Laser cutting involves using a high-powered laser to precisely cut materials such as metals, plastics, wood, and more. The process relies on the focused heat of the laser to melt, burn, or vaporize the material along a predetermined path, resulting in clean and precise cuts.Laser cutting has revolutionized manufacturing across various industries, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility. However, determining the cost and time involved in laser cutting isn’t always straightforward. It encompasses various elements that need careful consideration to arrive at accurate estimates. This comprehensive guide aims to break down the complexities involved in calculating laser cutting costs and time.

Factors Influencing Laser Cutting Costs
Laser cutting has emerged as a leading technology for precise and efficient material processing across diverse industries. From intricate designs to bulk production, the laser cutting process offers unparalleled accuracy and flexibility. However, determining the cost of laser cutting involves considering multiple factors that collectively impact the final expenses incurred. Understanding these influential elements is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their budgeting and project planning.
1. Material Type and Thickness
The material being cut significantly affects laser cutting costs. Different materials, such as metals, plastics, wood, or ceramics, have distinct characteristics influencing the cost of processing. Moreover, the thickness of the material directly impacts the time and energy required for cutting. Thicker materials demand more power and longer processing times, resulting in increased costs per unit of material cut.
2. Machine Setup Time and Complexity
Setting up a laser cutting machine for a specific job involves preparatory tasks, including loading materials, calibrating settings, and programming the cutting paths. The complexity of the design or pattern being cut also influences setup time. Intricate designs necessitate meticulous calibration, potentially extending setup duration and contributing to higher costs.
3. Cutting Speed and Precision
The speed at which the laser beam cuts through the material affects both time and cost. While faster cutting speeds can expedite the process, they might compromise precision, leading to the need for rework or increased material wastage. Balancing cutting speed with the desired level of accuracy is crucial in managing costs without compromising quality.
4. Machine Power and Efficiency
The power and efficiency of the laser cutting machine play a vital role in determining operational costs. Higher-powered machines might involve a higher initial investment but can significantly reduce processing time and energy consumption, ultimately impacting the overall cost per job.
5. Design Complexity and Intricacy
The complexity of the design being cut directly influences the time and precision required for laser cutting. Elaborate patterns or intricate geometries demand slower and more meticulous cutting, which can increase both time and cost per unit of material processed.
6. Material Waste and Optimization
Minimizing material waste is crucial in managing laser cutting costs. Efficiently arranging designs on materials to reduce leftover scraps or unused areas can contribute to cost savings. Optimization software and careful planning of cutting paths help in maximizing material utilization, thereby reducing waste and costs.
7. Labor Costs and Expertise
Labor costs encompass expenses related to programming designs, operating the laser cutting machine, material handling, and quality inspection. Skilled operators or technicians capable of handling complex jobs may command higher wages, impacting the overall cost of laser cutting services.
8. Overhead Expenses and Operational Costs
Apart from direct material and labor costs, overhead expenses such as facility maintenance, machine depreciation, electricity consumption, insurance, administrative overheads, and compliance requirements add to the total cost structure of laser cutting operations.
9. Volume and Frequency of Work
The volume and frequency of laser cutting jobs play a role in cost determination. Bulk orders or regular work might offer economies of scale, reducing costs per unit by spreading fixed expenses across a larger volume of work.
10. Market Dynamics and Geographic Influences
Local market conditions, including demand for laser cutting services, competition among service providers, and regional variations in labor costs, energy prices, taxes, and logistical expenses, can significantly influence the pricing strategies and overall cost structure of laser cutting services.
Calculating laser cutting costs is a multifaceted process involving an intricate interplay of material characteristics, machine capabilities, design intricacies, operational efficiency, and market dynamics.
Businesses that understand and effectively analyze these factors can make informed decisions, optimize their laser cutting processes, and develop competitive pricing strategies, ensuring efficient utilization of resources while maintaining quality standards.
