The number of single fibers contained in each bundle of carbon fibers is an important indicator of carbon fibers. Large tow carbon fibers usually refer to fiber bundles with more than 48,000 carbon fibers , including 50,000 , 60,000 , 120,000 , 360,000 , etc., while small tow carbon fibers refer to carbon fiber bundles with a number of fibers less than 48k, such as 1000 , 3000 , 12000 , 24000 , etc. In this article, the editor will talk about the research on the properties of large and small tow carbon fibers.
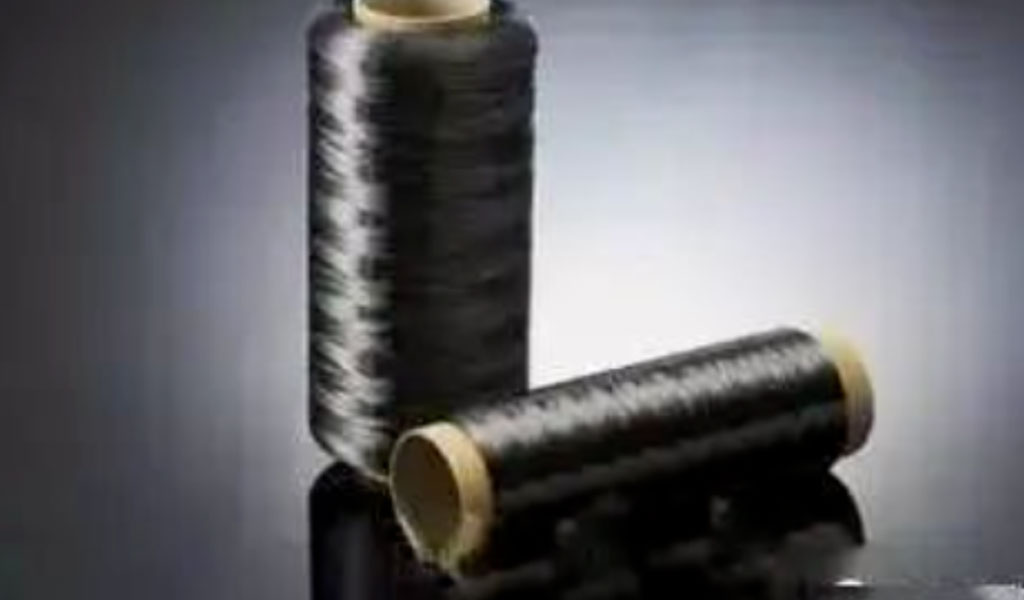

