleeves to create a secure and reliable electrical connection. They are commonly used in industrial settings.
- Terminal Blocks: Some welding machines use terminal blocks for connection, allowing for a customizable and flexible wiring setup.
When working with welding machines, it’s important to ensure that the plug and socket are compatible and that the electrical system can handle the power demands of the welding equipment. Safety precautions are crucial when dealing with high electrical currents and voltages, so proper installation and use of welding machine plugs are essential to prevent accidents and ensure the smooth operation of welding processes.
The Type Of Welding Machine Plug
Welding machine plugs come in various types and configurations, depending on the specific welding process, the power requirements of the machine, and regional standards. Here are some common types of welding machine plugs:
- NEMA Plugs: The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) provides standards for electrical plugs and receptacles in North America. Different NEMA plug configurations are used for different power levels and voltage requirements in welding machines. NEMA 6-50 and NEMA 14-50 are examples of plugs used for higher-powered welding machines.
- Twist-Lock Plugs: Twist-lock plugs and receptacles are designed to prevent accidental disconnection. They are commonly used in industrial settings and are available in various current and voltage ratings.
- Dinse Connectors: These connectors are popular in TIG and MIG welding machines. They consist of male and female connectors that use threaded components to securely connect.
- Cam-Lock Connectors: Cam-lock connectors use a cam mechanism for fast and secure connections. They are often used in applications where quick setup and teardown are important.
- Pin-and-Sleeve Connectors: These connectors are designed for heavy-duty applications and are known for their reliability and robustness. They use a system of pins and sleeves to ensure proper connection.
- CEE Plugs: Commonly used in Europe, the CEE (IEC 60309) plug and socket system comes in various configurations to accommodate different voltage and current requirements.
- Australian Plugs: Australia has its own set of standards for electrical plugs and sockets. Welding machines in Australia use plugs that comply with these standards.
- UK Plugs: The United Kingdom uses its own plug and socket standards, known as BS 1363. Welding machines in the UK would use plugs that conform to these standards.
It’s important to note that the specific plug type and configuration used for welding machines can vary by region and industry. When purchasing a welding machine or setting up welding equipment, it’s crucial to ensure that the plug and socket are compatible with the power supply and adhere to safety standards in your area. Additionally, consulting the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for the welding machine is essential to ensure proper electrical connections and safe operation.
How To Turning Welding Machine Plug
If you need to install or replace a welding machine plug, follow these general steps. Keep in mind that the specific procedure may vary based on the type of plug, the manufacturer’s instructions, and local electrical regulations. It’s always recommended to consult the manufacturer’s manual and, if necessary, seek assistance from a qualified electrician.
Note: Working with electrical connections can be hazardous, so always prioritize safety by disconnecting power sources and following proper procedures.
Tools and Materials You May Need:
- New welding machine plug
- Wire stripper or cutter
- Screwdrivers (flathead and Phillips)
- Wire connectors or crimping tools (if required)
- Electrical tape
- Wire nuts (if required)
- Multimeter (for testing)
Steps:
- Turn Off Power: Before working on any electrical connection, ensure the power source is turned off. If possible, unplug the machine from the power outlet.
- Identify Wiring: Note the existing wiring connections. Identify the hot (live) wire, neutral wire, and ground wire. Different plugs may have different color coding or labeling for these wires.
- Prepare Wires: If necessary, cut the wires to the appropriate length. Strip the ends of the wires to expose the conductive metal. The length of the exposed wire should match the length of the terminal on the plug.
- Prepare the Plug: Open the new welding machine plug and locate the terminals for the hot, neutral, and ground wires. The plug’s manual should indicate which terminal is for each wire.
- Connect Wires: Connect the wires to the appropriate terminals on the plug. This usually involves loosening the terminal screws, inserting the stripped wire ends, and tightening the screws securely. Follow any specific instructions provided by the plug’s manufacturer.
- Secure Wiring: Ensure that the wires are properly secured and that no exposed wires are visible outside the terminals. If needed, use wire connectors, crimping tools, or wire nuts to make secure connections.
- Check Connections: Double-check your connections to ensure that each wire is connected to the correct terminal and that all connections are tight and secure.
- Insulate Wires: Use electrical tape to wrap around the exposed wire ends and terminals to provide insulation and prevent accidental contact.
- Assemble the Plug: Carefully assemble the plug casing, ensuring that all wires are properly routed and not pinched or damaged.
- Test the Connection: Before using the welding machine, perform a continuity test using a multimeter to confirm that the connections are correct and there are no shorts or open circuits.
- Power On: Once you’re confident that the connections are correct and secure, you can plug in the welding machine and turn on the power source.
- Monitor for Issues: Keep an eye on the plug and connections during the initial use. If you notice any unusual heat, sparks, or other issues, immediately disconnect the power source and recheck your connections.
Remember, if you’re uncertain about any step or lack experience in working with electrical connections, it’s advisable to seek help from a qualified electrician to ensure a safe and proper installation.
The Advantages Of Brass Turning Welding Machine Plug
- – Excellent wear and impact resistance
- – Durable and solid, long lifetime
- – Good strength and electrical conductivity
- – Customization based on customer specification
Specifications of Brass Turning Welding Machine Plug
| Material | Brass 353 |
| Tolerance | +/-0.05mm |
| Surface Treatment | Custom |
| Main Process | Cnc Turning,Milling, drilling, 5 axis cnc machining |
| Quality Control | Strictly Quality control in the whole process, from material to packing, Coordinate-measuring machine |
| Usage | Machinery |
| Customized Drawings | Auto CAD, JPEG, PDF, STP, IGS, and most other file formats are accepted |
The Detail Of BE-CU cnc machining Shop
BE-CU.COM – As an accomplished CNC machining Service Manufacturer and CNC shop, BE-CU Prototype has been specialized in OEM CNC lathing, custom CNC machining parts production and rapid CNC machining services China for over 35 years and always maintaining the highest standard in delivery speed and reliable quality of precision CNC manufacturing components. With the help of high-level technology and efficient equipment, as well as rigorous attitude, BE-CU passed the ISO9001:2015 quality certification, which supports the long-term development of CNC milling services, CNC turning services, CNC milling-turning, CNC drilling services, 3/4/5 axis machining, gear machining services, CNC machining China custom parts and service, small parts machining, etc.Our CNC machining products can be utilized in a broad range of industries. Contact us for email: [email protected]