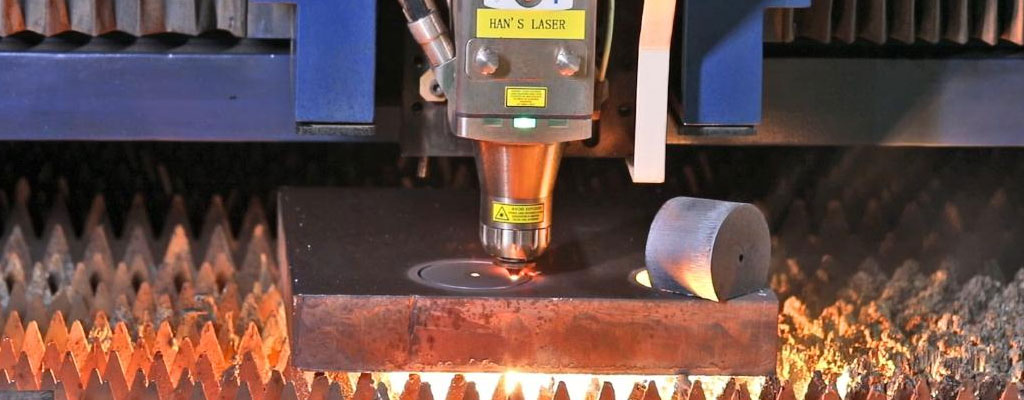

By comprehensively evaluating these influential factors, businesses can enhance their cost estimation accuracy, streamline operations, and drive cost-effective and efficient laser cutting solutions across various industries.

The Relationship Between Laser Cutting Time and Costs
Laser cutting, renowned for its precision and versatility, plays a pivotal role in various industries. The time taken for laser cutting directly impacts the overall costs incurred in manufacturing processes. Understanding the intricate relationship between cutting time and associated costs is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize efficiency, manage budgets, and deliver high-quality products.
The relationship between laser cutting time and costs is often directly proportional. Longer cutting times generally result in higher overall costs due to increased material consumption, higher machine operational expenses, and potentially elevated labor and setup costs.
However, this relationship is not always linear or straightforward. Optimization strategies, such as efficient design layouts to minimize waste material, advanced software utilization for optimizing cutting paths, and using higher-powered, more efficient machines, can mitigate increased costs associated with longer cutting times.
The relationship between laser cutting time and costs is intricate and multi-dimensional. While longer cutting times generally translate to higher costs, various strategies and optimizations exist to minimize expenses without sacrificing quality or efficiency. Businesses that understand this relationship can implement effective measures to streamline operations, optimize processes, and strike a balance between time efficiency and cost-effectiveness in laser cutting applications.
By leveraging technology, optimizing designs, and investing in efficient practices, businesses can navigate the relationship between cutting time and costs, ensuring competitive pricing, high-quality products, and efficient resource utilization in the realm of laser cutting.
Calculating Laser Cutting Cost In Actual Work
Let’s consider cutting a 4ft x 8ft sheet of stainless steel (304 grade) that’s 0.25 inches thick. The material cost is $5 per square foot. The machine setup cost is $100 per hour, and the cutting speed is 50 inches per minute. The machine’s operational cost is $20 per hour, and the estimated cutting time for the design is 2 hours.
- Material Cost = 4ft x 8ft x $5/sq ft = $160
- Machine Setup Cost = $100
- Cutting Time Cost = 2 hours x $20/hour = $40
- Machine Operational Cost = 2 hours x $20/hour = $40
Total Cost = Material Cost + Machine Setup Cost + Cutting Time Cost + Machine Operational Cost = $160 + $100 + $40 + $40 = $340
Mastering Laser Cutting Time Estimation
Calculating laser cutting time in actual work involves several steps and considerations. While the process can vary based on different machines, materials, and designs, here is a general guideline to help you estimate laser cutting time:
Step 1: Gather Information
- Material Details: Determine the type and thickness of the material to be cut. For example, stainless steel, aluminum, wood, acrylic, etc.
- Design Complexity: Assess the intricacy of the design. More intricate designs usually take longer to cut due to additional movements of the laser head.
- Laser Machine Specifications: Understand the capabilities of the laser machine, including its maximum power, cutting speed range, assist gas options, and any specific settings relevant to the material.
Step 2: Calculate Cutting Path Length
Measure or analyze the length of the cutting path in your design. CAD software often provides this information directly.
Step 3: Determine Cutting Speed and Power Settings
Based on your material and machine specifications, determine the optimal cutting speed and laser power. This information may come from experience, manufacturer recommendations, or test cuts.
Step 4: Calculate Cutting Time
Use the following formula as a basic guideline for estimating cutting time:
Cutting Time=Cutting Speed/Cutting Path Length
This formula gives you a rough estimate of the time required for the laser to traverse the entire cutting path at a specific speed.
Consider Additional Factors
- Pierce Time: For thicker materials or when starting a new cut, the laser needs time to pierce through the material before cutting along the path. This pierce time varies based on material thickness and machine settings.