Definition Of Large And Small Carbon Fiber Tows
PAN-based carbon fibers are classified according to the size of fiber tows and can be divided into two categories: small tows and large tows. The specific classification method is based on different K numbers.
Carbon fiber is composed of many parallel filaments, so it is also called carbon fiber tow. The number of tows refers to the number of single filaments in each bundle of carbon fibers. That 1K means that a bundle of carbon fibers contains 1,000 raw filaments. In the same way, 3K represents 3000K roots.
At present, in the carbon fiber industry, the number of carbon fibers per bundle is usually ≥48K, which is called large tow carbon fiber. That is, the number of tows 1k, 3K, 6K, 12K, and 24K is called small tow carbon fiber, and the number of tows exceeding 48K is called large tow or industrial grade carbon fiber.
Differences In The Production Process Of Large And Small Tows
Raw Silk
The key to carbon fiber preparation is carbon fiber precursor. The performance of raw silk directly determines the performance of the prepared carbon fiber. Japan’s Toray and Toho Corporation and the United States’ Hexel Corporation not only do not transfer the technology for preparing small-tow carbon fiber precursors, nor do they sell their products to external parties. However, large-tow carbon fiber raw silk belongs to the category of civilian polyacrylonitrile (that is, acrylic fiber) and can be freely bought and sold in foreign commodity markets without any restrictions. The price of raw filaments for preparing small-tow carbon fibers is four times that of civilian polyacrylonitrile raw filaments.
Process Differences
There are many technical problems in the application of large tow carbon fiber, mainly the yarn spreading process and effect. Compared with small tows, the fibers in large tows accumulate and the yarn spreading effect is not good, which will make it difficult for the yarn pieces to be evenly infiltrated, and the thickness and quality of the yarn pieces will be difficult to meet the product structure design requirements, and it will also easily occur during the yarn spreading process. Yarn wool leads to yarn tangle and yarn breakage, affecting production efficiency, product appearance and final product performance.
The stability of large tow carbon fiber is not as good as that of small tow carbon fiber, and the resin interface shear strength of large tow carbon fiber is lower than that of small tow carbon fiber. Compared with large tow carbon fiber materials, small tow carbon fiber carbonization equipment is better, the production process is strictly controlled, and its performance is generally better than large tow fiber. Since the development of small tow carbon fiber, it has been mostly used in high-end applications such as aerospace, military industry and national defense.
Cost Difference Between Large And Small Tows
In the early days, carbon fiber research was mainly focused on military applications, and it was difficult for large filament bundles to meet the demand (the performance was not satisfactory, and the stability was not as good as that of small filament bundles, etc.), so domestic research focused on small filament bundles at that time. With the development of the industry and the release of huge potential in the civilian market, high-quality, cost-effective large-tow carbon fiber is about to emerge.
Civilian polyacrylonitrile raw filaments are used to prepare large-tow carbon fibers. Usually, the price of raw filaments is about 60% of the cost of preparing carbon fibers. Since the price of large-tow raw filaments is relatively low, the selling price of large-tow carbon fiber can be controlled to about 50%-60% of that of small-tow carbon fiber. The main properties of some large-tow carbon fibers currently on the market are close to or even surpass those of some small-tow carbon fibers. For example, the tensile strength and modulus of the large-tow carbon fiber PAN-EX35 of the American Zoltek Company exceeds the small-tow T300 of the Japanese Toray Company, and the price is relatively low. At present, the tensile strength of large tow carbon fiber can reach 3.5-5.0Gpa, and the tensile modulus is 230-290Gpa. The tensile modulus of T300 and T700 is both 230Gpa, the tensile strength of T300 is 3.4Mpa, and the tensile strength of T700 is around 4.8Gpa.
List Of Large Tow Manufacturers
(1) Foreign Large Tow Manufacturers
- a. American Zoltek acquired by Toray of Japan. Among them, the most representative large-tow carbon fiber product is ZOLTEK PX35, which is a typical low-cost commercial carbon fiber. Application areas: automotive (polyurethane systems for structural and semi-structural applications), wind power beam caps, civil engineering (bridges), high-pressure gas storage bottles, offshore drilling pultruded rods, etc.
- b. European SGL (SGL): There are no 24k specification carbon fiber in the latest products. All are 50K specification large tow carbon fiber, and the mechanical properties have also been optimized. Its areas of application: Carbon fiber-based battery casings for automobiles, door frames for aerospace airliners as well as small aircraft, helicopters and air taxis, as well as in industry.
- c. Mitsubishi of Japan: Mitsubishi of Japan has developed large tow carbon fiber TRW40 (50K) and TRH50 (60K) in 50K and 60K specifications.
(2) Domestic Large Tow Manufacturers
At present, there are few domestic manufacturers that have made breakthroughs in large-tow carbon fiber technology. Typical representatives include Shanghai Petrochemical, Jilin Chemical Fiber, and Lanzhou Blue Star. In addition to the above three companies, Jilin Carbon Valley is currently building a 50K large tow raw silk production line, and Xinjiang Longju’s 48K carbon fiber production line has also been successfully tested. From a technical perspective, Shanghai Petrochemical and Blue Star both use the NaSCN (sodium hydrosulfide) wet process, and Jilin Carbon Valley raw silk technology is similar to SGL.
- a. Shanghai Petrochemical: Successfully trial-produced 48K large tow carbon fiber in 2018. In January 2021, Shanghai Petrochemical’s 12,000 tons/year 48K large tow carbon fiber project officially started construction, with a total investment of 3.5 billion yuan. In August 2022, Shanghai Petrochemical’s first large-tow carbon fiber production line was completed.
- b. Jilin Chemical Fiber: In 2017, it began to research 48K large-tow carbon fiber raw filaments. In 2018, it successfully developed 48K carbon fiber raw filament polymerization and spinning process technology. In 2019, it received the first batch of 120 tons of 48K large-tow carbon fiber raw filament export orders. In August 2022, the high-yield and high-performance 50K large tow carbonization line was put into operation, marking the completion of the 15,000-ton carbon fiber project that took two years to complete. Mainly used for wind power generation blades, etc. At present, Jilin Chemical Fiber’s total carbon fiber production capacity has increased to 35,000 tons.
- c. Lanzhou Blue Star: In 2018, Blue Star Group invested hundreds of millions in technological transformation of the existing raw silk production line, and the products were upgraded from the original 24K to 50K. In the second half of 2019, its 50K carbon fiber production line was fully approved. In 2022, the company plans to invest 370 million yuan to build a new raw silk spinning production line with a capacity of 5,000 tons and a carbon fiber production line with an annual capacity of 2,500 tons. Upon completion, Lanzhou Fiber will have an annual carbon fiber production capacity of 3,500-4,000 tons. The current production capacity of carbon fiber large tows is 1,500 tons and the production capacity of carbon fiber raw filaments is 4,000 tons.
As of 2018, Japanese companies led by Toray, Mitsubishi, and Toho accounted for 49% of the entire small tow market production capacity. In particular, Toray recently announced that it will invest in and increase production lines in its factories in Spartanburg, South Carolina, and its factory in Gumi, South Korea.
It is expected that starting from 2025, Toray will increase its annual production capacity of conventional carbon fiber (small tows) Increased to 35,000 tons, annual production capacity increased by more than 20%. As China’s Zhongfu Shenying’s 25,000-ton-per-year project in Xining is fully operational, the company’s annual production capacity will reach 28,500 tons per year by the end of 2023, ranking second in the world.
Three companies: Hexcel of the United States, SGL of Germany, and Mitsubishi of Japan basically monopolize the entire large-tow carbon fiber market, accounting for 58%, 31%, and 9% respectively.
Due to the influence of the aviation field and the demand for wind power resources in recent years, large-tow carbon fiber materials have been transformed from automotive materials to driving demand for wind power blades, hydrogen storage bottles, etc. The carbon fiber market has transformed into a dual-driven landscape of aerospace and industry.
- The sizing rate of large and small tow carbon fibers was tested. It was found that the sizing rate of domestic carbon fibers was generally higher than that of foreign carbon fibers. For 12K carbon fibers, the sizing rate of domestic carbon fibers was higher than 1%, while the sizing rate of foreign carbon fibers was generally low. For carbon fibers with different tow sizes, the surface sizing rate of 3K carbon fiber is the lowest, the surface sizing rate of 50K carbon fiber is the highest, and the sizing rate of other carbon fibers is similar.
- The single fiber strength test of carbon fiber was carried out. It was found that for 12k carbon fibers produced by different domestic and foreign manufacturers, the shape parameters of foreign carbon fiber single fiber strength were generally higher than those of domestic carbon fiber, indicating that the discreteness of foreign carbon fiber single fiber strength was smaller than that of domestic carbon fiber. Carbon fiber, that is, the stability is higher than that of domestic carbon fiber. The scale parameters of foreign carbon fibers are generally higher than those of domestic carbon fibers, indicating that the strength of foreign carbon fibers is higher than that of domestic carbon fibers. For carbon fibers with different tow sizes, the shape parameters of large tow carbon fibers fluctuate greatly, while the shape parameters of small tow carbon fibers fluctuate very little, indicating that the stability of large tow carbon fibers is not as good as that of small tow carbon fibers.
- The research on the interfacial shear properties of carbon fiber resins found that the interfacial shear properties of carbon fibers produced by the dry-jet wet spinning process were better than those produced by the wet spinning process; the interfacial shear properties of carbon fibers/resins in China were generally lower than Foreign carbon fiber; large tow carbon fiber has a fine resin boundary and the shear strength is lower than that of small tow carbon fiber.
As far as the current market is concerned, the usage of small tow carbon fibers is greater than that of large tow carbon fibers, and the quality of foreign carbon fibers is higher than that of domestic carbon fibers. The Japanese Toray T300 and T700 high-performance carbon fiber raw materials introduced by China Be-cu Prototype Material Technology Co., Ltd. can meet the application and manufacture of high-end parts and components in the fields of rail transit, automobiles, and automobiles.
Through the modification of the R&D team, it has passed UL94V-0, German DIN5510, British Japanese S6853, European Union EN45545 rail vehicle material fire test standards, reaching the advanced flame retardant level in the domestic industry, and related fiber composite materials have been exported to Europe and the United States for a long time.
ISO 9001 certified. BE-CU Prototype Offering CNC machining carbon fiber and other manufacturing services for carbon fiber marterial. Various capabilities include notching, labeling, drilling carbon fiber, grinding, laser cutting carbon fiber, finishing, plating, marking, CNC milling carbon fiber and turning carbon fiber.We stock high quality 3k carbon fiber sheet in a variety of thickness, types and finish. Its a great material used in applications where light weight and strength are needed such as drones. Unlike other workshops, we have no min order and are often filling orders with a single part. We also don’t make you pay for the full sheet and you only get charged for what is used. With a large selection of material, you should find everything you need to make your project come to life. We are also able to handle larger production runs and provide a competitive pricing. If we don’t have the material or finish you require, we are more the willing to look at bringing it in for you.
What Is Carbon Fiber?Carbon fiber is made of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) (or pitch, viscose) and other organic fibers by carbonization (removal of most elements except carbon) by pyrolysis method under inert gas at high temperature above 1,000 °C. Inorganic polymer fibers with a carbon content of more than 90%.
-