- Acceleration and Deceleration: These factors influence the overall time, especially for intricate designs with frequent changes in direction.
- Assist Gas and Focus: The type and pressure of the assist gas and proper focusing of the laser beam can impact cutting time significantly.
Conduct Test Runs
For precise estimates, conduct test runs with similar materials and designs. Measure the actual cutting time and use this data to refine your calculations for future projects.
Software Assistance
Utilize CAD/CAM software that incorporates algorithms to calculate cutting time based on input parameters. This can provide more accurate estimates, especially for complex designs.
Calculating laser cutting time in actual work involves a mix of understanding materials, machine capabilities, design intricacy, and test runs. While the formula provided offers a basic estimation, it’s crucial to consider additional factors and potentially use specialized software for more accurate predictions. Regular experimentation and recording of actual cutting times will enhance your ability to estimate cutting times more precisely over time.
Strategies for Reducing Laser Cutting Costs
Reducing laser cutting costs without compromising quality requires a strategic approach that considers various factors such as materials, design, machine settings, and workflow efficiency. Here are some effective strategies to help minimize laser cutting expenses:
Material Selection and Optimization:
- Material Efficiency: Optimize material usage by arranging designs efficiently on sheets to minimize waste. Nesting software can help maximize the utilization of materials, reducing scrap.
- Material Choice: Select cost-effective materials without compromising the project’s quality or structural integrity. Sometimes, alternate materials can offer similar properties at a lower cost.
- Thickness Consideration: Thicker materials require more energy and time to cut. When feasible, consider using thinner materials to reduce cutting time and cost.
Design Optimization:
- Simplify Designs: Minimize intricate details that may increase cutting time without significantly improving the final product. Simplifying designs can reduce cutting time and, consequently, costs.
- Standardize Parts: Create standardized designs or components wherever possible. Reusing designs across different projects can save time and optimize cutting processes.
Machine and Process Efficiency:
- Optimize Cutting Parameters: Fine-tune cutting speed, laser power, and assist gas pressure for each material type and thickness. Optimal settings reduce unnecessary energy consumption and improve cutting efficiency.
- Batch Processing: Group similar jobs together to reduce machine setup time and maximize continuous cutting, optimizing the machine’s utilization.
- Maintenance and Calibration: Regularly maintain and calibrate the laser cutting machine. Properly functioning equipment ensures efficiency, reduces errors, and prevents costly downtime.
Workflow and Operations:
- Streamline Processes: Review the workflow from design to production. Identify and eliminate bottlenecks or redundant steps that may increase production time and costs.
- Employee Training: Provide training to operators for efficient machine operation, material handling, and troubleshooting. Skilled operators can optimize processes and reduce errors.
Cost Analysis and Supplier Relations:
- Supplier Negotiation: Build strong relationships with material suppliers to negotiate better prices or bulk discounts for frequently used materials.
- Cost Tracking and Analysis: Regularly analyze the costs associated with laser cutting jobs. Identify areas where costs can be reduced without compromising quality.
Technology and Software Integration:
- CAD/CAM Software: Utilize advanced software that optimizes nesting, simulates cutting paths, and calculates precise cutting times. This helps in efficient material usage and accurate cost estimation.
- Automation and Robotics: Consider investing in automation and robotics for material handling or repetitive tasks to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Implementing a combination of these strategies can significantly reduce laser cutting costs while maintaining or improving product quality. Continuous evaluation, optimization, and adaptation to technological advancements will further enhance cost-saving measures in laser cutting operations.
Outsourcing Laser Cutting Services with Be-Cu Prototype
However, the choice of outsourcing location is critical. While outsourcing to firms in developed countries can be expensive, companies in regions with lower operational costs, like China, can offer competitive rates without compromising on quality.
For instance, China companies like Be-Cu provide high-quality laser cutting or medical laser cutting service at a fraction of the cost compared to their counterparts in more developed economies. This makes outsourcing a viable option for reducing overall machining costs, especially for businesses looking to optimize budgets without sacrificing quality.
Your laser cutting cost calculation will be simple when you work with Be-Cu,com. Our fast-quoting platform allows you to receive your quotation nearly instantly. We review your design and provide feedback within a day.
We also have one of the fastest lead times in the industry, thus guaranteeing your products get to you on time. So why wait? Start working on your laser cutting project and get laser cutting quotes!