3D Printing Continuous Fibres
-

3D Printing Short Fibre Filled Wires
-

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Positioning Keyboard
-

Cnc Turning Industrial Copper-Aluminum Clad Carbon Fiber Machinery Parts
-

Carbon Fiber Luggage Tag Ornaments
-

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Guitar Shape Crafts
-
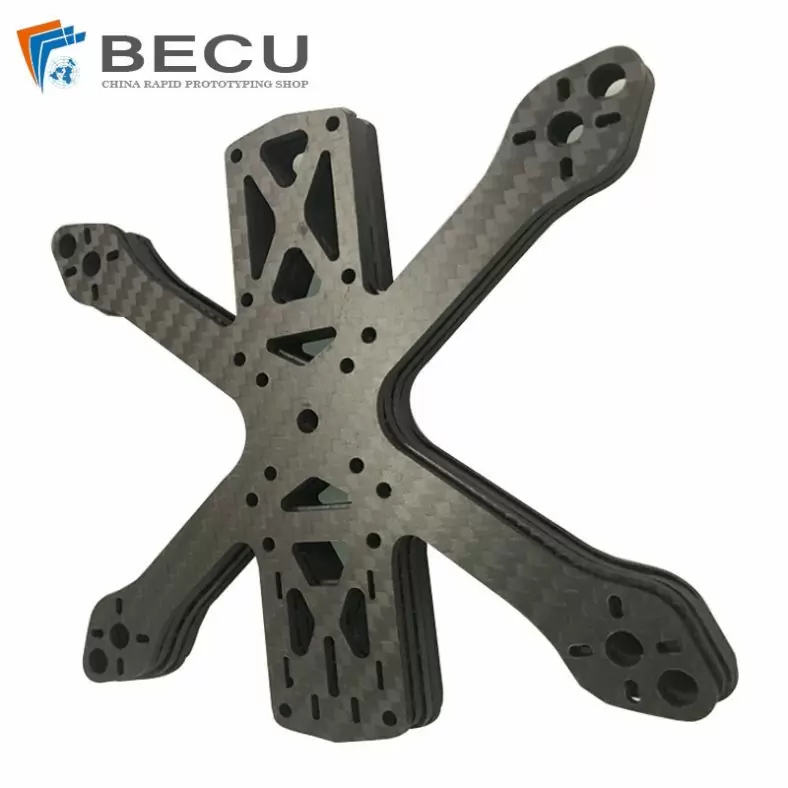

Laser Cutting Carbon Fiber Drone Rack
-
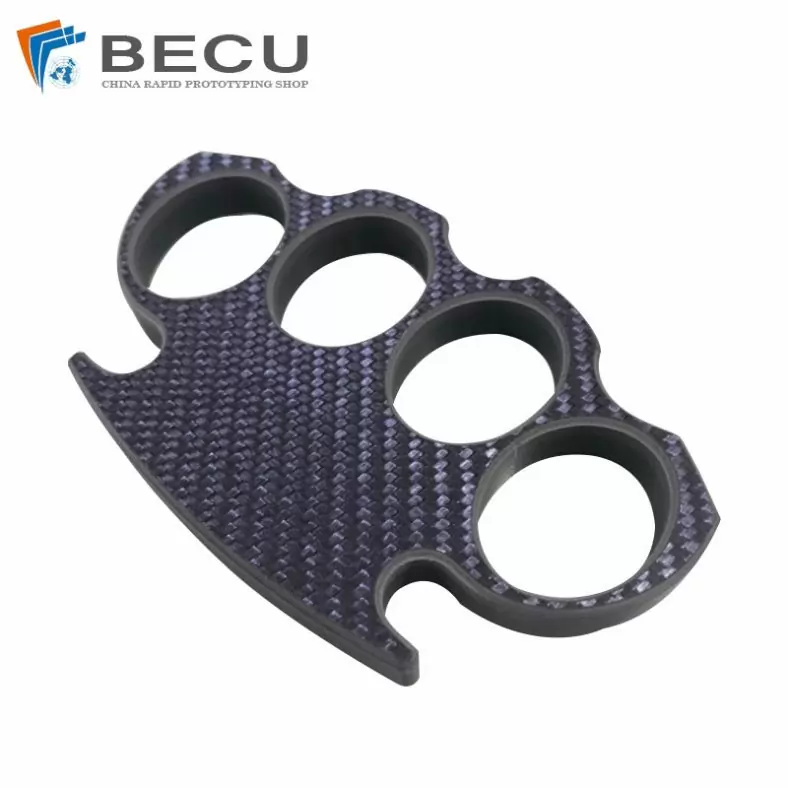

Cnc Milling Carbon Fiber Finger Buckle
